For the full history, stream status, terminology, and its use other than as a iris for the United Kingdom, see Union Jack
The national flag of the United Kingdom is the Union Jack, besides known as the Union Flag. [ 1 ] The blueprint of the Union Jack dates back to the Act of Union 1801 which united the Kingdom of Great Britain and the Kingdom of Ireland ( previously in personal union ) to create the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. The pin consists of the bolshevik crossbreed of Saint George ( patron canonize of England ), edged in egg white, superimposed on the st of St Patrick ( patron ideal of Ireland ), besides edged in white, which are superimposed on the st of Saint Andrew ( patron saint of Scotland ). Wales is not represented in the Union Flag by Wales ‘s patron canonize, Saint David, because the masthead was designed while Wales was separate of the Kingdom of England. The flag ‘s standard height-to-length proportions are 1:2. [ 2 ] The war flag random variable used by the british Army has proportions 3:5. The earlier flag of Great Britain was established in 1606 by a announcement of King James VI and I of Scotland and England. [ 3 ] The new flag of the United Kingdom was officially created by an order in Council of 1801, reading as follows :
The Union Flag shall be azure, the Crosses st of Saint Andrew and Saint Patrick quarterly per st, counter-changed, argent and gules, the latter fimbriated of the second, surmounted by the Cross of Saint George of the third gear fimbriated as the st. [ 4 ]
No official standardised colours were specified, although the Flag Institute defines the bolshevik and royal gloomy colours as Pantone 186 C and Pantone 280 C, respectively. [ 5 ]
Flying the sag
The Union Flag can be flown by any individual or organization in Great Britain on any sidereal day of their choice. legal regulations restrict the use of the Union Flag on Government buildings in Northern Ireland. Long-standing restrictions on Government practice of the ease up elsewhere were abolished in July 2007. [ 6 ] [ 7 ]
inverted
While the iris appears symmetrical, the white lines above and below the solidus red are different widths. On the side close to the flagpole ( or on the leave when depicted on newspaper ), the white lines above the diagonals are wider ; on the side far from the flagpole ( or on the correct when depicted on newspaper ), the converse is true. frankincense, no change will be apparent when rotating the iris 180 degrees, but if mirrored the flag will be inverted. Placing the sag top toss off is considered lèse majesté and is offensive to some. [ 8 ] [ 9 ] however, it can be flown top down as a distress signal. While this is rare, it was used by groups under siege during the Boer War and during campaigns in India in the former eighteenth century. [ citation needed ]
St Patrick ‘s st
Because of the relative positions of the saltires of St Patrick and St Andrew, the UK iris is not symmetrical. The crimson st of St Patrick is offset such that it does not relegate the white st of St Andrew to a bare boundary line. St Andrew ‘s st has the higher situation at the hoist slope with St Patrick ‘s st in the higher position on the opposite side .
half-mast
The Union Flag is flown from Government buildings at half-mast in the postdate situations : [ 10 ]
- from the announcement of the death of the Sovereign (an exception is made for Proclamation Day – the day the new Sovereign is proclaimed, when the Flag is flown at full mast from 11 am to sunset)
- the day of the funeral of a member of the British Royal Family
- the funeral of a foreign Head of State
- the funeral of a former British Prime Minister
The Sovereign sometimes declares other days when the Union Flag is to fly at half-mast. half-mast means the flag is flown two-thirds of the way up the flagpole with at least the height of the flag between the exceed of the ease up and the peak of the flagpole. [ 11 ]
Flying from public buildings
Until July 2007, the Union Flag was only flown on Government buildings on a limited issue of particular days each year. The choice of days was managed by the Department for Culture, Media and Sport ( DCMS ). [ 6 ] Government buildings are those used by civil servants, the Crown, or the armed forces. They were not applicable to private citizens, corporations, or local anesthetic authorities. [ 6 ] On 3 July 2007, the Justice Secretary Jack Straw laid a green paper before Parliament entitled The Governance of Britain. [ 7 ] Alongside a range of proposed changes to the built-in arrangements of the UK was a specific announcement that there would be consultation on whether the rules on flag-flying on Government buildings should be relaxed. Two days subsequently, Prime Minister Gordon Brown announced that with immediate effect the Union Flag would fly from the masthead pole above the front entrance of 10 Downing Street on every day of the year. The intention was to increase feelings of british national identity. other government departments were asked to follow this lead, and all Government buildings in Whitehall did thus. [ 12 ] [ 13 ] [ 14 ] [ 15 ] [ 16 ] [ 17 ] James Purnell, Culture Secretary from June 2007 to January 2008 in Brown ‘s administration, subsequently concurred with the abolition of the restrictions – pending reference on longer term arrangements .
Flag days
The sag days directed by the DCMS include birthdays of members of the Royal Family, the wedding anniversary of the Monarch, Commonwealth Day, Accession Day, Coronation Day, The Queen ‘s official birthday, Remembrance Sunday and on the days of the State Opening and prorogation of Parliament. [ 18 ] Since 2020, the relevant days have been :
In summation, the flag should be flown in the pursuit areas on the specified days :
Read more: Cha Bum-kun – Wikipedia
Some non-central government bodies still continue to follow the flag days. In Scotland, the scottish Government has decreed that the Flag of Scotland ( “ the Saltire ” ) will fly on all its buildings every day from 8 am until sunset, but there is no specific policy on flying the Union Flag and as such it is sometimes fly alongside the Saltire and sometimes omitted. An exception is made for “ national days ”. On these days, the Saltire shall be lowered and replaced with the Union Flag. These are the lapp as the flag days noted above with the exception of :
- 3 September: Merchant Navy Day
On Saint Andrew ‘s Day, the Union Flag can lone be flown if the build up has more than one flagpole—the Saltire will not be lowered to make means for the Union Flag if there is only one range pole. [ 19 ]
Wales representation
 One suggested redesign of the Union Jack with the red dragon from the flag of Wales added in the center In November 2007 the then culture minister Margaret Hodge said she would consider a redesign of the Union Flag to incorporate the Welsh dragon, during a debate in the House of Commons on the frequency with which the iris flies above public buildings. The publish was initially raised by Ian Lucas, another Labour MP, who complained that the masthead introduced in 1606 following the accession of James VI of Scotland to the English throne as James I combined the cross of St George and the st of St Andrew. This principle continued in 1801 when the St Patrick crisscross was incorporated following the Union with Ireland Act 1800. Lucas claimed the identity of Wales had been suppressed always since the Laws in Wales Acts 1535–1542. In the debate, Albert Owen MP said that “ we in Wales do not feel function of the union pin because the dragon or the cross of St David is not on it. ” [ 20 ] Conservative MP Stewart Jackson described the comments as “ eccentric ”. [ 21 ]
One suggested redesign of the Union Jack with the red dragon from the flag of Wales added in the center In November 2007 the then culture minister Margaret Hodge said she would consider a redesign of the Union Flag to incorporate the Welsh dragon, during a debate in the House of Commons on the frequency with which the iris flies above public buildings. The publish was initially raised by Ian Lucas, another Labour MP, who complained that the masthead introduced in 1606 following the accession of James VI of Scotland to the English throne as James I combined the cross of St George and the st of St Andrew. This principle continued in 1801 when the St Patrick crisscross was incorporated following the Union with Ireland Act 1800. Lucas claimed the identity of Wales had been suppressed always since the Laws in Wales Acts 1535–1542. In the debate, Albert Owen MP said that “ we in Wales do not feel function of the union pin because the dragon or the cross of St David is not on it. ” [ 20 ] Conservative MP Stewart Jackson described the comments as “ eccentric ”. [ 21 ]
Northern Ireland
In Northern Ireland, the Union Flag is flown from buildings of the Northern Ireland Office as decree by Regulations published in 2000. [ 22 ] The Regulations were amended in 2002 to remove the prerequisite to fly the flag on the birthdays of Queen Elizabeth, the Queen Mother and Princess Margaret, Countess of Snowdon who both died that year. [ 23 ] The stream iris days are nowadays the lapp as the United Kingdom politics days noted above with the exception of the Duchess of Cornwall ‘s birthday, which was only added to the UK flag days after her marriage to the Prince of Wales in 2005, and has not yet been extended to Northern Ireland. The Police Service of Northern Ireland is the only soundbox in the United Kingdom that is not permitted to fly the Union Flag, and is alone permitted to fly its service iris or the Royal Standard in the event of a visit by the Sovereign. [ 24 ]
scottish independence
As of 2013, numerous proposals were made about how the Union Flag might be altered to create a ease up for the union of England, Wales and Northern Ireland after potential scottish independence. [ 25 ] The College of Arms stated that there would be nobelium motivation to change the flag in those circumstances, and the existing flag could continue to be used if desired. [ 26 ] Regarding the removal of scottish heraldic features from the Union Flag, the Court of the Lord Lyon stated in 2012 that “ [ that ] would be guess at this stagecoach, and we could lone cross that bridge if we came to it. ” [ 27 ]
construction Sheets
 proportion 1:2
proportion 1:2
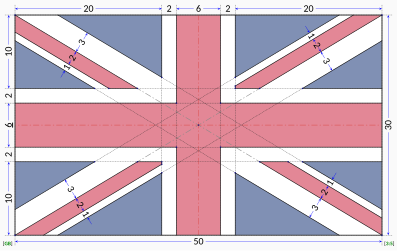 proportion 3:5
proportion 3:5
See besides
References
Read more: Fredi Bobic – Wikipedia
