state of matter of malaysia
Negeri Sembilan ( Malay pronunciation : [ ˈnəgəri səmbiˈlan ] ) is a country in Malaysia which lies on the western coast of Peninsular Malaysia. It borders Selangor on the north, Pahang in the east, and Melaka and Johor to the confederacy.
Reading: Negeri Sembilan – Wikipedia
The name is believed to derive from the nine ( sembilan ) villages or nagari in the Minangkabau language ( nowadays known as luak ) settled by the Minangkabau, a people originally from West Sumatra ( in contemporary Indonesia ). Minangkabau features are hush visible today in traditional architecture and the dialect of Malay speak. Unlike the familial sovereign of the other royal Malay states, the ruler of Negeri Sembilan is elected and is known as Yang di-Pertuan Besar rather of Sultan. The election of the Ruler is besides unique. He is selected by the council of Undangs who lead the four biggest territories of Sungai Ujong, Jelebu, Johol, and Rembau, making it one of the more democratic monarchies. The capital of Negeri Sembilan is Seremban. The royal capital is Seri Menanti in Kuala Pilah District. other crucial towns are Port Dickson, Bahau and Nilai. The Arabic honorific title of the country is Darul Khusus ( “ the special Abode ” ) .
etymology [edit ]
The name Negeri Sembilan is believed to derive from the nine ( sembilan ) chiefdoms or Nogoghi in the Negeri Sembilan dialect ( now known as luak ) settled by the Minangkabau. The size of Negeri Sembilan is now smaller than the master size of Negeri Sembilan .
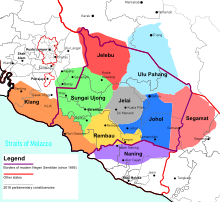 The master 9 chiefdoms of Negeri Sembilan, at Raja Melewar ‘s accession in 1773
The master 9 chiefdoms of Negeri Sembilan, at Raja Melewar ‘s accession in 1773
history [edit ]
Ancient and medieval history [edit ]
The earliest inhabitants of Negeri Sembilan were the ancestors of the Semelai, Semai, Semang, and Jakun peoples, who lived either as hunter-gatherer nomads or as subsistence farmers. Parameswara reportedly visited the village of Sening Ujong, which was located in what is now Seremban. The Minangkabaus from Sumatra settled in what is today Negeri Sembilan in the fifteenth hundred under the protection of the Malacca Sultanate, and late under the protection of its successor, the Sultanate of Johor. They besides brought their matrilineal custom, known as Adat Perpatih, with them and made it the local custom-made. [ 3 ] [ 4 ] The Linggi River along the westerly depart of the state was used as one of the main deal routes since the time of the Malacca Sultanate. With the Pahang River in equitable a walking distance to the east, the two rivers formed the Laluan Penarikan ( Portage Route ), which ensured easier entree between the Strait of Malacca and the South China Sea. As Johor weakened in the eighteenth century, attacks by the Bugis forced the Minangkabaus to seek protection from their fatherland. The Minangkabau rule, Sultan Abdul Jalil, obliged by sending his dear proportional, Raja Melewar. When he arrived, he found that another royal, Raja Khatib had already established himself as rule. He declared war against Raja Khatib and became the rule of Negeri Sembilan. The Sultan of Johor confirmed his position by granting the title Yamtuan Seri Menanti ( He Who is Highest Lord of the Seri Menanti ) in 1773. Negeri Sembilan, at the clock time of Raja Melewar ‘s accession, covered a larger area than its contemporary boundaries. Besides the entirety of modern Negeri Sembilan, it besides covered parts of what is today Selangor, Melaka, Pahang and Johor. The original nine chiefdoms or domains in 1773 that gave Negeri Sembilan its name are namely Sungai Ujong, Jelebu, Rembau, Johol, Jelai, Ulu Pahang, Naning, Segamat and Klang. The latter four chiefdoms were annexed into neighbouring states in the nineteenth century. Naning was annexed into the Straits Settlement of Melaka in 1832 following the Naning War ; Ulu Pahang became Bera region of Pahang, Segamat annexed into Johor and Klang became Kuala Langat region of Selangor. After Raja Melewar ‘s death, a serial of disputes arose over the succession. For a considerable period, the local nobles applied to the Minangkabau rule in Sumatra for a rule. however, competing interests supported different candidates, frequently resulting in imbalance and civil war .
Colonial history [edit ]
In 1874, the british intervened militarily in a leadership scuffle in Sungai Ujong to preserve british economic interests, and placed the knowledge domain under the control of a british Resident. Jelebu followed in 1883 and Rembau in 1887. The formation of modern Negeri Sembilan began in 1889, when the Seri Menanti domain, under the principle of Tuanku Muhammad ( son of Yamtuan Antah ), combined with the domains of Tampin and Rembau, forming the Seri Menanti Confederation as a single political entity. The domains of Sungai Ujong and Jelebu joined this confederation in 1895, forming the state of matter of Negeri Sembilan in its modern borders. [ 5 ] Martin Lister became the newly submit ‘s beginning Resident, and Negeri Sembilan became separate of the Federated Malay States the same year. The number of states [ clarification needed ] within Negeri Sembilan has fluctuated over the years, the confederation now consists of six states [ clarification needed ] and a number of sub-states [ clarification needed ] under their suzerainty. [ citation needed ]
modern history [edit ]
Negeri Sembilan endured japanese occupation in World War II between 1942 and 1945, joined the Federation of Malaya in 1948, and became a state of matter of malaysia in 1963. In the 1990s and 2000s, Seremban and Nilai attracted people who moved in from the overcrowd towns of the Klang Valley. These two cities besides became the sites of new factories and industrial parks, accelerating the development of the country into modern times. On 9 September, 2009, the Ministry of Housing and local Government approved the state das kapital of Seremban ‘s application to become a city ( Bandar Raya ), as it had attracted adequate people to become large. In order for that to happen, its city council had to be merged with the Nilai Municipal Council. After several times when it was postponed, Seremban achieved the condition of a city on 20 January, 2020. Later that class on 9 November, Negeri Sembilan was subjected to the Movement Control Order lockdown due to increasing COVID-19 infections .
population and demographics [edit ]
ethnicity [edit ]
Negeri Sembilan has a collective population of 1,098,500 as of 2015 ; [ 2 ] [ 6 ] the ethnic composition consisting of Malay 622,000 ( 56.6 % ) ( largely are Minangkabau origin ), other Bumiputras 20,700 ( 1.9 % ), chinese 234,300 ( 21.3 % ), indian 154,000 ( 14 % ), Others 4,200 ( 0.4 % ), and Non Citizens 63,300 ( 5.8 % ). [ 2 ] The state has the highest percentage of Indians when compared to early malaysian states. Up until today the state is known as the strongholds of Adat Perpatih in Malaysia .
religion [edit ]
According to the 2010 census, the population of Negeri Sembilan is 60.3 % Muslim, 21.2 % Buddhist, 13.4 % Hindu, 2.4 % Christian, 1.1 % of unknown affiliation, 0.8 % non-religious, 0.5 % taoist or chinese religion follower, and 0.3 % of followers of early religions. Statistics from the 2010 Census indicate that 92.9 % of the chinese population in Negeri Sembilan is identified as Buddhists, with significant minority of adherents identifying as Christians ( 3.6 % ), chinese folk music religions ( 1.9 % ) and Muslims ( 0.8 % ). The majority of the indian population are Hindus ( 89.0 % ), with a significant minorities of numbers identifying as Christians ( 5.0 % ), Muslims ( 3.2 % ) and Buddhists ( 1.4 % ). The non-Malay Bumiputera residential district are predominantly Atheists ( 39.7 % ), with significant minorities identifying as Christians ( 28.3 % ) and Muslims ( 20.2 % ). All Malays are Muslims. [ 8 ]
Languages [edit ]
Negeri Sembilan is a multiethnic submit in which every cultural group speaks their respective languages and dialects. The Negeri Sembilanese people speak a alone variety show of Malay known as Negeri Sembilan Malay or in their native language as Baso Nogoghi. It is not close related to other varieties of Malay in Peninsular Malaysia but more close related with Malay varieties spoken in neighbouring Sumatra particularly varieties of Minangkabau. Besides Malays, the Chinese community besides speak their languages and dialects. Orang Asli peoples like Temuans speak a language closely related to Malay. Standard Malay is widely used throughout the submit. Indians in Negeri Sembilan belong to diverse ethnicities. Tamil ( Mother tongue to Indian Tamils and Ceylon Tamils ) is used as a tongue franca among the other minor indian communities. Besides, a little phone number of Telugu, Malayalam and Punjabi exist in the towns of Negeri Sembilan .
government [edit ]
constitution [edit ]
The Constitution of Negeri Sembilan came into force out on 26 March 1959. It is divided into two sections. The constitution establishes that the state ‘s form of government is constitutional monarchy and the world ‘s only elective monarchy for matrilineal company. The system was partially the basis for the federal monarchy .
The Ruler [edit ]
 Istana Seri Menanti The official constitutional title of the Ruler of the state are Duli Yang Maha Mulia Yang di-Pertuan Besar Negeri Sembilan, ( presently Duli Yang Maha Mulia Yang di-Pertuan Besar Negeri Sembilan Darul Khusus Tuanku Muhriz ibni Almarhum Tuanku Munawir ), Yang Teramat Mulia Undang of Sungei Ujong, Yang Teramat Mulia Undang of Jelebu, Yang Teramat Mulia Undang of Johol, Yang Teramat Mulia Undang of Rembau and Yang Teramat Mulia Tengku Besar Tampin and they holds office for life.
Istana Seri Menanti The official constitutional title of the Ruler of the state are Duli Yang Maha Mulia Yang di-Pertuan Besar Negeri Sembilan, ( presently Duli Yang Maha Mulia Yang di-Pertuan Besar Negeri Sembilan Darul Khusus Tuanku Muhriz ibni Almarhum Tuanku Munawir ), Yang Teramat Mulia Undang of Sungei Ujong, Yang Teramat Mulia Undang of Jelebu, Yang Teramat Mulia Undang of Johol, Yang Teramat Mulia Undang of Rembau and Yang Teramat Mulia Tengku Besar Tampin and they holds office for life.
Read more: Chord (music) – Wikipedia
The express ‘s constitution proclaims the Yang di-Pertuan Besar, Undang of Sungei Ujong, Undang of Jelebu, Undang of Johol, Undang of Rembau and Tengku Besar Tampin are vested with the Executive Power of the state, are the Head of the Religion of Islam in the submit and are the fountain of all honor and dignity for the state. The current Yang di-Pertuan Besar is His royal Highness Tuanku Muhriz ibni Almarhum Tuanku Munawir. His Royal Highness succeeds Almarhum Tuanku Jaafar Ibni Almarhum Tuanku Abdul Rahman who died on 27 December 2008. Unlike Malaysia ‘s eight other Royal Malay states, the Ruler of Negeri Sembilan is elected to his office by the territorial chiefs or Ruling Chiefs of the state. These Ruling Chiefs are titled Undang. only four of the Undangs have the right to vote in the election for the Ruler of the State. They are :
- The Undang of Sungai Ujong
- The Undang of Jelebu
- The Undang of Johol
- The Undang of Rembau
The Undang themselves can not stand for election, and their choice of Ruler is limited to a male Muslim who is Malay and besides a “ legitimately begotten descendant of Raja Radin ibni Raja Lenggang ”. The Assembly convenes at the Wisma Negeri in the state capital, Seremban .
administrator and legislature [edit ]
The State Executive Council consists of the Menteri Besar, who is its chair, and ten other members. The Menteri Besar and the other members of the council are appointed by the Yang Di-Pertuan Besar from the members of the State Assembly of the governing party or coalition. The current Menteri Besar or Chief Minister of the state is Aminuddin Harun. The unicameral Negeri Sembilan State Legislative Assembly is the state of matter legislature of Negeri Sembilan. It consists of 36 members who represent single-member constituencies throughout the state of matter. Elections are held no more than five years apart, and are normally conducted simultaneously with elections to the federal parliament .
administrative divisions [edit ]
The country comprises 7 districts, each is headed by a zone officer. The districts besides have their own lands and district position and local politics .
It primitively consisted of 9 districts :
- Jelai (Inas)
- Jelebu
- Johol
- Klang (now a district in Selangor)
- Naning (now in Malacca)
- Rembau
- Segamat (now in Johor) / Pasir Besar (now in Tampin)
- Sungai Ujong
- Alu Panah (now divided between Jelebu and Pahang State)
economy [edit ]
The state ‘s fabricate sector contributes about half of the state ‘s gross domestic product ( GDP ), followed by services and tourism ( 40.3 % ), agribusiness ( 6 % ), construction ( 2.2 % ) and mine ( 0.3 % ). Manufacturing activities include electric supplies and electronics, textiles, furniture, chemicals, machinery, metal works and rubber eraser products. There are three main industrial areas, which includes Senawang, Sungai Gadut, Tuanku Jaafar Industrial Park, Nilai and Tanah Merah in Port Dickson. Coca-Cola was scheduled to operate a 1-billion ringgit bottle plant in Bandar Enstek. Negeri Sembilan is chiefly an agricultural state. however, the establishment of several industrial estates enhanced the fabricate sector as a significant subscriber to the state economy. The agricultural activity includes condom and oil decoration plantations, livestock, fruit orchards and vegetable farm. About 3,099 squarely kilometres are used for condom and oil handle plantations .
culture [edit ]
The Minangkabau people brought along with them a cultural inheritance which is silent preserved and practised today as the Adat perpatih, a matrilineal system of inheritance and administration that is singular to the state. It is a system where the husband is the head of the family and inheritance passes from the mother to the daughter. The Minangkabau ‘s divided into twelve suku or tribes and marriage between members of the lapp tribe or kin is prevent. The Minangkabau influence in the department of state can be found in dances and food vitamin a well .
Dances [edit ]
Negeri Sembilan besides has traditional music like the Caklempong, Dikir Rebana, Tumbuk Kalang, and Bongai. The musical instruments used to bear some illusion to Sumatra, the ancestral home of the Minangkabau people. Dances like the tarian lilin ( candle dance ) and rentak kuda ( the beat of the cavalry ) are popular in Negeri Sembilan and the align movements of the dancers in their colorful costumes in the Tarian Piring and the cheerful tempo of Tarian Randai. Unlike modern dance, each beat, rhythm and apparent motion in these dances combines to form a floor, possibly of a bygone myth or plainly a observation of the lifestyles of another earned run average. They are normally performed at traditional festivities, cultural events and dinner-cum-cultural shows .
cuisine [edit ]
traditional Negeri Sembilan food is hot and piquant, as one of the ingredients used is the chili padi, the hottest of chili peppers. popular dishes include rendang, ( pieces of beef cooked in coconut milk and chillies ). Another Negeri Sembilan forte is “ Lemang “, gluey rice cooked in coconut milk in a bamboo stem over an open open fire. This is normally served with Rendang, a deliciously thick and dry kernel curry. [ 3 ]
tourism [edit ]
The democratic attractions in Negeri Sembilan are :
- Galeri Diraja Tuanku Ja’afar – is a gallery in Seremban, Negeri Sembilan, Malaysia. The gallery is about the former Negeri Sembilan Yang di-Pertuan Besar Tuanku Ja’afar.
- Port Dickson Beach – A famous weekend retreat for city dwellers, said to have been named after British officer John Frederick Dickson in 1889[9]
- Seri Menanti Royal Museum – Originally a palace for the Negeri Sembilan Royal family until 1992, this five-storey wooden palace was built using no nails or screws. The palace exhibits costumes, weaponry, bed chambers as well as documents on the royal lineage on display in the museum[10]
- Army Museum – exhibits artefacts in regards to the history of the Royal Malaysian Army.[11]
- Mount Datuk – This 884-metre peak provides a good work out and excellent views from the top. It is easily accessible via a day trip from Kuala Lumpur.
- Mount Angsi – Gunung Angsi is one of Malaysia’s relatively mountains with a height of 2702 ft or 824m. It ranks 241st on my list of Malaysia’s highest mountains and it is the 3rd highest peak in Negeri Sembilan state, after Gunung Datuk and Bukit Bintongan which are both slightly higher. It is even closer to Kuala Lumpur and is a popular climbing spot. It also similar height with Mount Datuk and quite an exhausting walk.
- Mount Telapak Buruk – One of the state’s highest peaks though not so popular with day-trippers.
- Lukut Fort and Museum – In Lukut, the tourists can wander among the hilltop remains of a 19th-century fort before visiting the neighbouring Lukut Museum which contains a Lukut Historical Gallery and other interesting artefacts.
- Penarikan Portage – the spot close to Bahau town is Jalan Penarikan where boats were carried over the short gap between eastbound and westbound rivers of the Malay Peninsula allowing movement between both coasts of the peninsular.
- Gemencheh Bridge (Sungai Kelamah) Memorial – This memorial marks the site of a battle at Gemencheh Bridge during World War II where Allied forces ambushed advancing Japanese troops. Many lives were lost here.
education [edit ]
Negeri Sembilan has respective tertiary department of education institutions. Most of these department of education institutions are concentrated in major towns in Negeri Sembilan. The number below represents public and private university based in Negeri Sembilan state :
Public universities [edit ]
private universities and university colleges [edit ]
Hospitals [edit ]
There are public hospitals and secret hospitals in Negeri Sembilan : Public Hospitals
- Hospital Tuanku Jaafar, Seremban
- Hospital Tuanku Ampuan Najihah, Kuala Pilah
- Hospital Port Dickson
- Hospital Tampin
- Hospital Jelebu
- Hospital Jempol
- Hospital Rembau
Private Hospitals
- Nilai Medical Centre[12]
- Seremban Specialist Hospital[13]
- Columbia Asia Medical Centre – Seremban[14]
- Senawang Specialist Hospital
- NSCMH Medical Centre
- Columbia Asia Hospital
- Mawar Medical Centre
