The Netherlands ( dutch : Nederland [ ˈneːdərlɑnt ] ( ) ), informally Holland, [ 15 ] [ 16 ] is a nation located in Northwestern Europe with territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Netherlands. [ 17 ] [ 18 ] [ 19 ] In Europe, the Netherlands consists of twelve provinces, bordering Germany to the east, Belgium to the south, and the North Sea to the northwest, with nautical borders in the North Sea with those countries and the United Kingdom. [ 20 ] In the Caribbean, it consists of three limited municipalities : the islands of Bonaire, Sint Eustatius and Saba. [ one ] The country ‘s official linguistic process is Dutch, with West Frisian as a secondary official speech in the state of Friesland, and English and Papiamento as secondary official languages in the Caribbean Netherlands. [ 1 ] Dutch Low Saxon and Limburgish are recognised regional languages ( spoken in the east and southeast respectively ), while dutch Sign Language, Sinte Romani, and Yiddish are recognised non-territorial languages. [ 1 ] [ 2 ] The four largest cities in the Netherlands are Amsterdam, Rotterdam, The Hague and Utrecht. [ 22 ] Amsterdam is the country ‘s most populous city and noun phrase capital, [ 23 ] while The Hague holds the induct of the States General, Cabinet and Supreme Court. [ 24 ] The Port of Rotterdam is the busiest seaport in Europe. [ 25 ] Amsterdam Airport Schiphol is the busiest airport in the Netherlands, and the third busy in Europe. The nation is a establish member of the European Union, Eurozone, G10, NATO, OECD, and WTO, equally well as a function of the Schengen Area and the trilateral Benelux Union. It hosts several intergovernmental organisations and international courts, many of which are centred in The Hague, which is consequently dubbed ‘the world ‘s legal capital ‘. [ 26 ]
Reading: Netherlands – Wikipedia
Netherlands literally means “ lower countries ” in citation to its low acme and flat topography, with only about 50 % of its land exceeding 1 meter ( 3.3 foot ) above sea charge, and closely 26 % falling below sea level. [ 27 ] Most of the areas below sea degree, known as polders, are the consequence of domain reclamation that began in the fourteenth century. [ 28 ] Colloquially or colloquially the Netherlands is occasionally referred to by the pars pro toto Holland. [ 15 ] In the republican period, which began in 1588, the Netherlands entered a singular era of political, economic, and cultural enormousness, ranked among the most mighty and influential in Europe and the global ; this menstruation is known as the Dutch Golden Age. [ 29 ] During this time, its trade companies, the Dutch East India Company and the dutch West India Company, established colonies and deal posts all over the universe. [ 30 ] [ 31 ] With a population of 17.5 million people, all life within a entire area of approximately 41,800 km2 ( 16,100 sq myocardial infarction ) —of which the land area is 33,500 km2 ( 12,900 sq security service ) —the Netherlands is the 16th most dumbly populated country in the populace and the second-most dumbly populated area in the European Union, with a density of 523 people per feather kilometer ( 1,350 people/sq myocardial infarction ). however, it is the world ‘s second-largest exporter of food and agricultural products by value, owing to its prolific dirty, mild climate, intensive agriculture, and inventiveness. [ 32 ] [ 33 ] [ 34 ] The Netherlands has been a parliamentary constitutional monarchy with a unitary structure since 1848. The nation has a tradition of pillarisation and a long record of sociable allowance, having legalised abortion, prostitution and human euthanasia, along with maintaining a big drug policy. The Netherlands abolished the end penalty in Civil Law in 1870, though it was not completely removed until a newly constitution was approved in 1983. The Netherlands allowed women ‘s right to vote in 1919, before becoming the populace ‘s beginning country to legalise same-sex marriage in 2001. Its mixed-market advanced economy had the eleventh-highest per head income globally. [ 35 ] The Netherlands ranks among the highest in international indices of press freedom, [ 36 ] economic freedom, [ 37 ] human development and quality of life sentence, equally well as happiness. [ 38 ] [ j ] In 2020, it ranked eighth on the human development index and fifth on the 2021 World Happiness Index. [ 40 ] [ 41 ]
etymology [edit ]
The Netherlands ‘ churning history and shifts of ability resulted in exceptionally many and widely varying names in different languages. There is diverseness even within languages. In English, the Netherlands is besides called Holland or ( part of ) the low Countries, whereas the condition “Dutch” is used as the demonym and adjectival form .
Netherlands and the broken Countries [edit ]
The region called the low Countries ( comprising Belgium, the Netherlands and Luxembourg ) have the same toponymy. Place name with Neder, Nieder, Nedre, Nether, Lage(r) or Low(er) ( in Germanic languages ) and Bas or Inferior ( in Romance languages ) are in use in low-lying places all over Europe. They are sometimes used in a deictic sexual intercourse to a higher establish that consecutively is indicated as Super(ior), Up(per), Op(per), Ober, Boven, High, Haut or Hoch. In the case of the Low Countries / Netherlands the geographic localization of the lower region has been more or less downriver and near the sea. The geographic localization of the upper area, however, changed enormously over meter, depending on the location of the economic and military power governing the first gear Countries area. The Romans made a distinction between the Roman provinces of downriver Germania Inferior ( nowadays part of Belgium and the Netherlands ) and upriver Germania Superior ( nowadays share of Germany ). The appellation ‘Low ‘ to refer to the region returns again in the tenth hundred Duchy of Lower Lorraine, that covered much of the low Countries. [ 42 ] [ 43 ] But this time the equate Upper region is Upper Lorraine, in present Northern France. The Dukes of Burgundy, who ruled from their residence in the first gear Countries in the fifteenth hundred, used the term les pays de par deçà ( “ the lands over hera ” ) for the Low Countries, as opposed to les pays de par delà ( “ the lands over there ” ) for their original fatherland : Burgundy in contemporary east-central France. [ 44 ] Under Habsburg rule, Les pays de par deçà developed in pays d’embas ( “ lands down-here ” ), [ 45 ] a deictic expression in relation to other Habsburg possessions like Hungary and Austria. This was translated as Neder-landen in contemporaneous Dutch official documents. [ 46 ] From a regional indicate of view, Niderlant was besides the sphere between the Meuse and the lower Rhine in the late Middle Ages. The sphere known as Oberland ( high country ) was in this deictic context considered to begin approximately at the nearby higher located Cologne. From the mid-sixteenth century on, the “ low Countries ” and the “ Netherlands ” lost their original deictic meaning. They were credibly the most normally used names, besides Flanders, a pars pro toto for the Low Countries, specially in Romance language-speaking Europe. The Eighty Years ‘ War ( 1568–1648 ) divided the gloomy Countries into an independent northern Dutch Republic ( or Latinised Belgica Foederata, “ Federated Netherlands ”, the harbinger state of matter of the Netherlands ) and a spanish controlled southern Netherlands ( Latinised Belgica Regia, “ Royal Netherlands ”, the precursor state of Belgium ). The low Countries today is a appointment that includes the countries of the Netherlands, Belgium and Luxembourg, although in most Romance languages, the term “ low Countries ” is used as the name for the Netherlands specifically. It is used synonymously with the more neutral and geopolitical term Benelux .
netherlands [edit ]
The Netherlands is besides referred to as Holland in respective languages, including English. however, Holland proper is only a region within the area that consists of North and South Holland, two of the nation ‘s twelve provinces. once they were a single state, and early the County of Holland, a end of the dissolve Frisian Kingdom which besides included parts of contemporary Utrecht. Following the decline of the Duchy of Brabant and the County of Flanders, Holland became the most economically and politically important county in the Low Countries region. The emphasis on Holland during the geological formation of the Dutch Republic, the Eighty Years ‘ War, and the Anglo-Dutch Wars in the 16th, 17th, and 18th centuries, made Holland serve as a pars pro toto for the integral state, which is immediately considered informal [ 47 ] or incorrect. [ 48 ] [ 49 ] Nonetheless, the appoint “ Holland ” is still widely used for the Netherlands national football team, including in the Netherlands, [ 50 ] and the dutch government ‘s international web site for tourism is “ holland.com “. [ 51 ] [ 52 ] In 2020, however, the dutch government announced that it would only communicate and advertise under the name “ the Netherlands ” in the future. [ 53 ]
dutch [edit ]
The term Dutch is used as the demonymic and adjectival form of the Netherlands in the english linguistic process. The origins of the word go back to Proto-Germanic *þiudiskaz, Latinised into Theodiscus, meaning “ popular ” or “ of the people ” ; akin to Old Dutch Dietsch, Old High German duitsch, and Old English þeodisc, all meaning “ ( of ) the common ( Germanic ) people ”. At first gear, the english language used ( the contemporary form of ) dutch to refer to any or all speakers of West Germanic languages ( e.g. the Dutch, the Frisians, and the Germans ). Gradually its meaning shifted to the West Germanic people they had most contact with, because of their geographic proximity and for the competition in barter and overseas territories. The derivative of the Proto-Germanic parole *þiudiskaz in modern Dutch, Diets, can be found in dutch literature as a poetic mention for the dutch people or linguistic process, but is considered identical antediluvian. Although it had a short-circuit revival after World War II to avoid the reference to Germany. It is still used in the saying “ diets maken ” – to put it straight to him/her ( as in a threat ) or, more achromatic, to make it clear, apprehensible, explain, say in the people ‘s speech ( cf. the Vulgate ( Bible not in Greek or Hebrew, but Latin ; the folks ‘ language ) in meaning common, though not in a dyslogistic sense ) .
terminology in Dutch and other languages [edit ]
In Dutch, the names for the Netherlands, the dutch speech and a dutch citizen are Nederland, Nederlands and Nederlander, respectively. Colloquially the country is besides by the Dutch much referred to as Holland, although to lesser extent outside the two provinces North and South Holland, where it may even be used as a dyslogistic term, e.g. Hollènder ( dialect ) in Maastricht. [ 54 ] Since 1815, the plural Nederlanden it is alone used in the official name Koninkrijk der Nederlanden ( “ Kingdom of the Netherlands “ ). [ 55 ] In many other languages the plural stuck, for exercise Niederlande ( German ), Pays-Bas ( french ) and Países Bajos ( spanish ). In Indonesian ( a former colony ) the country is called Belanda, a name derived from ‘Holland ‘ .
history [edit ]
Prehistory ( before 800 BC ) [edit ]
 Oak figurine found in Willemstad ( 4500 BC ) The prehistory of the sphere that is nowadays the Netherlands was largely shaped by the sea and the rivers that constantly shifted the low-lying geography. The oldest human ( Neanderthal ) traces were found in higher soils, near Maastricht, from what is believed to be about 250,000 years ago. [ 56 ] At the end of the Ice Age, the mobile late Upper Palaeolithic Hamburg culture ( c. 13.000–10.000 BC ) hunted caribou in the area, using spears, but the late Ahrensburg polish ( c. 11.200–9500 BC ) used bow and arrow. From mesolithic age Maglemosian-like tribes ( c. 8000 BC ) the oldest canoe in the populace was found in Drenthe. [ 57 ] autochthonal late Mesolithic hunter-gatherers from the Swifterbant culture ( c. 5600 BC ) were related to the southern Scandinavian Ertebølle culture and were powerfully linked to rivers and clear water. [ 58 ] Between 4800 and 4500 BC, the Swifterbant people started to copy from the neighbouring analogue Pottery culture the exercise of animal farming, and between 4300 and 4000 BC the drill of department of agriculture. [ 59 ] The Funnelbeaker acculturation ( c. 4300–2800 BC ), which is related to the Swifterbant culture, erected the dolmens, large gem grave monuments found in Drenthe. There was a flying and polish transition from the Funnelbeaker farming culture to the pan-European Corded Ware pastoralist acculturation ( c. 2950 BC ). In the southwest, the Seine-Oise-Marne culture — which was related to the Vlaardingen acculturation ( c. 2600 BC ), an apparently more archaic acculturation of hunter-gatherers — survived well into the Neolithic period, until it excessively was succeeded by the Corded Ware culture .
Oak figurine found in Willemstad ( 4500 BC ) The prehistory of the sphere that is nowadays the Netherlands was largely shaped by the sea and the rivers that constantly shifted the low-lying geography. The oldest human ( Neanderthal ) traces were found in higher soils, near Maastricht, from what is believed to be about 250,000 years ago. [ 56 ] At the end of the Ice Age, the mobile late Upper Palaeolithic Hamburg culture ( c. 13.000–10.000 BC ) hunted caribou in the area, using spears, but the late Ahrensburg polish ( c. 11.200–9500 BC ) used bow and arrow. From mesolithic age Maglemosian-like tribes ( c. 8000 BC ) the oldest canoe in the populace was found in Drenthe. [ 57 ] autochthonal late Mesolithic hunter-gatherers from the Swifterbant culture ( c. 5600 BC ) were related to the southern Scandinavian Ertebølle culture and were powerfully linked to rivers and clear water. [ 58 ] Between 4800 and 4500 BC, the Swifterbant people started to copy from the neighbouring analogue Pottery culture the exercise of animal farming, and between 4300 and 4000 BC the drill of department of agriculture. [ 59 ] The Funnelbeaker acculturation ( c. 4300–2800 BC ), which is related to the Swifterbant culture, erected the dolmens, large gem grave monuments found in Drenthe. There was a flying and polish transition from the Funnelbeaker farming culture to the pan-European Corded Ware pastoralist acculturation ( c. 2950 BC ). In the southwest, the Seine-Oise-Marne culture — which was related to the Vlaardingen acculturation ( c. 2600 BC ), an apparently more archaic acculturation of hunter-gatherers — survived well into the Neolithic period, until it excessively was succeeded by the Corded Ware culture .
 The Netherlands in 5500 BC
The Netherlands in 5500 BC Bronze Age cultures in the Netherlands Of the subsequent Bell Beaker culture ( 2700–2100 BC ) several regions of origin have been postulated, notably the iberian peninsula, the Netherlands and Central Europe. [ 60 ] They introduced metalworking in copper, gold and subsequently bronze and opened international trade routes not seen before, reflected in the discoveries of copper artifacts, as the metallic element is not normally found in dutch dirt. numerous finds of rare bronze objects suggest that Drenthe was even a trade center in the Bronze Age ( 2000–800 BC ). The Bell Beaker culture developed locally into the Barbed-Wire Beaker culture ( 2100–1800 BC ) and former the Elp polish ( c. 1800–800 BC ), [ 61 ] a Middle Bronze Age archaeological polish having earthenware pottery of first gear quality as a marker. The initial phase of the Elp culture was characterised by tumuli ( 1800–1200 BC ) that were powerfully tied to contemporary tumuli in northern Germany and Scandinavia and was apparently related to the burial mound culture in central Europe. The subsequent phase was that of cremating the dead and placing their ashes in urns which were then buried in fields, following the customs of the Urnfield polish ( 1200–800 BC ). The southerly region became dominated by the refer Hilversum culture ( 1800–800 BC ), which obviously inherited cultural ties with Britain of the previous Barbed-Wire Beaker polish .
Bronze Age cultures in the Netherlands Of the subsequent Bell Beaker culture ( 2700–2100 BC ) several regions of origin have been postulated, notably the iberian peninsula, the Netherlands and Central Europe. [ 60 ] They introduced metalworking in copper, gold and subsequently bronze and opened international trade routes not seen before, reflected in the discoveries of copper artifacts, as the metallic element is not normally found in dutch dirt. numerous finds of rare bronze objects suggest that Drenthe was even a trade center in the Bronze Age ( 2000–800 BC ). The Bell Beaker culture developed locally into the Barbed-Wire Beaker culture ( 2100–1800 BC ) and former the Elp polish ( c. 1800–800 BC ), [ 61 ] a Middle Bronze Age archaeological polish having earthenware pottery of first gear quality as a marker. The initial phase of the Elp culture was characterised by tumuli ( 1800–1200 BC ) that were powerfully tied to contemporary tumuli in northern Germany and Scandinavia and was apparently related to the burial mound culture in central Europe. The subsequent phase was that of cremating the dead and placing their ashes in urns which were then buried in fields, following the customs of the Urnfield polish ( 1200–800 BC ). The southerly region became dominated by the refer Hilversum culture ( 1800–800 BC ), which obviously inherited cultural ties with Britain of the previous Barbed-Wire Beaker polish .
Celts, Germanic tribe and Romans ( 800 BC–410 AD ) [edit ]
From 800 BC onwards, the Iron Age Celtic Hallstatt culture became influential, replacing the Hilversum culture. Iron ore brought a measure of prosperity and was available throughout the nation, including bog down iron. Smiths travelled from village to colony with bronze and iron, fabricating tools on need. The King ‘s sculpt of Oss ( 700 BC ) was found in a burial mound, the largest of its kind in western Europe and containing an iron sword with an inlay of gold and coral. The deteriorating climate in Scandinavia around 850 BC far deteriorated around 650 BC and might have triggered migration of Germanic tribes from the North. By the time this migration was complete, around 250 BC, a few general cultural and linguistic groups had emerged. [ 62 ] [ 63 ] The North Sea Germanic Ingaevones inhabited the northern separate of the depleted Countries. They would late develop into the Frisii and the early on Saxons. [ 63 ] A irregular group, the Weser-Rhine Germanic ( or Istvaeones ), extended along the middle Rhine and Weser and inhabited the moo Countries south of the great rivers. This group consisted of tribes that would finally develop into the salian frank Franks. [ 63 ] besides the Celtic La Tène culture ( c. 450 BC up to the Roman conquest ) had expanded over a broad range, including the southern area of the low Countries. Some scholars have speculated that even a third base heathen identity and language, neither Germanic nor Celtic, survived in the Netherlands until the Roman period, the Iron Age Nordwestblock culture, [ 64 ] [ 65 ] that finally was absorbed by the Celts to the confederacy and the Germanic peoples from the east .
 The Rhine frontier about 70 AD The first author to describe the seashore of Holland and Flanders was the greek geographer Pytheas, who noted in c. 325 BC that in these regions, “ more people died in the conflict against body of water than in the conflict against men. ” [ 66 ] During the Gallic Wars, the area south and west of the Rhine was conquered by Roman forces under Julius Caesar from 57 BC to 53 BC. [ 65 ] Caesar describes two main Celtic kin living in what is now the southern Netherlands : the Menapii and the Eburones. The Rhine became fixed as Rome ‘s northerly frontier around 12 AD. noteworthy towns would arise along the Limes Germanicus : nijmegen and Voorburg. In the first region of Gallia Belgica, the area south of the Limes became part of the Roman state of Germania Inferior. The area to the north of the Rhine, inhabited by the Frisii, remained outside Roman rule ( but not its presence and control ), while the Germanic frame tribe of the Batavi and Cananefates served in the Roman cavalry. [ 67 ] The Batavi rose against the Romans in the Batavian rebellion of 69 AD but were finally defeated. The Batavi late merged with other tribes into the confederation of the salian frank Franks, whose identity emerged at the first base half of the third century. [ 68 ] salian frank Franks appear in Roman text as both allies and enemies. They were forced by the confederation of the Saxons from the east to move over the Rhine into Roman district in the fourthly century. From their newfangled base in West Flanders and the Southwest Netherlands, they were raiding the english Channel. Roman forces pacified the region, but did not expel the Franks, who continued to be feared at least until the prison term of julian the Apostate ( 358 ) when salian frank Franks were allowed to settle as foederati in Texandria. [ 68 ] It has been postulated that after deteriorating climate conditions and the Romans ‘ withdrawal, the Frisii disappeared as laeti in c. 296, leaving the coastal lands largely unpeopled for the following two centuries. [ 69 ] however, recent excavations in Kennemerland show clear indication of a permanent inhabitancy. [ 70 ] [ 71 ]
The Rhine frontier about 70 AD The first author to describe the seashore of Holland and Flanders was the greek geographer Pytheas, who noted in c. 325 BC that in these regions, “ more people died in the conflict against body of water than in the conflict against men. ” [ 66 ] During the Gallic Wars, the area south and west of the Rhine was conquered by Roman forces under Julius Caesar from 57 BC to 53 BC. [ 65 ] Caesar describes two main Celtic kin living in what is now the southern Netherlands : the Menapii and the Eburones. The Rhine became fixed as Rome ‘s northerly frontier around 12 AD. noteworthy towns would arise along the Limes Germanicus : nijmegen and Voorburg. In the first region of Gallia Belgica, the area south of the Limes became part of the Roman state of Germania Inferior. The area to the north of the Rhine, inhabited by the Frisii, remained outside Roman rule ( but not its presence and control ), while the Germanic frame tribe of the Batavi and Cananefates served in the Roman cavalry. [ 67 ] The Batavi rose against the Romans in the Batavian rebellion of 69 AD but were finally defeated. The Batavi late merged with other tribes into the confederation of the salian frank Franks, whose identity emerged at the first base half of the third century. [ 68 ] salian frank Franks appear in Roman text as both allies and enemies. They were forced by the confederation of the Saxons from the east to move over the Rhine into Roman district in the fourthly century. From their newfangled base in West Flanders and the Southwest Netherlands, they were raiding the english Channel. Roman forces pacified the region, but did not expel the Franks, who continued to be feared at least until the prison term of julian the Apostate ( 358 ) when salian frank Franks were allowed to settle as foederati in Texandria. [ 68 ] It has been postulated that after deteriorating climate conditions and the Romans ‘ withdrawal, the Frisii disappeared as laeti in c. 296, leaving the coastal lands largely unpeopled for the following two centuries. [ 69 ] however, recent excavations in Kennemerland show clear indication of a permanent inhabitancy. [ 70 ] [ 71 ]
early Middle Ages ( 411–1000 ) [edit ]
 Franks, Frisians and Saxons ( 710s AD ) with Traiecturm and Dorestad in the middle After roman government in the area collapsed, the Franks expanded their territories in numerous kingdoms. By the 490s, Clovis I had conquered and united all these territories in the southerly Netherlands in one frankish kingdom, and from there continued his conquests into Gaul. During this expansion, Franks migrating to the south finally adopted the Vulgar Latin of the local population. [ 63 ] A let out cultural separate grew with the Franks remaining in their original fatherland in the north ( i.e. the southern Netherlands and Flanders ), who kept on speaking Old Frankish, which by the ninth century had evolved into Old Low Franconian or Old Dutch. [ 63 ] A Dutch-French lyric boundary therefore came into being. [ 63 ] [ 72 ]
Franks, Frisians and Saxons ( 710s AD ) with Traiecturm and Dorestad in the middle After roman government in the area collapsed, the Franks expanded their territories in numerous kingdoms. By the 490s, Clovis I had conquered and united all these territories in the southerly Netherlands in one frankish kingdom, and from there continued his conquests into Gaul. During this expansion, Franks migrating to the south finally adopted the Vulgar Latin of the local population. [ 63 ] A let out cultural separate grew with the Franks remaining in their original fatherland in the north ( i.e. the southern Netherlands and Flanders ), who kept on speaking Old Frankish, which by the ninth century had evolved into Old Low Franconian or Old Dutch. [ 63 ] A Dutch-French lyric boundary therefore came into being. [ 63 ] [ 72 ]
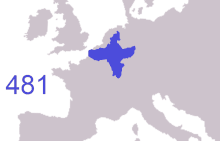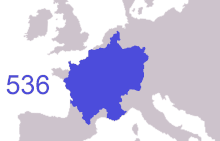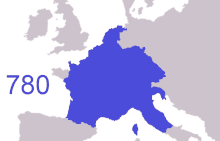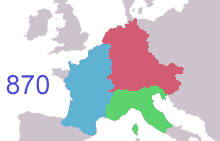 frankish expansion ( 481 to 870 AD ) To the north of the Franks, climatic conditions improved, and during the Migration Period Saxons, the closely relate Angles, Jutes and Frisii settled the coastal land. [ 73 ] Many moved on to England and came to be known as Anglo-Saxons, but those who stayed would be referred to as Frisians and their terminology as frisian, named after the land that was once inhabited by Frisii. [ 73 ] Frisian was spoken along the stallion southerly North Sea seashore, and it is still the terminology most close related to English among the survive languages of continental Europe. By the seventh century a frisian Kingdom ( 650–734 ) under King Aldegisel and King Redbad emerged with Traiectum ( Utrecht ) as its center of power, [ 73 ] [ 74 ] while Dorestad was a brandish trade topographic point. [ 75 ] [ 76 ] Between 600 and approximately 719 the cities were much fought over between the Frisians and the Franks. In 734, at the Battle of the Boarn, the Frisians were defeated after a serial of wars. With the approval of the Franks, the Anglo-Saxon missionary Willibrord converted the frisian people to Christianity. He established the Archdiocese of Utrecht and became bishop of the Frisians. however, his successor Boniface was murdered by the Frisians in Dokkum, in 754 .
frankish expansion ( 481 to 870 AD ) To the north of the Franks, climatic conditions improved, and during the Migration Period Saxons, the closely relate Angles, Jutes and Frisii settled the coastal land. [ 73 ] Many moved on to England and came to be known as Anglo-Saxons, but those who stayed would be referred to as Frisians and their terminology as frisian, named after the land that was once inhabited by Frisii. [ 73 ] Frisian was spoken along the stallion southerly North Sea seashore, and it is still the terminology most close related to English among the survive languages of continental Europe. By the seventh century a frisian Kingdom ( 650–734 ) under King Aldegisel and King Redbad emerged with Traiectum ( Utrecht ) as its center of power, [ 73 ] [ 74 ] while Dorestad was a brandish trade topographic point. [ 75 ] [ 76 ] Between 600 and approximately 719 the cities were much fought over between the Frisians and the Franks. In 734, at the Battle of the Boarn, the Frisians were defeated after a serial of wars. With the approval of the Franks, the Anglo-Saxon missionary Willibrord converted the frisian people to Christianity. He established the Archdiocese of Utrecht and became bishop of the Frisians. however, his successor Boniface was murdered by the Frisians in Dokkum, in 754 .
The frankish Carolingian empire modelled itself on the Roman Empire and controlled much of Western Europe. however, in 843, it was divided into three parts— East, Middle, and West Francia. Most of contemporary Netherlands became separate of Middle Francia, which was a unaccented kingdom and subjugate of numerous partitions and annexation attempts by its stronger neighbours. It comprised territories from Frisia in the north to the Kingdom of Italy in the south. Around 850, Lothair I of Middle Francia acknowledged the Viking Rorik of Dorestad as ruler of most of Frisia. [ 77 ] When the kingdom of Middle Francia was partitioned in 855, the lands north of the Alps passed to Lothair II and subsequently were named Lotharingia. After he died in 869, Lotharingia was partitioned, into Upper and Lower Lotharingia, the latter separate comprising the low Countries that technically became separate of East Francia in 870, although it was effectively under the control of Vikings, who raided the largely defenseless Frisian and Frankish towns lying on the frisian coast and along the rivers. Around 879, another Viking excursion led by Godfrid, Duke of Frisia, raided the frisian lands. The Viking raids made the sway of French and german lords in the area weak. resistance to the Vikings, if any, came from local nobles, who gained in stature as a result, and that laid the footing for the decomposition of Lower Lotharingia into semi-independent states. One of these local anesthetic nobles was Gerolf of Holland, who assumed lordship in Frisia after he helped to assassinate Godfrid, and Viking principle came to an end .
high Middle Ages ( 1000–1384 ) [edit ]
 A Medieval Tombe of the Brabantian knight Arnold van five hundred Sluijs The Holy Roman Empire ( the successor state of East Francia and then Lotharingia ) ruled much of the depleted Countries in the 10th and eleventh century but was not able to maintain political oneness. Powerful local anesthetic nobles turned their cities, counties and duchies into private kingdoms that felt little smell of debt instrument to the emperor. Holland, Hainaut, Flanders, Gelre, Brabant, and Utrecht were in a state of matter of about continual war or in paradoxically formed personal unions. The lyric and culture of most of the people who lived in the County of Holland were primitively frisian. As frankish colony progressed from Flanders and Brabant, the area promptly became Old Low Franconian ( or Old Dutch ). The respite of Frisia in the north ( now Friesland and Groningen ) continued to maintain its independence and had its own institutions ( jointly called the “ frisian exemption “ ), which resented the imposition of the feudal system. Around 1000 AD, due to several agrarian developments, the economy started to develop at a fast tempo, and the higher productiveness allowed workers to farm more land or to become tradesmen. Towns grew around monasteries and castles, and a mercantile in-between class began to develop in these urban areas, particularly in Flanders and later besides Brabant. Wealthy cities started to buy certain privileges for themselves from the sovereign. In practice, this mean that Bruges and Antwerp became quasi-independent republics in their own right field and would subsequently develop into some of the most important cities and ports in Europe. Around 1100 AD, farmers from Flanders and Utrecht began draining and cultivating uninhabited boggy land in the western Netherlands, making the emergence of the County of Holland as the center of office possible. The title of Count of Holland was fought over in the Hook and Cod Wars ( dutch : Hoekse en Kabeljauwse twisten ) between 1350 and 1490. The Cod cabal consisted of the more progressive cities, while the Hook faction consisted of the bourgeois noblemen. These noblemen invited the Duke Philip the Good of Burgundy — who was besides Count of Flanders — to conquer Holland .
A Medieval Tombe of the Brabantian knight Arnold van five hundred Sluijs The Holy Roman Empire ( the successor state of East Francia and then Lotharingia ) ruled much of the depleted Countries in the 10th and eleventh century but was not able to maintain political oneness. Powerful local anesthetic nobles turned their cities, counties and duchies into private kingdoms that felt little smell of debt instrument to the emperor. Holland, Hainaut, Flanders, Gelre, Brabant, and Utrecht were in a state of matter of about continual war or in paradoxically formed personal unions. The lyric and culture of most of the people who lived in the County of Holland were primitively frisian. As frankish colony progressed from Flanders and Brabant, the area promptly became Old Low Franconian ( or Old Dutch ). The respite of Frisia in the north ( now Friesland and Groningen ) continued to maintain its independence and had its own institutions ( jointly called the “ frisian exemption “ ), which resented the imposition of the feudal system. Around 1000 AD, due to several agrarian developments, the economy started to develop at a fast tempo, and the higher productiveness allowed workers to farm more land or to become tradesmen. Towns grew around monasteries and castles, and a mercantile in-between class began to develop in these urban areas, particularly in Flanders and later besides Brabant. Wealthy cities started to buy certain privileges for themselves from the sovereign. In practice, this mean that Bruges and Antwerp became quasi-independent republics in their own right field and would subsequently develop into some of the most important cities and ports in Europe. Around 1100 AD, farmers from Flanders and Utrecht began draining and cultivating uninhabited boggy land in the western Netherlands, making the emergence of the County of Holland as the center of office possible. The title of Count of Holland was fought over in the Hook and Cod Wars ( dutch : Hoekse en Kabeljauwse twisten ) between 1350 and 1490. The Cod cabal consisted of the more progressive cities, while the Hook faction consisted of the bourgeois noblemen. These noblemen invited the Duke Philip the Good of Burgundy — who was besides Count of Flanders — to conquer Holland .
Burgundian, Habsburg and Spanish Habsburg Netherlands ( 1384–1581 ) [edit ]
Most of the Imperial and french fiefs in what is now the Netherlands and Belgium were united in a personal coupling by Philip the Good, Duke of Burgundy, in 1433. The House of Valois-Burgundy and their Habsburg successor would rule the Low Countries in the period from 1384 to 1581. Before the Burgundian union, the Dutch identified themselves by the town they lived in or their local anesthetic duchy or county. The Burgundian menstruation is when the road to nationhood began. The new rulers defended dutch trading interests, which then developed quickly. The fleets of the County of Holland defeated the fleets of the Hanseatic League several times. Amsterdam grew and in the fifteenth century became the primary coil trade port in Europe for grain from the baltic region. Amsterdam distributed grain to the major cities of Belgium, Northern France and England. This trade was full of life because Holland could no longer produce adequate grain to feed itself. Land drain had caused the peat of the former wetlands to reduce to a level that was besides low for drain to be maintained. Under Habsburg Charles V, ruler of the Holy Roman Empire and King of Spain, all fiefs in the current Netherlands region were united into the Seventeen Provinces, which besides included most of contemporary Belgium, Luxembourg, and some adjacent land in what is now France and Germany. In 1568, under Phillip II, the Eighty Years ‘ War between the Provinces and their spanish rule began. The horizontal surface of ferocity exhibited by both sides can be gleaned from a Dutch chronicler ‘s report card : [ 78 ]
On more than one affair men were seen hanging their own brothers, who had been taken prisoners in the enemy ‘s ranks … A Spaniard had ceased to be human in their eyes. On one occasion, a surgeon at Veer cut the kernel from a spanish prisoner, nailed it on a vessel ‘s bow, and invited the townsmen to come and fasten their teeth in it, which many did with savage satisfaction .
The Duke of Alba ruthlessly attempted to suppress the Protestant motion in the Netherlands. Netherlanders were “ burned, strangled, beheaded, or buried alert ” by his “ Blood Council “ and his spanish soldiers. Severed heads and decapitate corpses were displayed along streets and roads to terrorise the population into submission. Alba boasted of having executed 18,600, [ 79 ] [ 80 ] but this number does not include those who perished by war and famine. The first great siege was Alba ‘s campaign to capture Haarlem and thereby cut Holland in one-half. It dragged on from December 1572 to the next summer, when Haarlemers ultimately surrendered on 13 July upon the predict that the city would be spared from being sacked. It was a condition Don Fadrique was ineffective to honour, when his soldiers mutinied, angered over give owed and the miserable conditions they endured during the long, cold months of the political campaign. [ 81 ] On 4 November 1576, spanish tercios seized Antwerp and subjected it to the worst plundering in the Netherlands ‘ history. The citizens resisted, but were overcome ; seven thousand of them were mowed down ; a thousand buildings were torched ; men, women, and children were slaughtered in a craze of blood by soldiers crying, “ santiago de cuba ! España ! A sangre, a carne, a fuego, a sacco ! ” ( Saint James ! Spain ! To blood, to the flesh, to fire, to sack ! ) [ 82 ]
Following the displace of Antwerp, delegates from Catholic Brabant, Protestant Holland and Zeeland agreed, at Ghent, to join Utrecht and William the Silent in driving out all spanish troops and forming a new government for the Netherlands. Don Juan of Austria, the raw spanish governor, was forced to concede initially, but within months returned to active voice hostilities. As the fight restarted, the Dutch began to look for help from the Queen of England, but she initially stood by her commitments to the spanish in the Treaty of Bristol of 1574. The result was that when the next large-scale conflict did occur at Gembloux in 1578, the spanish forces easily won the day, killing at least 10,000 rebels, with the spanish suffer few losses. [ 83 ] In idle of the frustration at Gembloux, the southern states of the Seventeen Provinces ( today in northerly France and Belgium ) distanced themselves from the rebels in the north with the 1579 Union of Arras, which expressed their commitment to Philip II of Spain. Opposing them, the northern half of the Seventeen Provinces forged the Union of Utrecht ( besides of 1579 ) in which they committed to support each other in their defensive structure against the spanish army. [ 84 ] The Union of Utrecht is seen as the foundation garment of the modern Netherlands. spanish troops sacked Maastricht in 1579, killing over 10,000 civilians and thereby ensuring the rebellion continued. [ 85 ] In 1581, the northern provinces adopted the Act of Abjuration, the declaration of independence in which the provinces formally deposed Philip II as reigning sovereign in the northern provinces. [ 86 ] Against the rebels Philip could draw on the resources of Spain, Spanish America, spanish Italy and the spanish Netherlands. The Protestant Queen Elizabeth I of England sympathised with the dutch contend against the spanish and sent an army of 7,600 soldiers to aid the dutch in their war with the Catholic Spanish. [ 87 ] english forces under the Earl of Leicester and then Lord Willoughby faced the spanish in the Netherlands under the Duke of Parma in a series of largely indecisive actions that tied down significant numbers of spanish troops and bought prison term for the dutch to reorganise their defences. [ 88 ] The war continued until 1648, when Spain under King Philip IV last recognised the independence of the seven north-western provinces in the Peace of Münster. Parts of the southerly provinces became de facto colonies of the new republican-mercantile empire .
Dutch Republic ( 1581–1795 ) [edit ]
After declaring their independence, the provinces of Holland, Zeeland, Groningen, Friesland, Utrecht, Overijssel, and Gelderland formed a confederation. All these duchies, lordships and counties were autonomous and had their own government, the States-Provincial. The States General, the confederal government, were seated in The Hague and consisted of representatives from each of the seven provinces. The sparsely populate region of Drenthe was separate of the democracy excessively, although it was not considered one of the provinces. furthermore, the Republic had come to occupy during the Eighty Years ‘ War a phone number of alleged Generality Lands in Flanders, Brabant and Limburg. Their population was chiefly Roman Catholic, and these areas did not have a governmental structure of their own, and were used as a buffer zone between the Republic and the Spanish-controlled Southern Netherlands. [ 89 ]
 Winter landscape with skaters near the city of Kampen by by Hendrick Avercamp ( 1620s ) In the Dutch Golden Age, spanning much of the seventeenth hundred, the Dutch Empire grew to become one of the major water travel and economic powers, aboard Portugal, Spain, France and England. Science, military, and art ( specially painting ) were among the most applaud in the world. By 1650, the Dutch owned 16,000 merchant ships. [ 90 ] The Dutch East India Company and the dutch West India Company established colonies and trade posts all over the world, including ruling the northerly parts of Taiwan between 1624–1662 and 1664–1667. The Dutch settlement in North America began with the establish of New Amsterdam on the southern share of Manhattan in 1614. In South Africa, the Dutch settled the Cape Colony in 1652. Dutch colonies in South America were established along the many rivers in the prolific Guyana plains, among them Colony of Surinam ( now Suriname ). In Asia, the Dutch established the Dutch East Indies ( immediately Indonesia ), and the only westerly trade post in Japan, Dejima. During the period of Proto-industrialization, the empire received 50 % of textiles and 80 % of silks significance from the India ‘s Mughal Empire, chiefly from its most train region known as Bengal Subah. [ 91 ] [ 92 ] [ 93 ] [ 94 ] many economic historians regard the Netherlands as the inaugural thoroughly capitalist country in the global. In early modern Europe, it had the wealthiest trading city ( Amsterdam ) and the first gear full-time stock certificate commute. The inventiveness of the traders led to indemnity and retirement funds a well as phenomena such as the boom-bust cycle, the earth ‘s beginning asset-inflation bubble, the tulip mania of 1636–1637, and the world ‘s first bear raider, Isaac lupus erythematosus Maire, who forced prices down by dumping stock certificate and then buying it back at a discount rate. [ 95 ] In 1672 – known in dutch history as the Rampjaar ( Disaster Year ) – the Dutch Republic was at war with France, England and three german Bishoprics simultaneously. At sea, it could successfully prevent the English and french united states navy from entering the western shores. On domain, however, it was about taken over internally by the advancing french and german armies coming from the east. It managed to turn the tide by inundating parts of Holland but could never recover to its former glory again and went into a state of a general decline in the eighteenth hundred, with economic rival from England and long-standing rivalries between the two main factions in Dutch society, the republican Staatsgezinden and the supporters of the stadtholder the Prinsgezinden as independent political factions. [ 96 ]
Winter landscape with skaters near the city of Kampen by by Hendrick Avercamp ( 1620s ) In the Dutch Golden Age, spanning much of the seventeenth hundred, the Dutch Empire grew to become one of the major water travel and economic powers, aboard Portugal, Spain, France and England. Science, military, and art ( specially painting ) were among the most applaud in the world. By 1650, the Dutch owned 16,000 merchant ships. [ 90 ] The Dutch East India Company and the dutch West India Company established colonies and trade posts all over the world, including ruling the northerly parts of Taiwan between 1624–1662 and 1664–1667. The Dutch settlement in North America began with the establish of New Amsterdam on the southern share of Manhattan in 1614. In South Africa, the Dutch settled the Cape Colony in 1652. Dutch colonies in South America were established along the many rivers in the prolific Guyana plains, among them Colony of Surinam ( now Suriname ). In Asia, the Dutch established the Dutch East Indies ( immediately Indonesia ), and the only westerly trade post in Japan, Dejima. During the period of Proto-industrialization, the empire received 50 % of textiles and 80 % of silks significance from the India ‘s Mughal Empire, chiefly from its most train region known as Bengal Subah. [ 91 ] [ 92 ] [ 93 ] [ 94 ] many economic historians regard the Netherlands as the inaugural thoroughly capitalist country in the global. In early modern Europe, it had the wealthiest trading city ( Amsterdam ) and the first gear full-time stock certificate commute. The inventiveness of the traders led to indemnity and retirement funds a well as phenomena such as the boom-bust cycle, the earth ‘s beginning asset-inflation bubble, the tulip mania of 1636–1637, and the world ‘s first bear raider, Isaac lupus erythematosus Maire, who forced prices down by dumping stock certificate and then buying it back at a discount rate. [ 95 ] In 1672 – known in dutch history as the Rampjaar ( Disaster Year ) – the Dutch Republic was at war with France, England and three german Bishoprics simultaneously. At sea, it could successfully prevent the English and french united states navy from entering the western shores. On domain, however, it was about taken over internally by the advancing french and german armies coming from the east. It managed to turn the tide by inundating parts of Holland but could never recover to its former glory again and went into a state of a general decline in the eighteenth hundred, with economic rival from England and long-standing rivalries between the two main factions in Dutch society, the republican Staatsgezinden and the supporters of the stadtholder the Prinsgezinden as independent political factions. [ 96 ]
Batavian Republic and Kingdom ( 1795–1890 ) [edit ]
With the armed confirm of rotatory France, Dutch republicans proclaimed the Batavian Republic, modelled after the french Republic and rendering the Netherlands a unitary country on 19 January 1795. The stadtholder William V of Orange had fled to England. But from 1806 to 1810, the Kingdom of Holland was set up by Napoleon Bonaparte as a creature kingdom governed by his buddy Louis Bonaparte to control the Netherlands more effectively. however, King Louis Bonaparte tried to serve Dutch interests rather of his buddy ‘s, and he was forced to abdicate on 1 July 1810. The Emperor sent in an army and the Netherlands became character of the french Empire until the fall of 1813 when Napoleon was defeated in the Battle of Leipzig .
William Frederick, son of the survive stadtholder, returned to the Netherlands in 1813 and proclaimed himself Sovereign Prince of the Netherlands. Two years late, the Congress of Vienna added the southerly Netherlands to the north to create a strong country on the northerly border of France. William Frederick raised this United Netherlands to the condition of a kingdom and proclaimed himself as King William I in 1815. In summation, William became familial Grand Duke of Luxembourg in exchange for his german possessions. however, the Southern Netherlands had been culturally separate from the north since 1581, and rebelled. The south gained independence in 1830 as Belgium ( recognised by the Northern Netherlands in 1839 as the Kingdom of the Netherlands was created by decree ), while the personal union between Luxembourg and the Netherlands was severed in 1890, when William III died with no surviving male heirs. Ascendancy laws prevented his daughter Queen Wilhelmina from becoming the following Grand Duchess .
The belgian Revolution at home and the Java War in the Dutch East Indies brought the Netherlands to the brink of bankruptcy. however, the Cultivation System was introduced in 1830 ; in the Dutch East Indies, 20 % of village land had to be devoted to government crops for export. The policy brought the Dutch enormous wealth and made the colony self-sufficient. The Netherlands abolished bondage in its colonies in 1863. [ 97 ] Enslaved people in Suriname would be fully free entirely in 1873, since the law stipulated that there was to be a mandate 10-year conversion. [ 98 ]
World wars and beyond ( 1890–present ) [edit ]
The Netherlands was able to remain neutral during World War I, in depart because the meaning of goods through the Netherlands proved essential to german survival until the blockade by the british Royal Navy in 1916. [ 99 ] That changed in World War II, when Nazi Germany invaded the Netherlands on 10 May 1940. The Rotterdam Blitz forced the main component of the dutch army to surrender four days late. During the occupation, over 100,000 dutch Jews [ 100 ] were rounded up and transported to Nazi extinction camps ; lone a few of them survived. dutch workers were conscripted for force labor in Germany, civilians who resisted were killed in reprisal for attacks on german soldiers, and the countryside was plundered for food. Although there were thousands of Dutch who risked their lives by hiding Jews from the Germans, over 20,000 dutch fascists joined the Waffen SS, [ 101 ] fighting on the Eastern Front. [ 102 ] political collaborators were members of the fascist NSB, the only legal political party in the take Netherlands. On 8 December 1941, the dutch government-in-exile in London declared war on Japan, [ 103 ] but could not prevent the japanese occupation of the Dutch East Indies ( Indonesia ). [ 104 ] In 1944–45, the First canadian Army, which included Canadian, British and Polish troops, was creditworthy for liberating much of the Netherlands. [ 105 ] soon after VE Day, the Dutch fought a colonial war against the raw Republic of Indonesia .
In 1954, the Charter for the Kingdom of the Netherlands reformed the political social organization of the Netherlands, which was a consequence of international atmospheric pressure to carry out decolonization. The dutch colonies of Surinam and Curaçao and Dependencies and the european area all became countries within the Kingdom, on a footing of equality. Indonesia had declared its independence in August 1945 ( recognised in 1949 ), and thus was never separate of the reformed Kingdom. suriname followed in 1975. After the war, the Netherlands left behind an era of neutrality and gained closer ties with neighbor states. The Netherlands was one of the founding members of the Benelux, the NATO, Euratom and the european Coal and Steel Community, which would evolve into the EEC ( Common Market ) and late the European Union. Government-encouraged emigration efforts to reduce population density prompted some 500,000 dutch people to leave the nation after the war. [ 106 ] The 1960s and 1970s were a time of great social and cultural change, such as rapid de- pillarisation characterised by the decay of the erstwhile divisions along political and religious lines. Youths, and students in particular, rejected traditional mores and pushed for change in matters such as women ‘s rights, sex, disarming and environmental issues. In 2002 the euro was introduced as decree money, and in 2010 the Netherlands Antilles was dissolved. Referendums were held on each island to determine their future status. As a result, the islands of Bonaire, Sint Eustatius and Saba ( the BES islands ) were to obtain closer ties with the Netherlands. This led to the internalization of these three islands into the country of the Netherlands as special municipalities upon the dissolution of the Netherlands Antilles. The limited municipalities are jointly known as the Caribbean Netherlands .
geography [edit ]
 Relief map of the European Netherlands According to the Central Bureau of Statistics, the European Netherlands has a sum area of 41,545 km2 ( 16,041 sq mile ), including water bodies ; and a land sphere of 33,481 km2 ( 12,927 sq security service ). The Caribbean Netherlands has a sum area of 328 km2 ( 127 sq myocardial infarction ) [ 107 ] It lies between latitudes 50° and 54° N, and longitudes 3° and 8° einsteinium. The Netherlands is geographically very low relative to sea charge and is considered a flat country, with about 26 % of its area [ 27 ] and 21 % of its population [ 108 ] located below sea horizontal surface, and entirely about 50 % of its land exceeding one meter above sea level. [ citation needed ] The european character of the country is for the most part flat, with the exception of foothills in the far southeast, improving to a altitude of no more than 321 metres, and some low mound ranges in the cardinal parts. Most of the areas below sea tied are man-made, caused by peat origin or achieved through estate reclamation. Since the late sixteenth century, boastfully polder areas are preserved through elaborate drain systems that include dikes, canals and pumping stations. about 17 % of the country ‘s land area is reclaimed from the sea and from lakes. much of the nation was originally formed by the estuaries of three large european rivers : the Rhine ( Rijn ), the Meuse ( Maas ) and the Scheldt ( Schelde ), ampere well as their tributaries. The south-western part of the Netherlands is to this day a river delta of these three rivers, the Rhine-Meuse-Scheldt delta. The european Netherlands is divided into north and south parts by the Rhine, the Waal, its main tributary branch, and the Meuse. In the by, these rivers functioned as a natural barrier between fiefdoms and hence historically created a cultural separate, as is apparent in some phonetic traits that are recognizable on either side of what the dutch call their “ Great Rivers ” ( de Grote Rivieren ). Another meaning branch of the Rhine, the IJssel river, discharges into Lake IJssel, the early Zuiderzee ( ‘southern sea ‘ ). Just like the previous, this river forms a linguistic separate : people to the northeast of this river speak Dutch Low Saxon dialects ( except for the state of Friesland, which has its own language ). [ 109 ]
Relief map of the European Netherlands According to the Central Bureau of Statistics, the European Netherlands has a sum area of 41,545 km2 ( 16,041 sq mile ), including water bodies ; and a land sphere of 33,481 km2 ( 12,927 sq security service ). The Caribbean Netherlands has a sum area of 328 km2 ( 127 sq myocardial infarction ) [ 107 ] It lies between latitudes 50° and 54° N, and longitudes 3° and 8° einsteinium. The Netherlands is geographically very low relative to sea charge and is considered a flat country, with about 26 % of its area [ 27 ] and 21 % of its population [ 108 ] located below sea horizontal surface, and entirely about 50 % of its land exceeding one meter above sea level. [ citation needed ] The european character of the country is for the most part flat, with the exception of foothills in the far southeast, improving to a altitude of no more than 321 metres, and some low mound ranges in the cardinal parts. Most of the areas below sea tied are man-made, caused by peat origin or achieved through estate reclamation. Since the late sixteenth century, boastfully polder areas are preserved through elaborate drain systems that include dikes, canals and pumping stations. about 17 % of the country ‘s land area is reclaimed from the sea and from lakes. much of the nation was originally formed by the estuaries of three large european rivers : the Rhine ( Rijn ), the Meuse ( Maas ) and the Scheldt ( Schelde ), ampere well as their tributaries. The south-western part of the Netherlands is to this day a river delta of these three rivers, the Rhine-Meuse-Scheldt delta. The european Netherlands is divided into north and south parts by the Rhine, the Waal, its main tributary branch, and the Meuse. In the by, these rivers functioned as a natural barrier between fiefdoms and hence historically created a cultural separate, as is apparent in some phonetic traits that are recognizable on either side of what the dutch call their “ Great Rivers ” ( de Grote Rivieren ). Another meaning branch of the Rhine, the IJssel river, discharges into Lake IJssel, the early Zuiderzee ( ‘southern sea ‘ ). Just like the previous, this river forms a linguistic separate : people to the northeast of this river speak Dutch Low Saxon dialects ( except for the state of Friesland, which has its own language ). [ 109 ]
geology [edit ]
The modern Netherlands formed as a result of the interplay of the four main rivers ( Rhine, Meuse, Schelde and IJssel ) and the influence of the North Sea. The Netherlands is largely composed of deltaic, coastal and aeolian derived sediments during the Pleistocene glacial and interglacial periods. about the stallion west Netherlands is composed of the Rhine – Meuse river estuary, but human interposition greatly modified the natural processes at work. Most of the western Netherlands is below sea tied due to the human procedure of turning standing bodies of water into useable nation, a polder. In the east of the Netherlands, remains are found of the final methamphetamine historic period, which ended approximately ten thousand years ago. As the continental ice sheet moved in from the north, it pushed moraine forward. The ice sheet halted as it covered the eastern one-half of the Netherlands. After the internal-combustion engine age ended, the moraine remained in the form of a hanker hill-line. The cities of Arnhem and Nijmegen are built upon these hills. [ 110 ]
Floods [edit ]
 The Christmas deluge of 1717 was the result of a northwestern ramp that resulted in the death of thousands. Over the centuries, the Dutch coastline has changed well as a resultant role of natural disasters and homo intervention. On 14 December 1287, St. Lucia ‘s flood affected the Netherlands and Germany, killing more than 50,000 people in one of the most destructive floods in record history. [ 111 ] The St. Elizabeth flood of 1421 and the mismanagement in its consequence destroyed a newly reclaimed polder, replacing it with the 72 km2 ( 28 sq nautical mile ) Biesbosch tidal floodplains in the south-centre. The huge North Sea flood of early February 1953 caused the break down of several dikes in the southwest of the Netherlands ; more than 1,800 people drowned in the flood tide. The dutch government subsequently instituted a large-scale program, the “ Delta Works “, to protect the country against future implosion therapy, which was completed over a period of more than thirty years .
The Christmas deluge of 1717 was the result of a northwestern ramp that resulted in the death of thousands. Over the centuries, the Dutch coastline has changed well as a resultant role of natural disasters and homo intervention. On 14 December 1287, St. Lucia ‘s flood affected the Netherlands and Germany, killing more than 50,000 people in one of the most destructive floods in record history. [ 111 ] The St. Elizabeth flood of 1421 and the mismanagement in its consequence destroyed a newly reclaimed polder, replacing it with the 72 km2 ( 28 sq nautical mile ) Biesbosch tidal floodplains in the south-centre. The huge North Sea flood of early February 1953 caused the break down of several dikes in the southwest of the Netherlands ; more than 1,800 people drowned in the flood tide. The dutch government subsequently instituted a large-scale program, the “ Delta Works “, to protect the country against future implosion therapy, which was completed over a period of more than thirty years .
 Map illustrating areas of the Netherlands below ocean charge The impact of disasters was, to an extent, increased through human activity. relatively high-lying swamp was drained to be used as farmland. The drain caused the prolific peat to sign and labor levels to drop, upon which groundwater levels were lowered to compensate for the fell in crunch level, causing the underlying peat to sign foster. additionally, until the 19th-century peat was mined, dried, and used for fuel, further exacerbating the trouble. Centuries of extensive and ill controlled peat extraction lowered an already gloomy land surface by respective metres. even in flood areas, peat extraction continued through turf dredge. Because of the flood, farm was difficult, which encouraged foreign deal, the solution of which was that the Dutch were involved in world affairs since the early 14th/15th century. [ 112 ]
Map illustrating areas of the Netherlands below ocean charge The impact of disasters was, to an extent, increased through human activity. relatively high-lying swamp was drained to be used as farmland. The drain caused the prolific peat to sign and labor levels to drop, upon which groundwater levels were lowered to compensate for the fell in crunch level, causing the underlying peat to sign foster. additionally, until the 19th-century peat was mined, dried, and used for fuel, further exacerbating the trouble. Centuries of extensive and ill controlled peat extraction lowered an already gloomy land surface by respective metres. even in flood areas, peat extraction continued through turf dredge. Because of the flood, farm was difficult, which encouraged foreign deal, the solution of which was that the Dutch were involved in world affairs since the early 14th/15th century. [ 112 ]

Delta Works [edit ]
After the 1953 catastrophe, the Delta Works was constructed, which is a comprehensive stage set of civil works throughout the Dutch coast. The project started in 1958 and was largely completed in 1997 with the completion of the Maeslantkering. Since then, modern projects have been sporadically started to renovate and renew the Delta Works. The main finish of the Delta visualize was to reduce the risk of flooding in South Holland and Zeeland to once per 10,000 years ( compared to once per 4000 years for the rest of the country ). This was achieved by raising 3,000 kilometer ( 1,900 michigan ) of out sea-dikes and 10,000 kilometer ( 6,200 mi ) of the inside, duct, and river dikes, and by closing off the sea estuaries of the Zeeland province. New risk assessments occasionally show problems requiring extra Delta project butch reinforcements. The Delta project is considered by the american Society of Civil Engineers as one of the seven wonders of the modern world. [ 119 ] It is anticipated that ball-shaped warm in the twenty-first hundred will result in a emanation in ocean level. The Netherlands is actively preparing for a low-lying rise. A politically achromatic Delta Commission has formulated an action plan to cope with a low-lying surface of 1.10 megabyte ( 4 foot ) and a coincident land height refuse of 10 curium ( 4 in ). The design encompasses the support of the existing coastal defences like dikes and dunes with 1.30 m ( 4.3 foot ) of extra flood protection. Climate change will not only threaten the Netherlands from the seaside but could besides alter rain patterns and river run-off. To protect the state from river implosion therapy, another program is already being executed. The Room for the River plan grants more stream space to rivers, protects the major populated areas and allows for periodic implosion therapy of indefensible lands. The few residents who lived in these alleged “ overflow areas ” have been moved to higher land, with some of that ground having been raised above anticipated flood levels. [ 120 ]
climate [edit ]
The prevailing wind instrument direction in the european Netherlands is southwest, which causes a balmy nautical climate, with reasonably affectionate summers and cool winters, and typically high humidity. This is particularly genuine close to the Dutch coastline, where the dispute in temperature between summer and winter, ampere well as between day and night is perceptibly smaller than it is in the southeast of the country. Ice days—maximum temperature below 0 °C ( 32 °F ) —usually occur from December until February, with the casual rare internal-combustion engine sidereal day prior to or after that period. Freezing days—minimum temperature below 0 °C ( 32 °F ) —occur much more often, normally ranging from mid-november to late March, but not rarely measured adenine early as mid-october and american samoa deep as mid-may. If one chooses the stature of measurement to be 10 curium ( 4 in ) above land alternatively of 150 centimeter ( 59 in ), one may flush find such temperatures in the middle of the summer. On average, snow can occur from November to April but sometimes occurs in May or October excessively. warm days—maximum temperature above 20 °C ( 68 °F ) —are normally found in April to October, but in some parts of the country these warm days can besides occur in March, or even sometimes in November or February ( normally not in De Bilt, however ). Summer days—maximum temperature above 25 °C ( 77 °F ) —are normally measured in De Bilt from May until September, tropical days—maximum temperature above 30 °C ( 86 °F ) —are rare and normally occur only in June to August. haste throughout the year is distributed relatively evenly each month. Summer and fall months tend to gather a little more precipitation than the other months, chiefly because of the intensity of the rain preferably than the frequency of rain days ( this is particularly the case in summer when lightning is besides much more patronize ). The number of sunlight hours is affected by the fact that because of the geographic latitude, the length of the days varies between barely eight hours in December and closely 17 hours in June. The following mesa are based on mean measurements by the KNMI weather station in De Bilt between 1991 and 2020. The highest commemorate temperature was reached on 25 July 2019 in Gilze-Rijen. [ 121 ]
| Climate data for De Bilt (1991–2020 averages), all KNMI locations (1901–2021 extremes), snowy days: (2003-2020 averages). | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 17.2 (63.0) |
20.5 (68.9) |
25.6 (78.1) |
32.2 (90.0) |
35.6 (96.1) |
38.4 (101.1) |
40.7 (105.3) |
38.6 (101.5) |
35.1 (95.2) |
30.1 (86.2) |
22.0 (71.6) |
17.8 (64.0) |
40.7 (105.3) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 6.1 (43.0) |
7.0 (44.6) |
10.5 (50.9) |
14.8 (58.6) |
18.3 (64.9) |
20.9 (69.6) |
23.1 (73.6) |
22.9 (73.2) |
19.5 (67.1) |
14.8 (58.6) |
9.9 (49.8) |
6.7 (44.1) |
14.5 (58.1) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 3.6 (38.5) |
3.9 (39.0) |
6.5 (43.7) |
9.8 (49.6) |
13.4 (56.1) |
16.2 (61.2) |
18.3 (64.9) |
17.9 (64.2) |
14.7 (58.5) |
10.9 (51.6) |
7.0 (44.6) |
4.2 (39.6) |
10.5 (50.9) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 0.9 (33.6) |
0.7 (33.3) |
2.4 (36.3) |
4.5 (40.1) |
8.0 (46.4) |
10.8 (51.4) |
13.0 (55.4) |
12.5 (54.5) |
10.0 (50.0) |
7.1 (44.8) |
3.9 (39.0) |
1.6 (34.9) |
6.0 (42.8) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −27.4 (−17.3) |
−26.8 (−16.2) |
−20.7 (−5.3) |
−9.4 (15.1) |
−5.4 (22.3) |
−1.2 (29.8) |
0.7 (33.3) |
1.3 (34.3) |
−3.7 (25.3) |
−8.5 (16.7) |
−14.4 (6.1) |
−22.3 (−8.1) |
−27.4 (−17.3) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 70.8 (2.79) |
63.1 (2.48) |
57.8 (2.28) |
41.6 (1.64) |
59.3 (2.33) |
70.5 (2.78) |
85.2 (3.35) |
83.6 (3.29) |
77.9 (3.07) |
81.1 (3.19) |
80.0 (3.15) |
83.8 (3.30) |
854.7 (33.65) |
| Average precipitation days ( ≥ 0.1 millimeter ) | 18 | 16 | 15 | 12 | 14 | 14 | 15 | 15 | 14 | 16 | 19 | 19 | 186 |
| Average snowy days ( ≥ 0 curium ) | 5 | 6 | 3 | 0 | — | — | — | — | — | 0 | 1 | 4 | 19 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 87 | 84 | 79 | 74 | 74 | 75 | 77 | 79 | 83 | 86 | 89 | 89 | 81 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 66.6 | 89.6 | 139.4 | 189.2 | 217.5 | 207.1 | 213.9 | 196.3 | 152.8 | 119.3 | 67.4 | 55.5 | 1,714.6 |
| Source: KNMI.nl[122] | |||||||||||||
Climate change [edit ]
nature [edit ]
The Netherlands has 20 national parks and hundreds of early nature reserves, that include lakes, heath, woods, dunes, and other habitats. Most of these are owned by Staatsbosbeheer, the national department for forestry and nature conservation and Natuurmonumenten ( literally ‘Natures monuments ‘ ), a secret organization that buys, protects and manages nature reserves. The dutch separate of the Wadden Sea in the north, with its tidal flats and wetlands, is rich in biological diversity, and was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Nature Site in 2009 .
The Oosterschelde, once the northeast estuary of the river Scheldt was designated a national ballpark in 2002, thereby making it the largest national ballpark in the Netherlands at an area of 370 km2 ( 140 sq nautical mile ). It consists chiefly of the strategic arms limitation talks waters of the Oosterschelde but besides includes mudflats, meadows, and shoals. Because of the big kind of sea animation, including unique regional species, the park is popular with Scuba divers. early activities include glide, fishing, motorbike, and bird watch. Phytogeographically, the european Netherlands is shared between the Atlantic European and Central European provinces of the Circumboreal Region within the Boreal Kingdom. According to the World Wide Fund for Nature, the European territory of the Netherlands belongs to the ecoregion of Atlantic mix forests. [ 128 ] In 1871, the last old original natural woods were cut devour, and most woods today are planted monocultures of trees like Scots pine and trees that are not native to the Netherlands. [ citation needed ] These woods were planted on anthropogenetic heaths and sand-drifts ( overgrazed heaths ) ( Veluwe ). The Netherlands had a 2019 Forest Landscape Integrity Index mean score of 0.6/10, ranking it 169th globally out of 172 countries. [ 129 ] The number of flying insects in the Netherlands has dropped by 75 % since the 1990s. [ 130 ]
Caribbean islands [edit ]
While Curaçao, Aruba and Sint Maarten have a component country status, the Caribbean Netherlands are three islands designated as particular municipalities of the Netherlands. The islands are part of the Lesser Antilles and have land borders with France ( Saint Martin ) and maritime borders with Anguilla, Curaçao, France ( Saint Barthélemy ), Saint Kitts and Nevis, Sint Maarten, the U.S. Virgin Islands and Venezuela. [ 21 ]
Within this island group :
The islands of the Caribbean Netherlands enjoy a tropical climate with warmly weather all class round off. The Leeward Antilles are quick and drier than the Windward islands. In summer, the Windward Islands can be subjugate to hurricanes .
Government and politics [edit ]
 The Binnenhof, where the lower and upper houses of the States General meet The Netherlands has been a built-in monarchy since 1815, and due to the efforts of Johan Rudolph Thorbecke [ 131 ] became a parliamentary democracy in 1848. The Netherlands is described as a consociational state. Dutch politics and government are characterised by an feat to achieve broad consensus on significant issues, within both the political community and society as a solid. In 2017, The Economist ranked the Netherlands as the 11th most democratic state in the universe. The monarch is the head of submit, at present King Willem-Alexander of the Netherlands. Constitutionally, the position is equipped with limited powers. By law, the King has the properly to be sporadically briefed and consulted on government affairs. Depending on the personalities and relationships of the King and the ministers, the monarch might have influence beyond the power granted by the Constitution of the Netherlands .
The Binnenhof, where the lower and upper houses of the States General meet The Netherlands has been a built-in monarchy since 1815, and due to the efforts of Johan Rudolph Thorbecke [ 131 ] became a parliamentary democracy in 1848. The Netherlands is described as a consociational state. Dutch politics and government are characterised by an feat to achieve broad consensus on significant issues, within both the political community and society as a solid. In 2017, The Economist ranked the Netherlands as the 11th most democratic state in the universe. The monarch is the head of submit, at present King Willem-Alexander of the Netherlands. Constitutionally, the position is equipped with limited powers. By law, the King has the properly to be sporadically briefed and consulted on government affairs. Depending on the personalities and relationships of the King and the ministers, the monarch might have influence beyond the power granted by the Constitution of the Netherlands .
The executive power is formed by the Council of Ministers, the deliberative organ of the dutch cabinet. The cabinet normally consists of 13 to 16 ministers and a deviate number of country secretaries. One to three ministers are ministers without portfolio. The question of politics is the Prime Minister of the Netherlands, who frequently is the leader of the largest party of the alliance. The Prime Minister is a primus inter pares, with no denotative powers beyond those of the other ministers. Mark Rutte has been Prime Minister since October 2010 ; the Prime Minister had been the drawing card of the largest party of the governing coalescence endlessly since 1973. The cabinet is responsible to the bicameral parliament, the States General, which besides has legislative powers. The 150 members of the House of Representatives, the lower house, are elected in aim elections on the basis of party-list proportional representation. These are held every four years, or sooner in case the cabinet falls ( for exemplar : when one of the chambers carries a motion of no confidence, the cabinet offers its resignation to the monarch ). The States-Provincial are directly elected every four years ampere well. The members of the provincial assemblies elect the 75 members of the Senate, the upper berth house, which has the exponent to reject laws, but not propose or amend them. Both houses send members to the Benelux Parliament, a advisory council .
political culture [edit ]
Both deal unions and employers organisations are consulted advance in policymaking in the fiscal, economic and social areas. They meet regularly with the government in the Social-Economic Council. This body advises government and its advice can not be put aside well. The Netherlands has a long tradition of social allowance. [ 132 ] In the eighteenth hundred, while the Dutch Reformed Church was the state religion, Catholicism, other forms of Protestantism, such as Baptists and Lutherans, vitamin a well as Judaism were tolerated but discriminated against. [ citation needed ] In the late nineteenth century this dutch custom of religious tolerance transformed into a system of pillarisation, in which religious groups coexisted individually and only interacted at the horizontal surface of government. This tradition of tolerance influences Dutch criminal justice policies on recreational drugs, prostitution, LGBT rights, euthanasia, and miscarriage, which are among the most broad in the worldly concern .
political parties [edit ]
Because of the multi-party system, no single party has held a majority in parliament since the nineteenth hundred, as a result, alliance cabinets had to be formed. Since right to vote became universal in 1917, the Dutch political arrangement has been dominated by three families of political parties : the strongest of which were the christian Democrats, presently represented by the Christian Democratic Appeal ( CDA ) ; moment were the Social Democrats, represented by the Labour Party ( PvdA ) ; and third gear were the Liberals, of which the rightist People ‘s Party for Freedom and Democracy ( VVD ) is the main representative. These parties co-operated in coalescence cabinets in which the Christian Democrats had always been a partner : then either a centre-left coalition of the christian Democrats and Social Democrats was ruling or a centre-right alliance of christian Democrats and Liberals. In the 1970s, the party organization became more volatile : the Christian Democratic parties lost seats, while newly parties became successful, such as the radical democrat and progressive free Democrats 66 ( D66 ) or the ecologist party GroenLinks ( GL ). In the 1994 election, the CDA lost its dominant position. A “ purple “ cabinet was formed by the VVD, D66, and PvdA. In the 2002 elections, this cabinet lost its majority, because of an increased subscribe for the CDA and the rise of the rightist LPF, a newfangled political party, around Pim Fortuyn, who was assassinated a week before the elections. A ephemeral cabinet was formed by CDA, VVD, and LPF, which was led by the CDA Leader Jan Peter Balkenende. After the 2003 elections, in which the LPF lost most of its seats, a cabinet was formed by the CDA, VVD, and D66. The cabinet initiated an ambitious program of reforming the social welfare state, the healthcare system, and immigration policy. In June 2006, the cabinet fell after D66 voted in favor of a motion of no assurance against the Minister of Immigration and Integration, Rita Verdonk, who had instigated an probe of the mental hospital procedure of Ayaan Hirsi Ali, a VVD MP. A caretaker cabinet was formed by the CDA and VVD, and cosmopolitan elections were held on 22 November 2006. In these elections, the CDA remained the largest party and the Socialist Party made the largest gains. The formation of a newfangled cabinet took three months, resulting in a alliance of CDA, PvdA, and Christian Union. On 20 February 2010, the cabinet fell when the PvdA refused to prolong the involvement of the dutch Army in Uruzgan, Afghanistan. [ 133 ] Snap elections were held on 9 June 2010, with devastate results for the previously largest party, the CDA, which lost about half of its seats, resulting in 21 seats. The VVD became the largest party with 31 seats, close followed by the PvdA with 30 seats. The big achiever of the 2010 elections was Geert Wilders, whose right wing PVV, [ 134 ] [ 135 ] the ideological successor to the LPF, more than doubled its number of seats. [ 136 ] Negotiation talks for a new government resulted in a minority government, led by VVD ( a first ) in coalescence with CDA, which was sworn in on 14 October 2010. This unprecedented minority government was supported by PVV, but proved ultimately to be unstable, [ 137 ] when on 21 April 2012, Wilders, drawing card of PVV, unexpectedly ‘torpedoed seven weeks of austerity talks ‘ on new austerity measures, paving the way for early elections. [ 138 ] [ 139 ] [ 140 ] VVD and PvdA won a majority in the House of Representatives during the 2012 general election. On 5 November 2012 they formed the second Rutte cabinet. After the 2017 general election, VVD, Christian Democratic Appeal, Democrats 66 and ChristenUnie formed the third Rutte cabinet. This cabinet resigned in January 2021, two months before the general election, after a child wellbeing fraud scandal. [ 141 ] In March 2021, centre-right VVD of Prime Minister Mark Rutte was the achiever of the elections, securing 35 out of 150 seats. The second biggest party was the centre-left D66 with 24 seats. Geert Wilders ‘ reactionary party lost documentation. Prime Minister Mark Rutte, in power since 2010, formed his one-fourth coalescence government. [ 142 ]
government [edit ]
administrative divisions [edit ]
The Netherlands is divided into twelve provinces, each under a King ‘s Commissioner ( Commissaris van de Koning ). colloquially in Limburg state this placement is named Governor ( Gouverneur ). All provinces are divided into municipalities ( gemeenten ), of which there are 345 ( 2022 ). [ 143 ] [ 144 ] The country is besides subdivided into 21 water districts, governed by a water control panel ( waterschap or hoogheemraadschap ), each having authority in matters concerning water management. [ 145 ] [ 146 ] The creation of water boards actually pre-dates that of the nation itself, the first appear in 1196. The dutch water boards are among the oldest democratic entities in the populace still in universe. lineal elections of the water boards take rate every four years. The administrative structure on the three BES islands, jointly known as the Caribbean Netherlands, is outside the twelve provinces. These islands have the status of openbare lichamen (public bodies). [ 147 ] In the Netherlands these administrative units are much referred to as special municipalities. The Netherlands has several Belgian exclaves [ 148 ] and within those even several enclaves which are separate of the province of North Brabant ( see Baarle-Nassau ). Because the Netherlands and Belgium are both in the Benelux, and more recently in the Schengen Area, citizens of respective countries can travel through these enclaves without controls .
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
extraneous relations [edit ]
The history of Dutch extraneous policy has been characterised by its neutrality. Since World War II, the Netherlands has become a member of a large number of international organisations, most prominently the UN, NATO and the EU. The dutch economy is very open and relies powerfully on international trade. The foreign policy of the Netherlands is based on four basic commitments : to Atlantic co-operation, to european integration, to international growth and to external police. One of the more controversial external issues surrounding the Netherlands is its free policy towards soft drugs. During and after the Dutch Golden Age, the dutch people built up a commercial and colonial conglomerate. The most important colonies were contemporary Suriname and Indonesia. Indonesia became mugwump after the indonesian National Revolution in the 1940s following a war of independence, international pressure and respective United Nations Security Council resolutions. Suriname became independent in 1975. The historical ties inherited from its colonial past still influence the alien relations of the Netherlands. In accession, many people from these countries are living permanently in the Netherlands .
military [edit ]
The Netherlands has one of the oldest stand armies in Europe ; it was first established as such by Maurice of Nassau in the late 1500s. The dutch army was used throughout the Dutch Empire. After the get the better of of Napoleon, the dutch army was transformed into a conscription united states army. The army was unsuccessfully deployed during the belgian Revolution in 1830. After 1830, it was deployed chiefly in the dutch colonies, as the Netherlands remained inert in european wars ( including the first World War ), until the Netherlands was invaded in World War II and defeated by the Wehrmacht in May 1940 .
The Netherlands abandoned its neutrality in 1948 when it signed the Treaty of Brussels, and became a initiation extremity of NATO in 1949. The dutch military was therefore part of the NATO potency in Cold War Europe, deploying its army to several bases in Germany. More than 3,000 dutch soldiers were assigned to the 2nd Infantry Division of the United States Army during the Korean War. In 1996 conscription was suspended, and the dutch army was once again transformed into a professional united states army. Since the 1990s the dutch united states army has been involved in the Bosnian War and the Kosovo War, it held a state in Iraq after the frustration of Saddam Hussein, and it was engaged in Afghanistan. The military is composed of four branches, all of which carry the prefix Koninklijke ( Royal ) :
- Koninklijke Marine (KM), the Royal Netherlands Navy, including the Naval Air Service and Marine Corps;
- Koninklijke Landmacht (KL), the Royal Netherlands Army;
- Koninklijke Luchtmacht (KLu), the Royal Netherlands Air Force;
- Koninklijke Marechaussee (KMar), the Royal Marechaussee (Military Police), tasks include military police and border control.
The bomber service opened to women on 1 January 2017. The Korps Commandotroepen, the special Operations Force of the Netherlands Army, is open to women, but because of the extremely high physical demands for initial train, it is about impossible for a woman to become a commando. [ 151 ] The Dutch Ministry of Defence employs more than 70,000 personnel, including over 20,000 civilians and over 50,000 military personnel. [ 152 ] In April 2011 the government announced a major reduction in its military because of a cut in government consumption, including a decrease in the issue of tanks, combatant aircraft, naval ships and senior officials. [ 153 ] The Netherlands has ratified many external conventions concerning war law. The Netherlands decided not to sign the UN treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons. [ 154 ]
economy [edit ]
 A proportional representation of Netherlands exports, 2019 The Netherlands has a develop economy and has been playing a particular function in the european economy for many centuries. Since the sixteenth century, ship, fish, agribusiness, trade, and bank have been leading sectors of the dutch economy. The Netherlands has a high charge of economic freedom. The Netherlands is one of the exceed countries in the Global Enabling Trade Report ( 2nd in 2016 ), and was ranked the fifth most competitive economy in the world by the swiss International Institute for Management Development in 2017. [ 155 ] In addition, the country was ranked the irregular most innovative nation in the earth in the 2018 Global Innovation Index. [ 156 ]
A proportional representation of Netherlands exports, 2019 The Netherlands has a develop economy and has been playing a particular function in the european economy for many centuries. Since the sixteenth century, ship, fish, agribusiness, trade, and bank have been leading sectors of the dutch economy. The Netherlands has a high charge of economic freedom. The Netherlands is one of the exceed countries in the Global Enabling Trade Report ( 2nd in 2016 ), and was ranked the fifth most competitive economy in the world by the swiss International Institute for Management Development in 2017. [ 155 ] In addition, the country was ranked the irregular most innovative nation in the earth in the 2018 Global Innovation Index. [ 156 ]
 The Netherlands is a heavily develop country. Shown here is a expressway sink by a polder with a drain windmill, and two wind instrument turbines in the background. As of 2020, the key trade partners of the Netherlands were Germany, Belgium, the United Kingdom, the United States, France, Italy, China and Russia. [ 157 ] The Netherlands is one of the populace ‘s 10 go exporting countries. Foodstuffs form the largest industrial sector. early major industries include chemicals, metallurgy, machinery, electric goods, trade, services and tourism. Examples of international Dutch companies operating in Netherlands include Randstad, Unilever, Heineken, KLM, fiscal services ( ING, ABN AMRO, Rabobank ), chemicals ( DSM, AKZO ), petroleum complicate ( Royal Dutch Shell ), electronical machinery ( Philips, ASML ), and satellite navigation ( TomTom ). The Netherlands has the 17th-largest economy in the world, and ranks 11th in GDP ( nominal ) per head. between 1997 and 2000 annual economic growth ( GDP ) averaged about 4 %, well above the european average. Growth slowed well from 2001 to 2005 with the ball-shaped economic slowdown, but accelerated to 4.1 % in the third stern of 2007. In May 2013, inflation was at 2.8 % per class. [ 158 ] In April 2013, unemployment was at 8.2 % ( or 6.7 % following the ILO definition ) of the british labour party military unit. [ 159 ] In February 2019, this was reduced to 3.4 %. [ 160 ] In Q3 and Q4 2011, the dutch economy contracted by 0.4 % and 0.7 %, respectively, because of european Debt Crisis, while in Q4 the Eurozone economy flinch by 0.3 %. [ 161 ] The Netherlands besides has a relatively first gear GINI coefficient of 0.326. Despite ranking 11th in GDP per caput, UNICEF ranked the Netherlands 1st in child wellbeing in ample countries, both in 2007 and in 2013. [ 162 ] [ 163 ] [ 164 ] On the Index of Economic Freedom Netherlands is the 14th most detached market capitalist economy out of 180 survey countries. Amsterdam is the fiscal and commercial enterprise capital of the Netherlands. [ 165 ] The Amsterdam Stock Exchange ( AEX ), depart of Euronext, is the earth ‘s oldest broth exchange and is one of Europe ‘s largest bourses. It is situated near Dam Square in the city ‘s center. As a establish member of the euro, the Netherlands replaced ( for accounting purposes ) its early currency, the “ guilder ” ( guilder ), on 1 January 1999, along with 15 other adopters of the euro. actual euro coins and banknotes followed on 1 January 2002. One euro was equivalent to 2.20371 dutch guilders. In the Caribbean Netherlands, the United States dollar is used rather of the euro .
The Netherlands is a heavily develop country. Shown here is a expressway sink by a polder with a drain windmill, and two wind instrument turbines in the background. As of 2020, the key trade partners of the Netherlands were Germany, Belgium, the United Kingdom, the United States, France, Italy, China and Russia. [ 157 ] The Netherlands is one of the populace ‘s 10 go exporting countries. Foodstuffs form the largest industrial sector. early major industries include chemicals, metallurgy, machinery, electric goods, trade, services and tourism. Examples of international Dutch companies operating in Netherlands include Randstad, Unilever, Heineken, KLM, fiscal services ( ING, ABN AMRO, Rabobank ), chemicals ( DSM, AKZO ), petroleum complicate ( Royal Dutch Shell ), electronical machinery ( Philips, ASML ), and satellite navigation ( TomTom ). The Netherlands has the 17th-largest economy in the world, and ranks 11th in GDP ( nominal ) per head. between 1997 and 2000 annual economic growth ( GDP ) averaged about 4 %, well above the european average. Growth slowed well from 2001 to 2005 with the ball-shaped economic slowdown, but accelerated to 4.1 % in the third stern of 2007. In May 2013, inflation was at 2.8 % per class. [ 158 ] In April 2013, unemployment was at 8.2 % ( or 6.7 % following the ILO definition ) of the british labour party military unit. [ 159 ] In February 2019, this was reduced to 3.4 %. [ 160 ] In Q3 and Q4 2011, the dutch economy contracted by 0.4 % and 0.7 %, respectively, because of european Debt Crisis, while in Q4 the Eurozone economy flinch by 0.3 %. [ 161 ] The Netherlands besides has a relatively first gear GINI coefficient of 0.326. Despite ranking 11th in GDP per caput, UNICEF ranked the Netherlands 1st in child wellbeing in ample countries, both in 2007 and in 2013. [ 162 ] [ 163 ] [ 164 ] On the Index of Economic Freedom Netherlands is the 14th most detached market capitalist economy out of 180 survey countries. Amsterdam is the fiscal and commercial enterprise capital of the Netherlands. [ 165 ] The Amsterdam Stock Exchange ( AEX ), depart of Euronext, is the earth ‘s oldest broth exchange and is one of Europe ‘s largest bourses. It is situated near Dam Square in the city ‘s center. As a establish member of the euro, the Netherlands replaced ( for accounting purposes ) its early currency, the “ guilder ” ( guilder ), on 1 January 1999, along with 15 other adopters of the euro. actual euro coins and banknotes followed on 1 January 2002. One euro was equivalent to 2.20371 dutch guilders. In the Caribbean Netherlands, the United States dollar is used rather of the euro .
The dutch location gives it prime access to markets in the UK and Germany, with the Port of Rotterdam being the largest port in Europe. early crucial parts of the economy are international trade ( Dutch colonialism started with co-operative individual enterprises such as the Dutch East India Company ), bank and conveyance. The Netherlands successfully addressed the publish of public finances and stagnating job growth long before its european partners. Amsterdam is the 5th-busiest tourist finish in Europe with more than 4.2 million international visitors. [ 166 ] Since the enlargement of the EU large numbers of migrant workers have arrived in the Netherlands from Central and Eastern Europe. [ 167 ] The Netherlands continues to be one of the leading european nations for attracting foreign direct investment and is one of the five largest investors in the United States. The economy experienced a slowdown in 2005, but in 2006 recovered to the fastest pace in six years on the back of increased exports and strong investment. The yard of occupation growth reached 10-year highs in 2007. The Netherlands is the fourth-most competitive economy in the global, according to the World Economic Forum ‘s Global Competitiveness Report. [ 168 ]
Read more: Chord (music) – Wikipedia
Natural flatulence [edit ]
 Natural gasoline concessions in the Netherlands. nowadays the Netherlands accounts for more than 25 % of all natural accelerator reserves in the EU. Beginning in the 1950s, the Netherlands discovered huge lifelike natural gas resources. The sale of natural flatulence generated enormous revenues for the Netherlands for decades, adding hundreds of billions of euros to the government ‘s budget. [ 169 ] however, the unanticipated consequences of the state ‘s huge department of energy wealth impacted the competitiveness of early sectors of the economy, leading to the hypothesis of dutch disease. [ 169 ]
Natural gasoline concessions in the Netherlands. nowadays the Netherlands accounts for more than 25 % of all natural accelerator reserves in the EU. Beginning in the 1950s, the Netherlands discovered huge lifelike natural gas resources. The sale of natural flatulence generated enormous revenues for the Netherlands for decades, adding hundreds of billions of euros to the government ‘s budget. [ 169 ] however, the unanticipated consequences of the state ‘s huge department of energy wealth impacted the competitiveness of early sectors of the economy, leading to the hypothesis of dutch disease. [ 169 ]
 The Groningen gasoline sphere whose discovery in 1959 transformed the dutch economy, generating €159 billion in gross since the mid-1970s. apart from coal and gas, the area has no mining resources. The last coal mine was closed in 1974. The Groningen gas field, one of the largest natural-gas fields in the populace, is situated near Slochteren. The exploitation of this field has resulted in €159 billion in tax income since the mid-1970s. [ 170 ] The sphere is operated by government-owned Gasunie and output is jointly exploited by the politics, Royal Dutch Shell, and Exxon Mobil through NAM ( Nederlandse Aardolie Maatschappij ). “ Gas origin has resulted in increasingly strong earth tremors, some measure a much as 3.6 on the Richter order of magnitude scale. The cost of price repairs, morphologic improvements to buildings, and compensation for home rate decreases has been estimated at €6.5 billion. Around 35,000 homes are said to be affected. ” [ 171 ] The Netherlands has an estimated 25 % of natural flatulence reserves in the EU. [ 172 ] The energy sector accounted for about 11 % of the GDP in 2014. [ 173 ] Netherlands ‘ economy, chiefly due to the large shares of natural accelerator reserves, is considered to have “ very high gear ” energy saturation denounce. [ 174 ] The Netherlands is faced with future challenges as the energy supply is forecasted to fall short of the necessitate by the year 2025 in the gasoline sector. This is attributed to the depletion of the Netherlands ‘ major gas playing field, Groningen, and the earthquakes that have hit the Groningen region. [ 175 ] In summation, there is ambiguity surrounding the feasibility of producing unconventional gasoline. The Netherlands relies heavily on natural gas to provide energy. Gas is the main source of heating for households in the Netherlands [ 172 ] and represented 35 % of the energy mix in 2014. [ 176 ] Furthermore, The European Union 2020 box ( 20 % decrease in GHG emissions, 20 % renewables in the department of energy mix and 20 % improvement in energy efficiency ) enacted in 2009 has influenced the domestic energy politics of Netherlands and pressured non-state actors to give accept to more aggressive energy reforms that would reduce reliance on natural resources as a informant of income to the economy. [ 177 ] Therefore, a passage towards renewable department of energy has been a winder objective by Netherlands in club to safeguard the energy security of the country from natural resources depletion, chiefly boast. [ 172 ] Netherlands has set a 14 % renewable energy target of the total energy shuffle by the year 2020. [ 178 ] however, the good continuation of providing tax breaks to electricity generated by coal and flatulence, and to the exploration and extraction of flatulence from fields that are “ insufficiently ” profitable, [ 179 ] renders a successful transition towards renewable energy more unmanageable to achieve due to inconsistencies in the policy mix. In 2011, it was estimated that the renewable department of energy sector received 31 % ( EUR 743MM ), while the conventional energy sector received 69 % ( EUR 1.6B ), of the sum energy subsidies by the government. [ 179 ] Furthermore, the energy market in the Netherlands remains to be dominated by few major corporations Nuon, RWE, E.ON, Eneco, and Delta that have significant influence over the energy policy. [ 180 ] Renewable energy parcel in the energy shuffle is estimated to reach 12.4 % by the year 2020, falling 1.6 % short of the 14 % target. [ 178 ] [ needs update ]
The Groningen gasoline sphere whose discovery in 1959 transformed the dutch economy, generating €159 billion in gross since the mid-1970s. apart from coal and gas, the area has no mining resources. The last coal mine was closed in 1974. The Groningen gas field, one of the largest natural-gas fields in the populace, is situated near Slochteren. The exploitation of this field has resulted in €159 billion in tax income since the mid-1970s. [ 170 ] The sphere is operated by government-owned Gasunie and output is jointly exploited by the politics, Royal Dutch Shell, and Exxon Mobil through NAM ( Nederlandse Aardolie Maatschappij ). “ Gas origin has resulted in increasingly strong earth tremors, some measure a much as 3.6 on the Richter order of magnitude scale. The cost of price repairs, morphologic improvements to buildings, and compensation for home rate decreases has been estimated at €6.5 billion. Around 35,000 homes are said to be affected. ” [ 171 ] The Netherlands has an estimated 25 % of natural flatulence reserves in the EU. [ 172 ] The energy sector accounted for about 11 % of the GDP in 2014. [ 173 ] Netherlands ‘ economy, chiefly due to the large shares of natural accelerator reserves, is considered to have “ very high gear ” energy saturation denounce. [ 174 ] The Netherlands is faced with future challenges as the energy supply is forecasted to fall short of the necessitate by the year 2025 in the gasoline sector. This is attributed to the depletion of the Netherlands ‘ major gas playing field, Groningen, and the earthquakes that have hit the Groningen region. [ 175 ] In summation, there is ambiguity surrounding the feasibility of producing unconventional gasoline. The Netherlands relies heavily on natural gas to provide energy. Gas is the main source of heating for households in the Netherlands [ 172 ] and represented 35 % of the energy mix in 2014. [ 176 ] Furthermore, The European Union 2020 box ( 20 % decrease in GHG emissions, 20 % renewables in the department of energy mix and 20 % improvement in energy efficiency ) enacted in 2009 has influenced the domestic energy politics of Netherlands and pressured non-state actors to give accept to more aggressive energy reforms that would reduce reliance on natural resources as a informant of income to the economy. [ 177 ] Therefore, a passage towards renewable department of energy has been a winder objective by Netherlands in club to safeguard the energy security of the country from natural resources depletion, chiefly boast. [ 172 ] Netherlands has set a 14 % renewable energy target of the total energy shuffle by the year 2020. [ 178 ] however, the good continuation of providing tax breaks to electricity generated by coal and flatulence, and to the exploration and extraction of flatulence from fields that are “ insufficiently ” profitable, [ 179 ] renders a successful transition towards renewable energy more unmanageable to achieve due to inconsistencies in the policy mix. In 2011, it was estimated that the renewable department of energy sector received 31 % ( EUR 743MM ), while the conventional energy sector received 69 % ( EUR 1.6B ), of the sum energy subsidies by the government. [ 179 ] Furthermore, the energy market in the Netherlands remains to be dominated by few major corporations Nuon, RWE, E.ON, Eneco, and Delta that have significant influence over the energy policy. [ 180 ] Renewable energy parcel in the energy shuffle is estimated to reach 12.4 % by the year 2020, falling 1.6 % short of the 14 % target. [ 178 ] [ needs update ]
farming and natural resources [edit ]
 Cows near the city of Arnhem From a biological resource perspective, the Netherlands has a low endowment : the Netherlands ’ biocapacity adds up to only 0.8 global hectares in 2016, 0.2 of which are dedicated to department of agriculture. The dutch biocapacity per person is good about half of the 1.6 global hectares of biocapacity per person available cosmopolitan. [ 182 ] In contrast, in 2016, the Dutch used on average 4.8 ball-shaped hectares of biocapacity – their ecological footprint of pulmonary tuberculosis. This means the dutch required closely six times ampere much biocapacity as the Netherlands contains. As a result, the Netherlands was running a biocapacity deficit of 4.0 global hectares per person in 2016. The dutch agrarian sector is highly mechanised, and has a strong focus on external exports. It employs about 4 % of the Dutch parturiency force but produces large surpluses in the food-processing industry and accounts for 21 % of the Dutch total export value. [ 183 ] The Dutch membership foremost in the European Union and irregular cosmopolitan in value of agrarian exports, behind merely the United States, [ 184 ] with agrarian exports earning €80.7 billion in 2014, [ 185 ] up from €75.4 billion in 2012. [ 33 ] In 2019 agricultural exports were worth €94.5 billion. [ 186 ] one-third of the populace ‘s exports of chili, tomatoes, and cucumbers goes through the nation. The Netherlands besides exports one-fifteenth of the world ‘s apples. [ 187 ] aside from that, a significant helping of Dutch agricultural exports consists of fresh-cut plants, flowers, and flower bulbs, with the Netherlands exporting two-thirds of the world ‘s full. [ 187 ]
Cows near the city of Arnhem From a biological resource perspective, the Netherlands has a low endowment : the Netherlands ’ biocapacity adds up to only 0.8 global hectares in 2016, 0.2 of which are dedicated to department of agriculture. The dutch biocapacity per person is good about half of the 1.6 global hectares of biocapacity per person available cosmopolitan. [ 182 ] In contrast, in 2016, the Dutch used on average 4.8 ball-shaped hectares of biocapacity – their ecological footprint of pulmonary tuberculosis. This means the dutch required closely six times ampere much biocapacity as the Netherlands contains. As a result, the Netherlands was running a biocapacity deficit of 4.0 global hectares per person in 2016. The dutch agrarian sector is highly mechanised, and has a strong focus on external exports. It employs about 4 % of the Dutch parturiency force but produces large surpluses in the food-processing industry and accounts for 21 % of the Dutch total export value. [ 183 ] The Dutch membership foremost in the European Union and irregular cosmopolitan in value of agrarian exports, behind merely the United States, [ 184 ] with agrarian exports earning €80.7 billion in 2014, [ 185 ] up from €75.4 billion in 2012. [ 33 ] In 2019 agricultural exports were worth €94.5 billion. [ 186 ] one-third of the populace ‘s exports of chili, tomatoes, and cucumbers goes through the nation. The Netherlands besides exports one-fifteenth of the world ‘s apples. [ 187 ] aside from that, a significant helping of Dutch agricultural exports consists of fresh-cut plants, flowers, and flower bulbs, with the Netherlands exporting two-thirds of the world ‘s full. [ 187 ]
Demographics [edit ]
 population of the Netherlands from 1900 to 2000 The Netherlands had an estimated population of 17,493,969 as of 30 April 2021. [ 149 ] It is the fifth most densely populate state in Europe, and except for identical small city-states like Monaco, Vatican City and San Marino, it is the most densely populated country in Europe. And it is the 16th most dumbly populate state in the earth with a density of 424 per square kilometer ( 1,100/sq mile ). It is the 67th most populous country in the universe. between 1900 and 1950, the state ‘s population about doubled from 5.1 to 10 million. From 1950 to 2000, the population further increased, to 15.9 million, though this represented a lower rate of population growth. [ 188 ] The calculate growth rate in 2013 is 0.44 %. [ 189 ]
population of the Netherlands from 1900 to 2000 The Netherlands had an estimated population of 17,493,969 as of 30 April 2021. [ 149 ] It is the fifth most densely populate state in Europe, and except for identical small city-states like Monaco, Vatican City and San Marino, it is the most densely populated country in Europe. And it is the 16th most dumbly populate state in the earth with a density of 424 per square kilometer ( 1,100/sq mile ). It is the 67th most populous country in the universe. between 1900 and 1950, the state ‘s population about doubled from 5.1 to 10 million. From 1950 to 2000, the population further increased, to 15.9 million, though this represented a lower rate of population growth. [ 188 ] The calculate growth rate in 2013 is 0.44 %. [ 189 ]
The birthrate rate in the Netherlands is 1.78 children per charwoman ( 2018 estimate ), [ 189 ] which is high compared with many other european countries, but below the pace of 2.1 children per woman required for natural population substitution, it remains well below the high of 5.39 children born per charwoman in 1879. [ 190 ] Netherlands subsequently has one of the oldest populations in the world, with the average age of 42.7 years. [ 189 ] Life anticipation is gamey in the Netherlands : 84.3 years for newborn girls and 79.7 for boys ( 2020 estimate ). [ 189 ] The country has a migration rate of 1.9 migrants per 1,000 inhabitants per year. [ 189 ] The majority of the population of the Netherlands is ethnically Dutch. According to a 2005 appraisal, the population was 80.9 % Dutch, 2.4 % indonesian, 2.4 % german, 2.2 % Turkish, 2.0 % Surinamese, 1.9 % Moroccan, 0.8 % Antillean and Aruban, and 7.4 % others. [ 191 ] Some 150,000 to 200,000 people living in the Netherlands are expatriates, by and large concentrated in and around Amsterdam and The Hague, now constituting about 10 % of the population of these cities. [ 192 ] [ 193 ] The Dutch are the tallest people in the global, by nationality, [ 194 ] with an average height of 1.81 metres ( 5 foot 11.3 in ) for pornographic males and 1.67 metres ( 5 foot 5.7 in ) for pornographic females in 2009. [ 195 ] People in the south are on average about 2 centimeter ( 0.8 inches ) shorter than those in the north .
 In Rotterdam about half the population has an immigrant backdrop. According to Eurostat, in 2010 there were 1.8 million foreign-born residents in the Netherlands, corresponding to 11.1 % of the total population. Of these, 1.4 million ( 8.5 % ) were born outside the EU and 0.43 million ( 2.6 % ) were born in another EU Member State. [ 196 ] On 21 November 2016, there were 3.8 million residents in the Netherlands with at least one foreign-born rear ( “ migration background ” ). [ 197 ] On 1 January 2016, 26,2 % of persons aged 0-50 had at least one rear born in a foreign country. 11,4 % of persons aged 0-50 ‘of Dutch setting ‘ belonged to the ‘third generation ‘. Of these 739,000 had western grandparents, 120,000 non-western. The third generation constitutes from persons born from two second genesis immigrants or one irregular genesis immigrant and one person with a dutch background. First and second generation immigrants and the one-third generation were 34,5 % of the population aged 0-50. [ 198 ] Over half the young people in Amsterdam and Rotterdam have a non-western backdrop. [ 199 ] Dutch people, or descendants of dutch people, are besides found in migrant communities worldwide, notably in Canada, Australia, South Africa and the United States. According to the United States Census Bureau ( 2006 ), more than 5 million Americans claim sum or partial derivative Dutch ancestry. [ 200 ] There are close up to 3 million Dutch-descended Afrikaners living in South Africa. [ 201 ] In 1940, there were 290,000 Europeans and Eurasians in Indonesia, [ 202 ] but most have since left the area. [ 203 ] The Randstad is the country ‘s largest conurbation located in the west of the nation and contains the four largest cities : Amsterdam in the province North Holland, Rotterdam and The Hague in the province South Holland, and Utrecht in the province Utrecht. The Randstad has a population of about 8.2 million inhabitants [ 204 ] and is the fifth largest metropolitan area in Europe. According to Dutch Central Statistics Bureau, in 2015, 28 per penny of the dutch population had a expendable income above 45,000 euros ( which does not include spending on health worry or education ). [ 205 ]
In Rotterdam about half the population has an immigrant backdrop. According to Eurostat, in 2010 there were 1.8 million foreign-born residents in the Netherlands, corresponding to 11.1 % of the total population. Of these, 1.4 million ( 8.5 % ) were born outside the EU and 0.43 million ( 2.6 % ) were born in another EU Member State. [ 196 ] On 21 November 2016, there were 3.8 million residents in the Netherlands with at least one foreign-born rear ( “ migration background ” ). [ 197 ] On 1 January 2016, 26,2 % of persons aged 0-50 had at least one rear born in a foreign country. 11,4 % of persons aged 0-50 ‘of Dutch setting ‘ belonged to the ‘third generation ‘. Of these 739,000 had western grandparents, 120,000 non-western. The third generation constitutes from persons born from two second genesis immigrants or one irregular genesis immigrant and one person with a dutch background. First and second generation immigrants and the one-third generation were 34,5 % of the population aged 0-50. [ 198 ] Over half the young people in Amsterdam and Rotterdam have a non-western backdrop. [ 199 ] Dutch people, or descendants of dutch people, are besides found in migrant communities worldwide, notably in Canada, Australia, South Africa and the United States. According to the United States Census Bureau ( 2006 ), more than 5 million Americans claim sum or partial derivative Dutch ancestry. [ 200 ] There are close up to 3 million Dutch-descended Afrikaners living in South Africa. [ 201 ] In 1940, there were 290,000 Europeans and Eurasians in Indonesia, [ 202 ] but most have since left the area. [ 203 ] The Randstad is the country ‘s largest conurbation located in the west of the nation and contains the four largest cities : Amsterdam in the province North Holland, Rotterdam and The Hague in the province South Holland, and Utrecht in the province Utrecht. The Randstad has a population of about 8.2 million inhabitants [ 204 ] and is the fifth largest metropolitan area in Europe. According to Dutch Central Statistics Bureau, in 2015, 28 per penny of the dutch population had a expendable income above 45,000 euros ( which does not include spending on health worry or education ). [ 205 ]
functional urban areas [edit ]
 Population concentration in the Netherlands by municipality. The largest urban area, the Randstad is intelligibly visible along the west coast .
Population concentration in the Netherlands by municipality. The largest urban area, the Randstad is intelligibly visible along the west coast .
linguistic process [edit ]
 [208] Knowledge of foreign languages in the Netherlands, in per penny of the population over the age of 15, as of 2006 The official speech is Dutch, which is spoken by the huge majority of the inhabitants. Besides Dutch, West Frisian is recognised as a second official terminology in the northern province of Friesland ( Fryslân in West Frisian ). [ 209 ] West Frisian has a formal status for government correspondence in that province. In the european partially of the kingdom two other regional languages are recognised under the european Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. [ 210 ] The first of these recognised regional languages is low Saxon ( Nedersaksisch in Dutch ). low Saxon consists of several dialects of the depleted german linguistic process spoken in the north and east of the Netherlands, like Tweants in the region of Twente, and Drents in the province of Drenthe. second, Limburgish is besides recognised as a regional speech. It consists of Dutch varieties of Meuse-Rhenish Franconian languages and is spoken in the south-eastern province of Limburg. [ 109 ] The dialects most spoken in the Netherlands are the Brabantian – Hollandic dialects. [ 211 ] Ripuarian linguistic process, which is spoken in Kerkrade and Vaals in the class of, respectively, the Kerkrade dialect and the Vaals dialect [ 212 ] [ 213 ] are legally treated ampere Limburgish as well – see southeast Limburgish dialect. English has a formal condition in the special municipalities of Saba and Sint Eustatius. It is wide spoken on these islands. Papiamento has a conventional status in the particular municipality of Bonaire. yiddish and the Romani language were recognised in 1996 as non-territorial languages. [ 214 ] The Netherlands has a tradition of learning extraneous languages, formalised in dutch education laws. Some 90 % of the sum population bespeak they are able to converse in English, 70 % in german, and 29 % in French. [ 215 ] English is a compulsory course in all secondary schools. [ 216 ] In most lower level junior-grade school educations ( vmbo ), one extra modern extraneous language is compulsory during the first two years. [ 217 ] In higher degree secondary schools ( HAVO and VWO ), the acquisition of two extra modern foreign lyric skills is mandate during the first three years. only during the last three years in VWO one extraneous language is mandate. Besides English, the criterion modern languages are french and german, although schools can replace one of these modern languages with Chinese, Spanish, Russian, Italian, Turkish or Arabic. [ 218 ] Additionally, schools in Friesland teach and have exams in West Frisian, and schools across the country teach and have exams in Ancient Greek and Latin for secondary coil school ( called Gymnasium or VWO+ ) .
[208] Knowledge of foreign languages in the Netherlands, in per penny of the population over the age of 15, as of 2006 The official speech is Dutch, which is spoken by the huge majority of the inhabitants. Besides Dutch, West Frisian is recognised as a second official terminology in the northern province of Friesland ( Fryslân in West Frisian ). [ 209 ] West Frisian has a formal status for government correspondence in that province. In the european partially of the kingdom two other regional languages are recognised under the european Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. [ 210 ] The first of these recognised regional languages is low Saxon ( Nedersaksisch in Dutch ). low Saxon consists of several dialects of the depleted german linguistic process spoken in the north and east of the Netherlands, like Tweants in the region of Twente, and Drents in the province of Drenthe. second, Limburgish is besides recognised as a regional speech. It consists of Dutch varieties of Meuse-Rhenish Franconian languages and is spoken in the south-eastern province of Limburg. [ 109 ] The dialects most spoken in the Netherlands are the Brabantian – Hollandic dialects. [ 211 ] Ripuarian linguistic process, which is spoken in Kerkrade and Vaals in the class of, respectively, the Kerkrade dialect and the Vaals dialect [ 212 ] [ 213 ] are legally treated ampere Limburgish as well – see southeast Limburgish dialect. English has a formal condition in the special municipalities of Saba and Sint Eustatius. It is wide spoken on these islands. Papiamento has a conventional status in the particular municipality of Bonaire. yiddish and the Romani language were recognised in 1996 as non-territorial languages. [ 214 ] The Netherlands has a tradition of learning extraneous languages, formalised in dutch education laws. Some 90 % of the sum population bespeak they are able to converse in English, 70 % in german, and 29 % in French. [ 215 ] English is a compulsory course in all secondary schools. [ 216 ] In most lower level junior-grade school educations ( vmbo ), one extra modern extraneous language is compulsory during the first two years. [ 217 ] In higher degree secondary schools ( HAVO and VWO ), the acquisition of two extra modern foreign lyric skills is mandate during the first three years. only during the last three years in VWO one extraneous language is mandate. Besides English, the criterion modern languages are french and german, although schools can replace one of these modern languages with Chinese, Spanish, Russian, Italian, Turkish or Arabic. [ 218 ] Additionally, schools in Friesland teach and have exams in West Frisian, and schools across the country teach and have exams in Ancient Greek and Latin for secondary coil school ( called Gymnasium or VWO+ ) .
religion [edit ]
The population of the Netherlands was predominantly christian until the late twentieth hundred, divided into a issue of denominations. Although significant religious diverseness remains, there has been a refuse of religious adhesiveness. The Netherlands is immediately one of the most laic societies in the world. In 2019, Statistics Netherlands found that 54.1 % of the total population declared itself to be non-religious. Groups that represent the non-religious in the Netherlands include Humanistisch Verbond. Catholics comprised 20.1 % of the sum population, Protestants ( 14.8 % ). Muslims comprised 5.0 % of the sum population and followers of other christian denominations and other religions ( like Judaism, Buddhism and Hinduism ) comprised the remaining 5.9 %. [ 4 ] A 2015 surveil from another source found that Protestants outnumbered Catholics. [ 219 ] The southern provinces of North Brabant and Limburg have historically been powerfully Catholic, and some residents consider the Catholic Church as a base for their cultural identity. protestantism in the Netherlands consists of a phone number of churches within diverse traditions. The largest of these is the protestant church in the Netherlands ( PKN ), a connect church which is Calvinist and Lutheran in orientation. [ 220 ] It was formed in 2004 as a amalgamation of the Dutch Reformed Church, the Reformed Churches in the Netherlands and a smaller Lutheran Church. respective orthodox calvinist and free churches did not merge into the PKN. Although in the Netherlands as a wholly christendom has become a minority, the Netherlands contains a bible belt from Zeeland to the northern parts of the province Overijssel, in which Protestant ( particularly Calvinist ) beliefs remain solid, and even has majorities in municipal councils. Islam is the second largest religion in the state. In 2012, there were about 825,000 Muslims in the Netherlands ( 5 % of the population ). [ 221 ] The Muslim population increased from the 1960 as a consequence of big numbers of migrant workers. This included migrant workers from Turkey and Morocco, deoxyadenosine monophosphate well as migrants from former Dutch colonies, such as Surinam and Indonesia. During the 1990s, Muslim refugees arrived from countries like Bosnia and Herzegovina, Iran, Iraq, Somalia, and Afghanistan. [ 222 ] Another religion practised is Hinduism, with around 215,000 adherents ( slenderly over 1 % of the population ). Most of these are Indo-Surinamese. There are besides ample populations of Hindu immigrants from India and Sri Lanka, and some western adherents of Hinduism-orientated newfangled religious movements such as Hare Krishnas. The Netherlands has an estimated 250,000 Buddhists or people powerfully attracted to this religion, chiefly cultural dutch people. In addition, there are about 45,000 Jews in the Netherlands. The Constitution of the Netherlands guarantees exemption of education, which means that all schools that stand by to general quality criteria receive the lapp government fund. This includes schools based on religious principles by religious groups ( specially Catholic and assorted Protestant ). Three political parties in the Dutch parliament, ( CDA, and two humble parties, ChristianUnion and SGP ) are based upon the christian impression. respective Christian religious holidays are national holidays ( Christmas, Easter, Pentecost and the Ascension of Jesus ). [ 223 ] Upon the country ‘s independence, Protestants were predominant in most of the nation, while roman Catholics were dominant in the south, particularly North Brabant and Limburg. In the late nineteenth hundred, secularism, atheism and pillarisation gained adherents. By 1960, Catholics equalled Protestants in count ; thereafter, both Christian branches began to decline. conversely, Islam grew well as the solution of immigration. Since 2000 there has been raised awareness of religion, chiefly due to Muslim extremism. [ 224 ] The Dutch royal syndicate has been traditionally associated with Calvinism, specifically the dutch Reformed Church, which has merged into the Protestant Church in the Netherlands. The dutch Reformed Church was the only major Protestant church in the Netherlands from the Reformation until the nineteenth hundred. denominational splits in 1834 and in 1886 diversified Dutch Calvinism. In 2013, a Catholic became Queen consort. A surveil in December 2014 concluded that for the first time there were more atheists ( 25 % ) than theists ( 17 % ) in the Netherlands, while the remainder of the population was agnostic ( 31 % ) or ietsistic ( 27 % ). [ 225 ] In 2015, a huge majority of the inhabitants of the Netherlands ( 82 % ) said they had never or about never visited a church, and 59 % stated that they had never been to a church of any kind. Of all the people questioned, 24 % saw themselves as atheist, an increase of 11 % compared to the previous study done in 2006. [ 226 ] The expect advance of spirituality ( ietsism ) has come to a stem according to inquiry in 2015. In 2006, 40 % of respondents considered themselves apparitional ; in 2015 this has dropped to 31 %. The number who believed in the being of a higher might fell from 36 % to 28 % over the lapp period. [ 227 ]
education [edit ]
 An external primary school in The Hague
An external primary school in The Hague view on the Utrecht Science Park of Utrecht University. The build in the center is the library. education in the Netherlands is compulsory between the ages of 5 and 16. If a child does not have a “ startle reservation ” ( HAVO, VWO or MBO 2+ degree ) they are still forced to attend classes until they achieve such a qualification or reach the senesce of 18. [ 228 ] All children in the Netherlands normally attend elementary school from ( on average ) ages 4 to 12. It comprises eight grades, the first of which is facultative. Based on an aptitude test, the eighth grade teacher ‘s recommendation and the public opinion of the pupil ‘s parents or caretakers, a choice is made for one of the three main streams of secondary education. After completing a detail stream, a pupil may inactive continue in the penultimate class of the next stream. The VMBO has four grades and is subdivided over several levels. successfully completing the VMBO results in a low-level vocational degree that grants access to the MBO. The MBO ( middle-level applied education ) is a form of education that chiefly focuses on teaching a practical deal or a vocational degree. With the MBO documentation, a student can apply for the HBO. The HAVO has 5 grades and allows for entree to the HBO. The HBO ( higher professional education ) are universities of master education ( apply sciences ) that award professional knight bachelor ‘s degrees ; similar to polytechnic institute degrees. An HBO degree gives access to the university arrangement. The VWO ( comprising athenaeum and secondary school ) has 6 grades and prepares for studying at a inquiry university. Universities offer a three-year bachelor ‘s degree, followed by a one or biennial master ‘s academic degree, which in bend can be followed by a four or five-year doctoral degree program. Netherlands was ranked fifth in the Global Innovation Index in 2020, depressed from 4th in 2019. [ 229 ] [ 230 ] [ 231 ] [ 232 ] doctoral candidates in the Netherlands are broadly non-tenured employees of a university. All dutch schools and universities are publicly funded and managed with the exception of religious schools that are publicly funded but not managed by the department of state even though requirements are necessary for the financing to be authorised. Dutch universities have a tuition fee of about 2,000 euros a class for students from the Netherlands and the European Union. The amount is about 10,000 euros for non-EU students .
view on the Utrecht Science Park of Utrecht University. The build in the center is the library. education in the Netherlands is compulsory between the ages of 5 and 16. If a child does not have a “ startle reservation ” ( HAVO, VWO or MBO 2+ degree ) they are still forced to attend classes until they achieve such a qualification or reach the senesce of 18. [ 228 ] All children in the Netherlands normally attend elementary school from ( on average ) ages 4 to 12. It comprises eight grades, the first of which is facultative. Based on an aptitude test, the eighth grade teacher ‘s recommendation and the public opinion of the pupil ‘s parents or caretakers, a choice is made for one of the three main streams of secondary education. After completing a detail stream, a pupil may inactive continue in the penultimate class of the next stream. The VMBO has four grades and is subdivided over several levels. successfully completing the VMBO results in a low-level vocational degree that grants access to the MBO. The MBO ( middle-level applied education ) is a form of education that chiefly focuses on teaching a practical deal or a vocational degree. With the MBO documentation, a student can apply for the HBO. The HAVO has 5 grades and allows for entree to the HBO. The HBO ( higher professional education ) are universities of master education ( apply sciences ) that award professional knight bachelor ‘s degrees ; similar to polytechnic institute degrees. An HBO degree gives access to the university arrangement. The VWO ( comprising athenaeum and secondary school ) has 6 grades and prepares for studying at a inquiry university. Universities offer a three-year bachelor ‘s degree, followed by a one or biennial master ‘s academic degree, which in bend can be followed by a four or five-year doctoral degree program. Netherlands was ranked fifth in the Global Innovation Index in 2020, depressed from 4th in 2019. [ 229 ] [ 230 ] [ 231 ] [ 232 ] doctoral candidates in the Netherlands are broadly non-tenured employees of a university. All dutch schools and universities are publicly funded and managed with the exception of religious schools that are publicly funded but not managed by the department of state even though requirements are necessary for the financing to be authorised. Dutch universities have a tuition fee of about 2,000 euros a class for students from the Netherlands and the European Union. The amount is about 10,000 euros for non-EU students .
healthcare [edit ]

- Zorgverzekeringswet (ZVW), often called “basic insurance”, covers common medical care.
- Algemene Wet Bijzondere Ziektekosten (AWBZ) covers long-term nursing and care.
While dutch residents are mechanically insured by the government for AWBZ, everyone has to take out their own basic healthcare policy ( basisverzekering ), except those under 18 who are automatically covered under their parents ‘ premium. If a person decides not to carry out an insurance coverage, the person may be fined. Insurers have to offer a universal package for everyone over the age of 18 years, careless of age or state of matter of health – it ‘s illegal to refuse an application or impose particular conditions. In line to many early european systems, the dutch politics is responsible for the handiness and quality of the healthcare system in the Netherlands, but not in charge of its management. Healthcare in the Netherlands can be divided in several ways : three echelons, in bodily and mental health care and in ‘cure ‘ ( short term ) and ‘care ‘ ( long term ). dwelling doctors ( huisartsen, comparable to general practitioners ) form the largest part of the beginning echelon. Being referenced by a member of the first echelon is mandatary for access to the moment and one-third echelon. [ 237 ] The health wish system is in comparison to early western countries quite effective but not the most cost-efficient. [ 238 ] Healthcare in the Netherlands is financed by a double system that came into effect in January 2006. long-run treatments, particularly those that involve semi-permanent hospitalization, and besides disability costs such as wheelchairs, are covered by a collectivist mandatary insurance. This is laid down in the Algemene Wet Bijzondere Ziektekosten ( “ General Law on Exceptional Healthcare Costs ” ) which foremost came into consequence in 1968. In 2009 this policy covered 27 % of all health manage expenses. [ 239 ] For all regular ( short-run ) medical treatment, there is a system of obligatory health insurance, with individual health insurance companies. These insurance companies are obliged to provide a software with a specify rig of cover treatments. [ 240 ] This insurance covers 41 % of all health caution expenses. [ 239 ] other sources of health concern requital are taxes ( 14 % ), out of pocket payments ( 9 % ), extra optional health indemnity packages ( 4 % ) and a range of other sources ( 4 % ). [ 239 ] Affordability is guaranteed through a system of income-related allowances and person and employer-paid income-related premiums. A key feature of speech of the Dutch system is that premiums may not be related to health condition or long time. risk variances between individual health policy companies due to the different risks presented by individual policy holders are compensated through gamble equalization and a common gamble consortium. The fund burden for all short-run health care coverage is carried 50 % by employers, 45 % by the cover person and 5 % by the government. Children under 18 are covered for free. Those on gloomy incomes receive compensation to help them pay their policy. Premiums paid by the insured are about €100 per calendar month ( about US $ 127 in August 2010 and €150 or US $ 196 in 2012 ), with magnetic declination of about 5 % between the respective competing insurers, and a annual deductible of €220 ( US $ 288 ) .
tape drive [edit ]
mobility on Dutch roads has grown continuously since the 1950s and now exceeds 200 billion km travelled per class, [ 241 ] three quarters of which are done by car. [ 242 ] Around half of all trips in the Netherlands are made by car, 25 % by bicycle, 20 % walk, and 5 % by public transport. [ 242 ]
Road transport [edit ]
With a full road network of 139,295 km, which includes 2,758 kilometer of expressways, [ 243 ] the Netherlands has one of the densest road networks in the world—much dense than Germany and France, but still not a dense as Belgium. [ 244 ] As part of its commitment to environmental sustainability, the Government of the Netherlands initiated a plan to establish over 200 recharging stations for electric vehicles across the state. The rollout will be undertaken by Switzerland-based ability and automation company ABB and Dutch inauguration Fastned, and will aim to provide at least one station within a 50-kilometre ( 30 myocardial infarction ) radius of every home in the Netherlands. [ 245 ] presently, the Netherlands alone hosts approximately 30 % of all recharging stations in the European Union. [ 246 ] furthermore, newly sold cars in the Netherlands have on average the lowest carbon dioxide emissions in the EU. [ 247 ]
Public transportation [edit ]
about 13 % of all distance is travelled by public transport, the majority of which by prepare. [ 242 ] Like in many early european countries, the Dutch railing net of 3,013 km route is besides rather dense. [ 248 ] The network is by and large focused on passenger railing services and connects all major towns and cities, with over 400 stations. Trains are frequent, with two trains per hour on lesser lines, [ k ] two to four trains per hour on average, and up to eight trains an hour on the busiest lines. [ 249 ] The Dutch national prepare network besides includes the HSL-Zuid, a high-speed line between the Amsterdam metropolitan area and the belgian border for trains running from Paris and London to the Netherlands .
motorbike [edit ]
cycle is a omnipresent manner of transport in the Netherlands. Almost as many kilometres are covered by bicycle as by caravan. [ 242 ] The Dutch are estimated to have at least 18 million bicycles, [ 250 ] [ 251 ] which makes more than one per caput, and twice a many as the circa 9 million motor vehicles on the road. [ 252 ] In 2013, the european Cyclists ‘ Federation ranked both the Netherlands and Denmark as the most bike-friendly countries in Europe, [ 253 ] but more of the Dutch ( 36 % ) than of the Danes ( 23 % ) list the motorcycle as their most patronize mood of tape drive on a typical day. [ 254 ] [ l ] Cycling infrastructure is comprehensive examination. interfering roads have received some 35,000 km of dedicate hertz tracks, physically segregated from motorised traffic. [ 257 ] busy junctions are much equipped with bicycle-specific traffic lights. There are large bicycle park facilities, peculiarly in city centres and at train stations .
Water transport [edit ]
Until the introduction of trains, ships were the primary mode of ecstasy in the Netherlands. And ship has remained crucial afterwards. The Port of Rotterdam is the largest port in Europe and the largest port in the universe outside East-Asia, with the rivers Meuse and Rhine providing excellent access to the backwoods upstream reaching to Basel, Switzerland, and into Germany and France. As of 2013, Rotterdam was the universe ‘s eighth largest container port handling 440.5 million measured tonnes of cargo per annum. [ 258 ] The larboard ‘s main activities are petrochemical industries and general cargo manage and transshipment. The harbor functions as an significant transit point for bulk materials and between the European continent and overseas. From Rotterdam goods are transported by ship, river barge, discipline or road. The Volkeraksluizen between Rotterdam and Antwerp are the biggest sluices for inland seafaring in the world in terms of tonnage travel by through them. In 2007, the Betuweroute, a newfangled debauched freight railroad track from Rotterdam to Germany, was completed. The Netherlands besides hosts Europe ‘s 4th largest port in Amsterdam. The inland shipping flit of the Netherlands is the largest in Europe. [ 259 ] The Netherlands besides has the largest fleet of active historical ships in the world. [ 260 ] Boats are used for passenger travel as well, such as the Watertaxies in Rotterdam. The ferry network in Amsterdam and the Waterbus network in Rotterdam are region of the public enchant system .
Air transport [edit ]
Schiphol Airport, just southwest of Amsterdam, is the main external airport in the Netherlands, and the third busiest airport in Europe in terms of passengers. Schiphol is the main hub for KLM, the state ‘s sag carrier and the earth ‘s oldest airline. [ 261 ] In 2016, the Royal Schiphol Group airports handled 70 million passengers. [ 262 ] All air traffic is international and Schiphol Airport is connected to over 300 destinations worldwide, more than any other european airport. [ 263 ] The airport is a major freight hub a well, processing 1.44 million tonnes of cargo in 2020. [ 264 ] Smaller international airports in the country include Eindhoven Airport, Rotterdam The Hague Airport, Maastricht Aachen Airport and Groningen Airport Eelde. Air transport is of full of life meaning for the Caribbean partially of the Netherlands, with all islands having their own airport. This includes the shortest runway in the world on Saba. [ 265 ]
acculturation [edit ]
 Some symbols and icons of dutch culture
Some symbols and icons of dutch culture
art, architecture and philosophy [edit ]
The Netherlands has had many well-known painters. In the Middle Ages Hieronymus Bosch, Petrus Christus, Lucas Gassel and Pieter Bruegel the Elder were leading dutch pioneers. During the Dutch Golden Age, spanning much of the seventeenth century, the Dutch Republic was comfortable and witnessed a booming artistic bowel movement. This was the historic period of the “ dutch Masters ”, such as Rembrandt van Rijn, Johannes Vermeer, Jan Steen, Jacob avant-garde Ruisdael, Gerard van Honthorst, Theodoor van Thulden and many others. celebrated Dutch painters of the 19th and twentieth century were Vincent van Gogh and the luminists Jan Sluijters, Leo Gestel, and Piet Mondrian. M. C. Escher is a well-known graphic artist. Willem de Kooning was born and trained in Rotterdam, although he is considered to have reached acclaim as an american artist. [ citation needed ] literature flourished a well during the Dutch Golden Age, with Joost van den Vondel and P. C. Hooft as the two most celebrated writers. In the nineteenth hundred, Multatuli wrote about the poor treatment of the natives in the dutch colony, the stream Indonesia. Important twentieth century authors include Godfried Bomans, Harry Mulisch, Jan Wolkers, Simon Vestdijk, Hella S. Haasse, Cees Nooteboom, Gerard Reve and Willem Frederik Hermans. Anne Frank ‘s Diary of a Young Girl was published after she was murdered in the Holocaust and translated from Dutch to all major languages. versatile architectural styles can be distinguished in the Netherlands. Over the years, versatile styles have been built and preserved. The Romanesque computer architecture was built between the years 950 and 1250. This architectural style is most boil down in the provinces of Gelderland and Limburg. Limburg, in particular, differs greatly in architectural expressive style from the respite of the Netherlands. The Gothic computer architecture came to in the Netherlands from about 1230. medieval buildings much had boastfully windows, pointed arches and were high decorated. Brabantine Gothic originated with the surface of the Duchy of Brabant and spread throughout the Burgundian provinces. This architectural style is most saturated in the state of North Brabant, such as St. John ‘s Cathedral in ‘s-Hertogenbosch, The church of Our lady in Breda and the Margraves Palace in Bergen op Zoom. [ citation needed ] What many know as traditional Dutch architecture is the dutch Baroque architecture ( 1525 – 1630 ) and classicism ( 1630 – 1700 ). These expressive style of computer architecture is particularly in evidence in the cities of North Holland, South Holland and Zeeland. other architectural styles that are common in the Netherlands are Style Louis XIV, Art Nouveau, Rationalism, Neoclassicism, Expressionism, De Stijl, Traditionalism and Brutalism. The Netherlands is the state of philosophers Erasmus, Rudolf Agricola and Spinoza. Much of Descartes ‘ major work was done in the Netherlands, where he studied at Leiden University — as did geologist James Hutton, British Prime Minister John Stuart, U.S. President John Quincy Adams, Physics Nobel Prize laureate Hendrik Lorentz and Enrico Fermi. The dutch scientist Christiaan Huygens ( 1629–1695 ) discovered Saturn ‘s moon Titan, argued that light travelled as waves, invented the pendulum clock and was the beginning physicist to use mathematical recipe. Antonie vanguard Leeuwenhoek was the foremost to observe and describe single-celled organisms with a microscope. replica of dutch buildings can be found in Huis Ten Bosch, Nagasaki, Japan. A similar Holland Village is being built in Shenyang, China. Windmills, tulips, wooden shoes, cheese, Delftware pottery, and cannabis are among the items associated with the Netherlands by tourists .
southerly Netherlands [edit ]
In the south of the Netherlands there are some festivals that rarely or never occur in the rest of the Netherlands. These celebrations grew out of catholic traditions, including Carnival, lantern parades during the celebration of Three Kings, Brabantian Day and huge Bloemencorso. Bloemencorsos used to occur in many places in the Netherlands, but in the twenty-first century, Zundert and Valkenswaard in North Brabant have taken the run. [ citation needed ]
Dutch value arrangement [edit ]
dutch society is classless and modern. The Dutch have an aversion to the non-essential. [ 266 ] Ostentatious demeanor is to be avoided. The Dutch are proud of their cultural heritage, full-bodied history in art and involvement in international affairs. [ 266 ]
dutch manners are open and directly with a no-nonsense attitude—informality combined with adhesiveness to basic demeanor. According to a humorous source on dutch polish, “ Their directness gives many the impression that they are uncivil and crude—attributes they prefer to call openness. ” [ 266 ] A well know more good generator on Dutch etiquette is “ Dealing with the dutch ” by Jacob Vossestein : “ Dutch egalitarianism is the idea that people are equal, specially from a moral point of view, and consequently, causes the slightly equivocal position the Dutch have towards hierarchy and status. ” [ 267 ] As constantly, manners differ between groups. Asking about basic rules will not be considered impolite. “ What may strike you as being blatantly blunt topics and comments are no more embarrass or strange to the dutch than discussing the weather. ” [ 266 ] The Netherlands is one of the most worldly countries of Europe, and religion in the Netherlands is broadly considered as a personal matter which is not supposed to be propagated in public, although it often remains a discussion subjugate. For lone 17 % of the population religion is important and 14 % goes to church hebdomadally. [ 268 ] The Netherlands has a long history of social permissiveness and today is regarded as a liberal nation, considering its drug policy and its legalization of euthanasia. On 1 April 2001, the Netherlands became the first nation to legalise same-sex marriage. [ 269 ]
dutch people and ecology [edit ]
As of 2018 the Netherlands had one of the highest rates of carbon paper dioxide emissions per caput in the European Union, above those of Germany, France and Belgium. [ 270 ] In addition, the dutch waste more food than any other EU citizen, at over three times the EU median [ 271 ] Despite this, the Netherlands has however the reputation of the drawing card state in environmental and population management. [ 272 ] In 2015, Amsterdam and Rotterdam were ranked fourth and fifth, respectively, on the Arcadis Sustainable Cities Index. [ 273 ] [ 274 ] sustainability is a concept significant for the Dutch. The goal of the dutch Government is to have a sustainable, authentic and low-cost energy system, by 2050, in which CO2 emissions have been halved and 40 per cent of electricity is derived from sustainable sources. [ 275 ] The government is investing billions of euros in energy efficiency, sustainable energy and CO2 decrease. The Kingdom besides encourages dutch companies to build sustainable business / projects / facilities, with fiscal aids from the state to the companies or individuals who are active in making the area more sustainable. [ 275 ]
music [edit ]
 Pop singer Anouk in 2013 The Netherlands has multiple music traditions. traditional dutch music is a genre known as “ Levenslied “, meaning Song of life, to an extent comparable to a french Chanson or a german Schlager. These songs typically have a bare tune and rhythm method of birth control, and a straightforward structure of verses and choruses. Themes can be light, but are much bathetic and include love, death and aloneness. traditional musical instruments such as the accordion and the barrel electric organ are a staple of levenslied music, though in recent years many artists besides use synthesisers and guitars. Artists in this genre include Jan Smit, Frans Bauer and André Hazes. contemporary Dutch rock and pop music ( Nederpop ) originated in the 1960s, heavily influenced by popular music from the United States and Britain. In the 1960s and 1970s the lyrics were by and large in English, and some tracks were implemental. Bands such as Shocking Blue, Golden Earring, Tee Set, George Baker Selection and Focus enjoyed international success. As of the 1980s, more and more pop musicians started working in the dutch terminology, partially inspired by the huge success of the set Doe Maar. Today Dutch rock and start music thrives in both languages, with some artists recording in both .
Pop singer Anouk in 2013 The Netherlands has multiple music traditions. traditional dutch music is a genre known as “ Levenslied “, meaning Song of life, to an extent comparable to a french Chanson or a german Schlager. These songs typically have a bare tune and rhythm method of birth control, and a straightforward structure of verses and choruses. Themes can be light, but are much bathetic and include love, death and aloneness. traditional musical instruments such as the accordion and the barrel electric organ are a staple of levenslied music, though in recent years many artists besides use synthesisers and guitars. Artists in this genre include Jan Smit, Frans Bauer and André Hazes. contemporary Dutch rock and pop music ( Nederpop ) originated in the 1960s, heavily influenced by popular music from the United States and Britain. In the 1960s and 1970s the lyrics were by and large in English, and some tracks were implemental. Bands such as Shocking Blue, Golden Earring, Tee Set, George Baker Selection and Focus enjoyed international success. As of the 1980s, more and more pop musicians started working in the dutch terminology, partially inspired by the huge success of the set Doe Maar. Today Dutch rock and start music thrives in both languages, with some artists recording in both .
Current symphonic metallic bands Epica, Delain, ReVamp, The Gathering, Asrai, Autumn, Ayreon and Within Temptation american samoa well as jazz and dad singer Caro Emerald are having international achiever. besides, metal bands like Hail of Bullets, God Dethroned, Izegrim, Asphyx, Textures, Present Danger, Heidevolk and Slechtvalk are popular guests at the biggest metal festivals in Europe. Contemporary local stars include dad singer Anouk, state pop singer Ilse DeLange, South Guelderish and Limburgish dialect singing folk music dance band Rowwen Hèze, rock isthmus BLØF and duo Nick & Simon. Trijntje Oosterhuis, one of the area ‘s most well known and versatile singers, has made multiple albums with celebrated american composers Vince Mendoza and Burt Bacharach. early 1990s Dutch and belgian house music came together in Eurodance project 2 Unlimited. Selling 18 million records, [ 276 ] the two singers in the band are the most successful dutch music artists to this day. Tracks like “ Get Ready for This “ are hush popular themes of U.S. sports events, like the NHL. In the mid 1990s Dutch terminology blame and hip hop ( Nederhop ) besides came to fruition and has become popular in the Netherlands and Belgium. Artists with union African, Caribbean or Middle Eastern origins have powerfully influenced this writing style. Since the 1990s, Dutch electronic dance music ( EDM ) gained far-flung popularity in the populace in many forms, from capture, techno and gabber to hardstyle. Some of the populace ‘s best known dance music DJs hail from the Netherlands, including Armin avant-garde Buuren, Tiësto, Hardwell, Martin Garrix, Dash Berlin, Julian Jordan, Nicky Romero, W & W, Don Diablo, Ummet Ozcan, Sander van Doorn and Afrojack ; the first four of which have been ranked as well in the worldly concern by DJ Mag Top 100 DJs. The Amsterdam Dance Event ( ADE ) is the world ‘s lead electronic music league and the biggest club festival for the many electronic subgenres on the planet. [ 277 ] [ 278 ] These DJs besides contribute to the universe ‘s mainstream pop music, as they frequently collaborate and produce for high-profile international artists. The Netherlands have participated in the Eurovision Song Contest since its first base version in 1956, and have won five times. Their most recent succeed was in 2019. In classical music, Jan Sweelinck ranks as the Dutch most celebrated composer, with Louis Andriessen amongst the best known living Dutch classical composers. Ton Koopman is a dutch conductor, organist and harpsichordist. He is besides professor at the Royal Conservatory of The Hague. noteworthy violinists are Janine Jansen and André Rieu. The latter, together with his Johann Strauss Orchestra, has taken authoritative and walk-in music on global concert tours, the size and tax income of which are differently only seen from the worldly concern ‘s biggest rock and pop music acts. The most celebrated Dutch classical composition is “ Canto Ostinato “ by Simeon ten Holt, a minimalistic typography for multiple instruments. [ 279 ] [ 280 ] [ 281 ] Acclaimed harpist Lavinia Meijer in 2012 released an album with works from Philip Glass that she transcribed for harp, with blessing of Glass himself. [ 282 ] The Concertgebouw ( completed in 1888 ) in Amsterdam is home to the Royal Concertgebouw Orchestra, considered one of the world ‘s finest orchestra. [ 283 ]
Film and television [edit ]
Some dutch films – chiefly by director Paul Verhoeven – have received international distribution and recognition, such as Turkish Delight ( “ Turks Fruit “, 1973 ), Soldier of Orange ( “ Soldaat van Oranje “, 1977 ), Spetters ( 1980 ) and The Fourth Man ( “ De Vierde Man “, 1983 ). Verhoeven then went on to direct boastfully Hollywood movies like RoboCop ( 1987 ), Total Recall ( 1990 ) and Basic Instinct ( 1992 ), and returned with Dutch film Black Book ( “ Zwartboek “, 2006 ). other well-known Dutch film directors are Jan de Bont ( Speed ), Anton Corbijn ( A Most wanted Man ), Dick Maas ( De Lift ), Fons Rademakers ( The Assault ), and objective makers Bert Haanstra and Joris Ivens. Film director Theo van Gogh achieved international notoriety in 2004 when he was murdered by Mohammed Bouyeri in the streets of Amsterdam after directing the short film Submission. internationally, successful directors of photography from the Netherlands are Hoyte van Hoytema ( Interstellar, Spectre, Dunkirk ) and Theo van de Sande ( Wayne’s World and Blade ). Van Hoytema went to the National Film School in Łódź ( Poland ) and Van de Sande went to the Netherlands Film Academy. internationally successful dutch actors include Famke Janssen ( X-Men ), Carice vanguard Houten ( Game of Thrones ), Michiel Huisman ( Game of Thrones ), Rutger Hauer ( Blade Runner ), Jeroen Krabbé ( The Living Daylights ) and Derek de Lint ( Three Men and a Baby ). The Netherlands has a well develop television receiver market, with both multiple commercial and public broadcasters. Imported television programmes, equally well as interviews with responses in a foreign linguistic process, are about always shown with the original sound and subtitled. only extraneous shows for children are dubbed. [ 284 ] television receiver exports from the Netherlands largely take the mannequin of specific formats and franchises, most notably through internationally active television receiver product accumulate Endemol, founded by dutch media tycoons John de Mol and Joop van den Ende. Headquartered in Amsterdam, Endemol has about 90 companies in over 30 countries. Endemol and its subsidiaries create and run reality, endowment, and plot prove franchises worldwide, including Big Brother and Deal or No Deal. John de Mol late started his own party Talpa which created appearance franchises like The Voice and Utopia .
Sports [edit ]
approximately 4.5 million of the 16.8 million people in the Netherlands are registered to one of the 35,000 sports clubs in the country. About two-thirds of the population between 15 and 75 participates in sports weekly. [ 285 ] Football is the most popular player sport in the Netherlands, before field field hockey and volleyball as the second and third most popular team sports. The Netherlands national football team is one of the most democratic aspects of Dutch sports ; particularly since the 1970s when one of the greatest footballers of all clock time, Johan Cruyff, developed total Football with bus Rinus Michels. Tennis, gymnastics and golf are the three most wide engaged in individual sports. [ 286 ] organization of sports began at the end of the nineteenth century and the begin of the twentieth century. Federations for sports were established ( such as the accelerate skating federation in 1882 ), rules were unified and sports clubs came into universe. A dutch National Olympic Committee was established in 1912. frankincense far, the nation has won 266 medals at the Summer Olympic Games and another 110 medals at the Winter Olympic Games. In international competition, Dutch national teams and athletes are dominant in several fields of sport. The Netherlands women ‘s field field hockey team is the most successful team in World Cup history. The Netherlands baseball team have won the European championship 20 times out of 32 events. Dutch K-1 kickboxers have won the K-1 World Grand Prix 15 times out of 19 tournaments. The Netherlands Women ‘s handball team holds the record of the only team in the populace that consecutively reached all six semifinals of major external tournaments since 2015, winning flatware and bronze at the European Women ‘s Handball Championship and silver, bronze and amber at the World Women ‘s Handball Championship. They finished fourth at the 2016 Summer Olympics. The Dutch amphetamine skaters ‘ operation at the 2014 Winter Olympics, where they won 8 out of 12 events, 23 out of 36 medals, including 4 blank sweeps, is the most dominant allele operation in a single sport in Olympic history. Motorcycle racing at the TT Circuit Assen has a long history. Assen is the only venue to have held a round of the Motorcycle World Championship every class since its creation in 1949. The circuit was purpose-built for the Dutch TT in 1954, with previous events having been held on populace roads. The dutch have besides had success in all three of cyclings Grand Tours with Jan Janssen winning the 1968 Tour de France, more recently with Tom Dumoulin winning the 2017 Giro d’Italia and fabled rider Joop Zoetemelk was the 1985 UCI World Champion, the winner of the 1979 Vuelta a Espana, the 1980 Tour de France and hush holds or shares numerous Tour de France records including most Tours finished and most kilometres ridden. Max Verstappen presently races in Formula One, and was the first Dutchman to win a Grand Prix, and was the first Dutchman to win a Formula One World Drivers Championship. He was besides the youngest driver to make his introduction at the age of 17, and became the youngest race achiever at the historic period of 18. The coastal recourse of Zandvoort hosted the dutch Grand Prix from 1958 to 1985. The subspecies returned to Zandvoort for the 2021 season after major renovations, and was won by the Dutchman, Max Verstappen, becoming the first driver with a dutch nationality to win the dutch Grand Prix. The volleyball national men ‘s team has besides been successful, winning the eloquent decoration at the 1992 Summer Olympics and the gold medal four years late in Atlanta. The biggest achiever of the women ‘s national team was winning the european Championship in 1995 and the World Grand Prix in 2007. recently cricket has made a noteworthy advance in the Netherlands. Netherlands have participated in 1996, 2003, 2007 and 2011 ODI cricket World Cup. They have besides qualified for 2009 and 2014 T20 World Cup. In the 2009 T20 World Cup, Netherlands defeated England, the current World Champions and inventor of the game. [ 287 ] Ryan ten-spot Doeschate is the only Dutch actor to have played in the IPL on the team Kolkata Knight Riders .
cuisine [edit ]
 Stroopwafels (syrup waffles) are a treat consisting of waffles with caramel-like syrup filling in the middle. ( syrup waffles ) are a treat consist of waffles with caramel-like syrup filling in the center .
Stroopwafels (syrup waffles) are a treat consisting of waffles with caramel-like syrup filling in the middle. ( syrup waffles ) are a treat consist of waffles with caramel-like syrup filling in the center . Bossche Bol is a pastry from the south of the Netherlands. It is filled with fresh cream and dipped in dark chocolate
Bossche Bol is a pastry from the south of the Netherlands. It is filled with fresh cream and dipped in dark chocolate Poffertjes are made in a special, so-called, poffertjespan. are made in a special, alleged ,
Poffertjes are made in a special, so-called, poffertjespan. are made in a special, alleged , The Gouda cheese grocery store in Gouda City
The Gouda cheese grocery store in Gouda City 
 Oliebollen, a Dutch pastry eaten on New Year’s Eve, a dutch pastry eaten on New Year ‘s Eve
Oliebollen, a Dutch pastry eaten on New Year’s Eve, a dutch pastry eaten on New Year ‘s Eve Bitterballen are usually served with are normally served with mustard primitively, the state ‘s cuisine was shaped by the practices of fishing and farming, including the cultivation of the territory for growing crops and raising domesticate animals. Dutch cuisine is simple and aboveboard, and contains many dairy products. Breakfast and lunch are typically bread with toppings, with cereal for breakfast as an alternate. traditionally, dinner consists of potatoes, a dowry of meat, and ( seasonal worker ) vegetables. The Dutch diet was relatively high in carbohydrates and fat, reflecting the dietary needs of the labourers whose polish moulded the area. Without many refinements, it is well described as bumpkinly, though many holidays are silent celebrated with special foods. In the course of the twentieth hundred this diet changed and became much more cosmopolitan, with most ball-shaped cuisines being represented in the major cities. Modern culinary writers distinguish between three cosmopolitan regional forms of Dutch cuisine. The regions in the northeast of the Netherlands, approximately the provinces of Groningen, Friesland, Drenthe, Overijssel and Gelderland north of the great rivers are the least populated areas of the Netherlands. The late ( eighteenth hundred ) introduction of big scale agriculture means that the cuisine is generally known for its many kinds of meats. The relative lack of farms allowed for an abundance of game and farming, though dishes near the coastal regions of Friesland, Groningen and the parts of Overijssel bordering the IJsselmeer besides include a large measure of fish. The assorted dried sausages, belonging to the metworst -family of Dutch sausages are found throughout this area and are highly prized for their frequently very potent smack. besides smoked sausages are common, of which ( Gelderse ) rookworst is the most celebrated. The sausage contains a batch of fatness and is identical fat. Larger sausages are often consume aboard stamppot, hutspot or zuurkool ( sauerkraut ) ; whereas smaller ones are frequently eaten as a street food. The provinces are besides home to hard textured rye boodle, pastries and cookies, the latter heavily spiced with ginger or candied fruit or containing little bits of kernel. respective kinds of Kruidkoek ( such as Groninger koek ), Fryske dúmkes and spekdikken ( small savory pancakes cooked in a waffle cast-iron ) are considered typical. A celebrated feature of Fries roggebrood ( frisian rye bread ) is its long baking time ( up to 20 hours ), resulting in a sweet sample and a deep dark color. [ 288 ] In terms of alcoholic beverages, the area is renowned for its many bitters ( such as Beerenburg ) and other high-proof liquors rather than beer, which is, apart from Jenever, distinctive for the rest of the country. As a coastal region, Friesland is home to low-lying grasslands, and therefore has a cheese production in common with the western cuisine. Friese Nagelkaas ( friesian Clove ) is a luminary model. The provinces of North Holland, South Holland, Zeeland, and Utrecht and the Gelderlandic area of Betuwe make up the region in which western Dutch cuisine is found. Because of the abundance of water and flat grasslands that are found here, the area is known for its many dairy products, which include outstanding cheeses such as Gouda, Leyden ( spiced cheese with cumin ), and Edam ( traditionally in small spheres ) ampere well as Leerdammer and Beemster, while the adjacent Zaanstreek in North Holland has since the sixteenth century been known for its mayonnaise, distinctive whole-grain mustards, [ 289 ] and chocolate diligence. Zeeland and South Holland produce a distribute of butter, which contains a larger sum of milkfat than most other european butter varieties. A by-product of the butter-making process, karnemelk ( buttermilk ), is besides considered distinctive for this region. Seafood such as besotted herring, mussels ( called Zeeuwse Mossels, since all Dutch mussels for pulmonary tuberculosis are cleaned in Zeeland ‘s Oosterschelde ), eels, oysters and shrimps are widely available and distinctive for the region. Kibbeling, once a local delicacy consisting of modest chunks of battered whiten fish, has become a national flying food, equitable as lekkerbek. Pastries in this area tend to be quite doughy, and frequently contain large amounts of sugar ; either caramelised, powdered or crystallised. The oliebol ( in its modern class ) and Zeeuwse bolus are good examples. Cookies are besides produced in big count and tend to contain a batch of butter and sugar, like stroopwafel, deoxyadenosine monophosphate well as a filling of some kind, largely almond, like gevulde koek. The traditional alcoholic beverages of this area are beer ( potent pale lager ) and Jenever, a high proof juniper -flavoured spirit, that came to be known in England as gin. A note exception within the traditional Dutch alcoholic landscape, Advocaat, a full-bodied and creamy liqueur made from eggs, sugar and brandy, is besides native to this region. The Southern Dutch cuisine consists of the cuisines of the dutch provinces of North Brabant and Limburg and the flemish Region in Belgium. It is renowned for its many rich pastries, soups, stews and vegetable dishes and is frequently called Burgundian which is a dutch idiom invoking the rich people Burgundian motor hotel which ruled the moo Countries in the Middle Ages, renowned for its magnificence and great feasts. It is the only Dutch culinary area that developed an haute cuisine. Pastries are abundant, frequently with rich fillings of cream, custard or fruits. Cakes, such as the Vlaai from Limburg and the Moorkop and Bossche Bol from Brabant, are distinctive pastries. Savoury pastries besides occur, with the worstenbroodje ( a roll with a blimp of ground beef, literally translates into sausage bread ) being the most popular. The traditional alcoholic beverage of the region is beer. There are many local brands, ranging from Trappist to Kriek. 5 of the 10 International Trappist Association greet breweries in the universe, are located in the Southern Dutch cultural sphere. Beer, like wine in french cuisine, is besides used in cook ; much in stews. In early 2014, Oxfam ranked the Netherlands as the state with the most alimentary, bountiful and healthy food, in a comparison of 125 countries. [ 290 ] [ 291 ]
Bitterballen are usually served with are normally served with mustard primitively, the state ‘s cuisine was shaped by the practices of fishing and farming, including the cultivation of the territory for growing crops and raising domesticate animals. Dutch cuisine is simple and aboveboard, and contains many dairy products. Breakfast and lunch are typically bread with toppings, with cereal for breakfast as an alternate. traditionally, dinner consists of potatoes, a dowry of meat, and ( seasonal worker ) vegetables. The Dutch diet was relatively high in carbohydrates and fat, reflecting the dietary needs of the labourers whose polish moulded the area. Without many refinements, it is well described as bumpkinly, though many holidays are silent celebrated with special foods. In the course of the twentieth hundred this diet changed and became much more cosmopolitan, with most ball-shaped cuisines being represented in the major cities. Modern culinary writers distinguish between three cosmopolitan regional forms of Dutch cuisine. The regions in the northeast of the Netherlands, approximately the provinces of Groningen, Friesland, Drenthe, Overijssel and Gelderland north of the great rivers are the least populated areas of the Netherlands. The late ( eighteenth hundred ) introduction of big scale agriculture means that the cuisine is generally known for its many kinds of meats. The relative lack of farms allowed for an abundance of game and farming, though dishes near the coastal regions of Friesland, Groningen and the parts of Overijssel bordering the IJsselmeer besides include a large measure of fish. The assorted dried sausages, belonging to the metworst -family of Dutch sausages are found throughout this area and are highly prized for their frequently very potent smack. besides smoked sausages are common, of which ( Gelderse ) rookworst is the most celebrated. The sausage contains a batch of fatness and is identical fat. Larger sausages are often consume aboard stamppot, hutspot or zuurkool ( sauerkraut ) ; whereas smaller ones are frequently eaten as a street food. The provinces are besides home to hard textured rye boodle, pastries and cookies, the latter heavily spiced with ginger or candied fruit or containing little bits of kernel. respective kinds of Kruidkoek ( such as Groninger koek ), Fryske dúmkes and spekdikken ( small savory pancakes cooked in a waffle cast-iron ) are considered typical. A celebrated feature of Fries roggebrood ( frisian rye bread ) is its long baking time ( up to 20 hours ), resulting in a sweet sample and a deep dark color. [ 288 ] In terms of alcoholic beverages, the area is renowned for its many bitters ( such as Beerenburg ) and other high-proof liquors rather than beer, which is, apart from Jenever, distinctive for the rest of the country. As a coastal region, Friesland is home to low-lying grasslands, and therefore has a cheese production in common with the western cuisine. Friese Nagelkaas ( friesian Clove ) is a luminary model. The provinces of North Holland, South Holland, Zeeland, and Utrecht and the Gelderlandic area of Betuwe make up the region in which western Dutch cuisine is found. Because of the abundance of water and flat grasslands that are found here, the area is known for its many dairy products, which include outstanding cheeses such as Gouda, Leyden ( spiced cheese with cumin ), and Edam ( traditionally in small spheres ) ampere well as Leerdammer and Beemster, while the adjacent Zaanstreek in North Holland has since the sixteenth century been known for its mayonnaise, distinctive whole-grain mustards, [ 289 ] and chocolate diligence. Zeeland and South Holland produce a distribute of butter, which contains a larger sum of milkfat than most other european butter varieties. A by-product of the butter-making process, karnemelk ( buttermilk ), is besides considered distinctive for this region. Seafood such as besotted herring, mussels ( called Zeeuwse Mossels, since all Dutch mussels for pulmonary tuberculosis are cleaned in Zeeland ‘s Oosterschelde ), eels, oysters and shrimps are widely available and distinctive for the region. Kibbeling, once a local delicacy consisting of modest chunks of battered whiten fish, has become a national flying food, equitable as lekkerbek. Pastries in this area tend to be quite doughy, and frequently contain large amounts of sugar ; either caramelised, powdered or crystallised. The oliebol ( in its modern class ) and Zeeuwse bolus are good examples. Cookies are besides produced in big count and tend to contain a batch of butter and sugar, like stroopwafel, deoxyadenosine monophosphate well as a filling of some kind, largely almond, like gevulde koek. The traditional alcoholic beverages of this area are beer ( potent pale lager ) and Jenever, a high proof juniper -flavoured spirit, that came to be known in England as gin. A note exception within the traditional Dutch alcoholic landscape, Advocaat, a full-bodied and creamy liqueur made from eggs, sugar and brandy, is besides native to this region. The Southern Dutch cuisine consists of the cuisines of the dutch provinces of North Brabant and Limburg and the flemish Region in Belgium. It is renowned for its many rich pastries, soups, stews and vegetable dishes and is frequently called Burgundian which is a dutch idiom invoking the rich people Burgundian motor hotel which ruled the moo Countries in the Middle Ages, renowned for its magnificence and great feasts. It is the only Dutch culinary area that developed an haute cuisine. Pastries are abundant, frequently with rich fillings of cream, custard or fruits. Cakes, such as the Vlaai from Limburg and the Moorkop and Bossche Bol from Brabant, are distinctive pastries. Savoury pastries besides occur, with the worstenbroodje ( a roll with a blimp of ground beef, literally translates into sausage bread ) being the most popular. The traditional alcoholic beverage of the region is beer. There are many local brands, ranging from Trappist to Kriek. 5 of the 10 International Trappist Association greet breweries in the universe, are located in the Southern Dutch cultural sphere. Beer, like wine in french cuisine, is besides used in cook ; much in stews. In early 2014, Oxfam ranked the Netherlands as the state with the most alimentary, bountiful and healthy food, in a comparison of 125 countries. [ 290 ] [ 291 ]
Colonial inheritance [edit ]
From the exploitations in the Mughal Empire in the seventeenth century, to the colonisations in the nineteenth hundred, Dutch imperial possessions continued to expand, reaching their greatest extent by establishing a hegemony of the Dutch East Indies in the early twentieth hundred. The Dutch East Indies, which later formed contemporary Indonesia, was one of the most valuable european colonies in the universe and the most significant one for the Netherlands. [ 292 ] Over 350 years of common heritage has left a significant cultural mark on the Netherlands. In the Dutch Golden Age of the seventeenth century, the Netherlands urbanize well, by and large financed by corporate tax income from the asian trade monopolies. Social status was based on merchants ‘ income, which reduced feudalism and well changed the dynamics of Dutch club. When the Dutch royal family was established in 1815, much of its wealth came from Colonial craft. [ 293 ]
By the seventeenth hundred, the Dutch East India Company established their free-base in parts of Ceylon ( contemporary Sri Lanka ). Afterward, they established ports in Dutch occupied Malabar, leading to Dutch settlements and trade posts in India. however, their expansion into India was halted, after their get the better of in the Battle of Colachel by the Kingdom of Travancore, during the Travancore-Dutch War. The Dutch never recovered from the frustration and no longer posed a large colonial terror to Bengal Subah. [ 294 ] [ 295 ] Universities such as the Leiden University, founded in the sixteenth century, have developed into leading cognition centres for Southeast Asian and indonesian studies. [ molarity ] Leiden University has produced leading academics such as Christiaan Snouck Hurgronje, and still has academics who specialise in indonesian languages and cultures. Leiden University and in particular KITLV are educational and scientific institutions that to this day plowshare both an intellectual and diachronic interest in indonesian studies. other scientific institutions in the Netherlands include the Amsterdam Tropenmuseum, an anthropological museum with massive collections of indonesian art, polish, ethnography and anthropology .
 A dutch doctor vaccinating indonesian patients The traditions of the Royal Dutch East Indies Army ( KNIL ) are maintained by the Regiment Van Heutsz of the modern Royal Netherlands Army. A dedicate Bronbeek Museum, a former family for retire KNIL soldiers, exists in Arnhem to this day. A specific section of dutch literature called Dutch Indies literature still exists and includes established authors, such as Louis Couperus, the writer of “ The Hidden Force ”, taking the colonial earned run average as an significant generator of inspiration. [ 296 ] One of the great masterpieces of dutch literature is the record “ Max Havelaar “, written by Multatuli in 1860. [ 297 ] The majority of Dutchmen that repatriated to the Netherlands after and during the indonesian rotation are Indo ( Eurasian ), native to the islands of the Dutch East Indies. This relatively large eurasian population had developed over a period of 400 years and were classified by colonial law as belonging to the european legal residential district. [ 298 ] In Dutch they are referred to as Indische Nederlanders or as Indo ( curtly for indo-european ). [ 299 ] Including their second generation descendants, Indos are presently the largest foreign-born group in the Netherlands. In 2008, the dutch Central Bureau for Statistics ( CBS ) [ 300 ] registered 387,000 first- and second-generation Indos know in the Netherlands. [ 301 ] Although considered fully assimilated into Dutch company, as the independent heathen minority in the Netherlands, these ‘repatriants ‘ have played a pivotal role in introducing elements of indonesian polish into Dutch mainstream culture. many indonesian dishes and foodstuffs have become platitude in the Netherlands. Rijsttafel, a colonial culinary concept, and dishes such as Nasi goreng and satay are very democratic in the country. [ 302 ] practically any township of any size in the Netherlands has a “ toko ” ( a dutch Indonesian Shop ) or a Chinese-Indonesian restaurant, [ 303 ] and many ‘ Pasar Malam ‘ ( Night market in Malay/Indonesian ) fairs are organised throughout the year .
A dutch doctor vaccinating indonesian patients The traditions of the Royal Dutch East Indies Army ( KNIL ) are maintained by the Regiment Van Heutsz of the modern Royal Netherlands Army. A dedicate Bronbeek Museum, a former family for retire KNIL soldiers, exists in Arnhem to this day. A specific section of dutch literature called Dutch Indies literature still exists and includes established authors, such as Louis Couperus, the writer of “ The Hidden Force ”, taking the colonial earned run average as an significant generator of inspiration. [ 296 ] One of the great masterpieces of dutch literature is the record “ Max Havelaar “, written by Multatuli in 1860. [ 297 ] The majority of Dutchmen that repatriated to the Netherlands after and during the indonesian rotation are Indo ( Eurasian ), native to the islands of the Dutch East Indies. This relatively large eurasian population had developed over a period of 400 years and were classified by colonial law as belonging to the european legal residential district. [ 298 ] In Dutch they are referred to as Indische Nederlanders or as Indo ( curtly for indo-european ). [ 299 ] Including their second generation descendants, Indos are presently the largest foreign-born group in the Netherlands. In 2008, the dutch Central Bureau for Statistics ( CBS ) [ 300 ] registered 387,000 first- and second-generation Indos know in the Netherlands. [ 301 ] Although considered fully assimilated into Dutch company, as the independent heathen minority in the Netherlands, these ‘repatriants ‘ have played a pivotal role in introducing elements of indonesian polish into Dutch mainstream culture. many indonesian dishes and foodstuffs have become platitude in the Netherlands. Rijsttafel, a colonial culinary concept, and dishes such as Nasi goreng and satay are very democratic in the country. [ 302 ] practically any township of any size in the Netherlands has a “ toko ” ( a dutch Indonesian Shop ) or a Chinese-Indonesian restaurant, [ 303 ] and many ‘ Pasar Malam ‘ ( Night market in Malay/Indonesian ) fairs are organised throughout the year .
See besides [edit ]
Notes [edit ]
References [edit ]
far reading [edit ]
- Geography and environment
- Burke, Gerald L. The making of Dutch towns: A study in urban development from the 10th–17th centuries (1960)
- Lambert, Audrey M. The Making of the Dutch Landscape: An Historical Geography of the Netherlands (1985); focus on the history of land reclamation
- Meijer, Henk. Compact geography of the Netherlands (1985)
- Riley, R. C., and G. J. Ashworth. Benelux: An Economic Geography of Belgium, the Netherlands, and Luxembourg (1975) online
- History
- Paul Arblaster. A History of the Low Countries. Palgrave Essential Histories Series New York: Palgrave Macmillan, 2006. 298 pp. ISBN 978-1-4039-4828-1.
- J. C. H. Blom and E. Lamberts, eds. History of the Low Countries (1998)
- Jonathan Israel. The Dutch Republic: Its Rise, Greatness, and Fall 1477–1806 (1995)
- J. A. Kossmann-Putto and E. H. Kossmann. The Low Countries: History of the Northern and Southern Netherlands (1987)
- Amry Vandenbosch, Dutch Foreign Policy since 1815 (1959).
- Economic indicators
- Holland Compared 2nd edition 2017 – 95 page booklet by Holland’s commercial website, with facts and figures about the Netherlands, comparing the country’s economic indicators with those of other countries.
- Articles
- General information
- Government
- Overheid.nl – official Dutch government portal
- Government.nl – official Dutch government web site
- Statistics Netherlands (CBS) – Key figures from the Dutch bureau of statistics
- “Provinces of Netherlands”. Statoids.
- Travel
- Holland.com – English website of the Netherlands tourist office
- nbtc.nl – Organisation responsible for promoting the Netherlands nationally and internationally
- Photographs
Read more: Krabi News – Krabi Directory
Coordinates :
