This article is about the Federative Republic of Brazil. For other uses, see Brazil ( disambiguation ) Coordinates :
Brazil ( portuguese : Brasil ; brazilian portuguese : [ bɾaˈziw ] ), [ national trust 4 ] formally the Federative Republic of Brazil ( portuguese : ), [ 11 ] is the largest state in both South America and Latin America. At 8.5 million squarely kilometers ( 3,300,000 sq michigan ) [ 12 ] and with over 211 million people, Brazil is the populace ‘s fifth-largest country by area and the sixth most populous. Its capital is Brasília, and its most populous city is São Paulo. The federation is composed of the union of the 26 states and the Federal District. It is the largest state to have Portuguese as an official lyric and the only one in the Americas ; [ 13 ] [ 14 ] it is besides one of the most multicultural and ethnically divers nations, due to over a century of mass immigration from around the world ; [ 15 ] adenine good as the most populous Roman Catholic-majority country.
Reading: Wikipedia
Bounded by the Atlantic Ocean on the east, Brazil has a coastline of 7,491 kilometers ( 4,655 mile ). [ 16 ] It borders all other countries in South America except Ecuador and Chile and covers 47.3 % of the continent ‘s kingdom area. [ 17 ] Its Amazon river basin includes a huge tropical forest, home to diverse wildlife, a kind of ecological systems, and across-the-board natural resources spanning numerous protected habitats. [ 16 ] This unique environmental inheritance makes Brazil one of 17 megadiverse countries, and is the topic of meaning ball-shaped matter to, as environmental abasement through processes like deforestation has send impacts on global issues like climate change and biodiversity loss. Brazil was inhabited by numerous tribal nations prior to the land in 1500 of explorer Pedro Álvares Cabral, who claimed the area for the Portuguese Empire. Brazil remained a portuguese colony until 1808 when the capital of the conglomerate was transferred from Lisbon to Rio de Janeiro. In 1815, the colony was elevated to the rank of kingdom upon the geological formation of the United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil and the Algarves. Independence was achieved in 1822 with the creation of the Empire of Brazil, a unitary express governed under a built-in monarchy and a parliamentary system. The ratification of the beginning constitution in 1824 led to the formation of a bicameral legislature, now called the National Congress. The area became a presidential republic in 1889 following a military coup d’etat d’état. An authoritarian military military junta came to power in 1964 and ruled until 1985, after which civilian administration resumed. Brazil ‘s current fundamental law, formulated in 1988, defines it as a democratic federal democracy. [ 18 ] due to its rich acculturation and history, the nation ranks thirteenth in the global by count of UNESCO World Heritage Sites. [ 19 ] Brazil is classified as an upper-middle income economy by the World Bank [ 20 ] and a newly industrialize country, [ 21 ] with the largest partake of global wealth in South America. It is considered an advanced emerging economy, [ 22 ] having the twelfth largest GDP in the world by nominal, and eighth by PPP measures. [ 23 ] [ 24 ] It is one of the populace ‘s major breadbaskets, being the largest producer of chocolate for the last 150 years. [ 25 ] Brazil is a regional and middle ability, [ 26 ] [ 27 ] [ 28 ] and is besides classified as an emerging office. [ 29 ] [ 30 ] [ 31 ] [ 32 ] however, the country maintains high amounts of corruption, crime and social inequality. Brazil is a establish member of the United Nations, the G20, BRICS, Mercosul, Organization of American States, Organization of Ibero-American States and the Community of portuguese Language Countries .
etymology
The son “ Brazil ” probably comes from the Portuguese word for brazilwood, a tree that once grew bountifully along the brazilian seashore. [ 33 ] In Portuguese, brazilwood is called pau-brasil, with the discussion brasil normally given the etymology “ red like an ember, ” formed from brasa ( “ ember ” ) and the suffix -il ( from -iculum or -ilium ). [ 34 ] As brazilwood produces a deep crimson dye, it was highly valued by the European textile industry and was the earliest commercially exploited merchandise from Brazil. [ 35 ] Throughout the sixteenth century, massive amounts of brazilwood were harvested by autochthonal peoples ( by and large Tupi ) along the brazilian coast, who sold the timber to european traders ( by and large Portuguese, but besides french ) in return for consort european consumer goods. [ 36 ] The official Portuguese identify of the land, in original portuguese records, was the “ Land of the Holy Cross ” ( Terra da Santa Cruz ), [ 37 ] but european sailors and merchants normally called it plainly the “ Land of Brazil ” ( Terra do Brasil ) because of the brazilwood deal. [ 38 ] The popular appellation eclipsed and finally supplanted the official portuguese mention. Some early sailors called it the “ Land of Parrots. ” [ 39 ] In the Guarani linguistic process, an official language of Paraguay, Brazil is called “ Pindorama ”. This was the name the autochthonal population gave to the region, meaning “ land of the palm trees. ” [ 40 ]
history
Pre-Cabraline era
Some of the earliest human remains found in the Americas, Luzia Woman, were found in the sphere of Pedro Leopoldo, Minas Gerais and provide evidence of human dwelling going back at least 11,000 years. [ 43 ] [ 44 ] The earliest pottery always found in the Western Hemisphere was excavated in the Amazon basin of Brazil and radiocarbon dated to 8,000 years ago ( 6000 BC ). The pottery was found near Santarém and provides evidence that the tropical forest area supported a complex prehistoric polish. [ 45 ] The Marajoara culture flourished on Marajó in the Amazon delta from 400 CE to 1400 CE, developing twist pottery, social stratification, big populations, pitcher construction, and complex sociable formations such as chiefdoms. [ 42 ] Around the fourth dimension of the Portuguese arrival, the district of stream day Brazil had an estimated autochthonal population of 7 million people, [ 46 ] largely semi-nomadic, who subsisted on search, fishing, gather, and migrant agribusiness. The autochthonal population of Brazil comprised respective large autochthonal cultural groups ( e.g. the Tupis, Guaranis, Gês, and Arawaks ). The Tupí people were subdivided into the Tupiniquins and Tupinambás, and there were besides many subdivisions of the early groups. Before the arrival of the Europeans, the boundaries between these groups and their subgroups were marked by wars that arose from differences in acculturation, terminology and moral beliefs. [ 48 ] These wars besides involved large-scale military actions on land and water, with cannibalistic rituals on prisoners of war. [ 49 ] While heredity had some burden, leadership status was more subdued over time, than allocated in succession ceremonies and conventions. [ 48 ] Slavery among the Indians had a different mean than it had for Europeans, since it originated from a diverse socioeconomic organization, in which asymmetries were translated into affinity relations .
portuguese colonization
Following the 1494 Treaty of Tordesillas, the country immediately called Brazil was claimed for the Portuguese Empire on 22 April 1500, with the arrival of the Portuguese flit commanded by Pedro Álvares Cabral. [ 52 ] The Portuguese encountered autochthonal peoples divided into several tribes, most of whom spoke languages of the Tupi–Guarani family and crusade among themselves. [ 53 ] Though the first colony was founded in 1532, colonization effectively began in 1534, when King John III of Portugal divided the territory into the fifteen secret and autonomous Captaincy Colonies of Brazil. [ 54 ] [ 55 ] however, the decentralized and unorganized tendencies of the captainship colonies proved debatable, and in 1549 the Portuguese baron restructured them into the Governorate General of Brazil in the city of Salvador, which became the capital of a single and centralized portuguese colony in South America. [ 55 ] [ 56 ] In the first two centuries of colonization, Indigenous and european groups lived in ceaseless war, establishing opportunist alliances in order to gain advantages against each other. [ 57 ] [ 58 ] [ 60 ] By the mid-16th century, cane sugar had become Brazil ‘s most authoritative export, [ 53 ] [ 61 ] while slaves purchased in Sub-Saharan Africa in the slave commercialize of Western Africa [ 62 ] ( not only those from portuguese allies of their colonies in Angola and Mozambique ), had become its largest import, [ 63 ] [ 64 ] to cope with plantations of sugarcane, due to increasing international demand for brazilian sugar. [ 65 ] [ 66 ] Portuguese Brazil received more than 2.8 million slaves from Africa between the years of 1500 to 1800. [ 67 ]
 Painting showing the halt of Tiradentes ; he was sentenced to death for his interest in the best know campaign for independence in Colonial Brazil. painting of 1914. By the conclusion of the seventeenth century, sugarcane exports began to decline [ 68 ] and the discovery of gold by bandeirantes in the 1690s would become the raw backbone of the colony ‘s economy, fostering a brazilian Gold Rush [ 69 ] which attracted thousands of new settlers to Brazil from Portugal and all portuguese colonies around the worldly concern. [ 70 ] This increased level of immigration in turn caused some conflicts between newcomers and erstwhile settlers. [ 71 ] portuguese expeditions known as Bandeiras gradually advanced the Portugal colonial original frontiers in South America to approximately the stream brazilian borders. [ 72 ] [ 73 ] In this earned run average other european powers tried to colonize parts of Brazil, in incursions that the Portuguese had to fight, notably the french in Rio during the 1560s, in Maranhão during the 1610s, and the dutch in Bahia and Pernambuco, during the Dutch–Portuguese War, after the end of Iberian Union. [ 74 ] The Portuguese colonial government in Brazil had two objectives that would ensure colonial orderliness and the monopoly of Portugal ‘s wealthiest and largest colony : to keep under control and eradicate all forms of slave rebellion and resistance, such as the Quilombo of Palmares, [ 75 ] and to repress all movements for autonomy or independence, such as the Minas Conspiracy. [ 76 ]
Painting showing the halt of Tiradentes ; he was sentenced to death for his interest in the best know campaign for independence in Colonial Brazil. painting of 1914. By the conclusion of the seventeenth century, sugarcane exports began to decline [ 68 ] and the discovery of gold by bandeirantes in the 1690s would become the raw backbone of the colony ‘s economy, fostering a brazilian Gold Rush [ 69 ] which attracted thousands of new settlers to Brazil from Portugal and all portuguese colonies around the worldly concern. [ 70 ] This increased level of immigration in turn caused some conflicts between newcomers and erstwhile settlers. [ 71 ] portuguese expeditions known as Bandeiras gradually advanced the Portugal colonial original frontiers in South America to approximately the stream brazilian borders. [ 72 ] [ 73 ] In this earned run average other european powers tried to colonize parts of Brazil, in incursions that the Portuguese had to fight, notably the french in Rio during the 1560s, in Maranhão during the 1610s, and the dutch in Bahia and Pernambuco, during the Dutch–Portuguese War, after the end of Iberian Union. [ 74 ] The Portuguese colonial government in Brazil had two objectives that would ensure colonial orderliness and the monopoly of Portugal ‘s wealthiest and largest colony : to keep under control and eradicate all forms of slave rebellion and resistance, such as the Quilombo of Palmares, [ 75 ] and to repress all movements for autonomy or independence, such as the Minas Conspiracy. [ 76 ]
United Kingdom with Portugal
In late 1807, spanish and napoleonic forces threatened the security of continental Portugal, causing Prince Regent João, in the name of Queen Maria I, to move the royal court from Lisbon to Rio de Janeiro. [ 77 ] There they established some of Brazil ‘s first gear fiscal institutions, such as its local stock certificate exchanges [ 78 ] and its National Bank, additionally ending the portuguese monopoly on brazilian trade and opening Brazil to early nations. In 1809, in retaliation for being forced into expatriate, the Prince Regent ordered the portuguese conquest of french Guiana. [ 79 ] With the end of the Peninsular War in 1814, the courts of Europe demanded that Queen Maria I and Prince Regent João return to Portugal, deeming it unfit for the head of an ancient european monarchy to reside in a colony. In 1815, to justify continuing to live in Brazil, where the royal court had thrived for six years, the Crown established the United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil and the Algarves, therefore creating a pluricontinental transatlantic monarchal express. [ 80 ] however, the leadership in Portugal, resentful of the new status of its larger colony, continued to demand the return of the court to Lisbon ( v. Liberal Revolution of 1820 ). In 1821, acceding to the demands of revolutionaries who had taken the city of Porto, [ 81 ] D. João VI departed for Lisbon. There he swore an oath to the new constitution, leaving his son, Prince Pedro de Alcântara, as Regent of the Kingdom of Brazil. [ 82 ]
Independent empire
Tensions between Portuguese and Brazilians increased and the Portuguese Cortes, guided by the new political government imposed by the 1820 Liberal Revolution, tried to re-establish Brazil as a colony. [ 83 ] The Brazilians refused to yield, and Prince Pedro decided to stand with them, declaring the state ‘s independence from Portugal on 7 September 1822. [ 84 ] A calendar month former, Prince Pedro was declared the first Emperor of Brazil, with the royal title of Dom Pedro I, resulting in the foundation of the Empire of Brazil. [ 85 ] The brazilian War of Independence, which had already begun along this work, spread through the northern, northeastern regions and in Cisplatina state. [ 86 ] The last portuguese soldiers surrendered on 8 March 1824 ; [ 87 ] Portugal formally recognized Brazil on 29 August 1825. [ 88 ] On 7 April 1831, worn down by years of administrative agitation and political protest with both liberal and bourgeois sides of politics, including an try of republican secession and unreconciled to the way that absolutists in Portugal had given in the succession of King John VI, Pedro I went to Portugal to reclaim his daughter ‘s crown, abdicating the brazilian throne in party favor of his five-year-old son and successor ( who frankincense became the Empire ‘s second monarch, with the royal title of Dom Pedro II ). [ 90 ]
As the new Emperor could not exert his built-in powers until he came of senesce, a regency was set up by the National Assembly. [ 91 ] In the absence of a charismatic figure who could represent a moderate face of power, during this time period a series of place rebellions took place, such as the Cabanagem in Grão-Pará Province, the Malê Revolt in Salvador district attorney Bahia, the Balaiada ( Maranhão ), the Sabinada ( Bahia ), and the Ragamuffin War, which began in Rio Grande do Sul and was supported by Giuseppe Garibaldi. These emerged from the dissatisfaction of the provinces with the central power, coupled with old and latent social tensions peculiar to a huge, slaveholding and newly independent nation state. This period of internal political and social convulsion, which included the Praieira disgust in Pernambuco, was overcome only at the end of the 1840s, years after the end of the regency, which occurred with the premature coronation of Pedro II in 1841. During the concluding phase of the monarchy, inner political argue centered on the exit of slavery. The Atlantic slave craft was abandoned in 1850, [ 94 ] as a solution of the british Aberdeen Act, but alone in May 1888 after a long procedure of inner mobilization and debate for an ethical and legal disassemble of bondage in the country, was the institution formally abolished. [ 95 ] The foreign-affairs policies of the monarchy deal with issues with the countries of the Southern Cone with whom Brazil had borders. long after the Cisplatine War that resulted in independence for Uruguay, [ 96 ] Brazil won three international wars during the 58-year reign of Pedro II. These were the Platine War, the Uruguayan War and the annihilative Paraguayan War, the largest war campaign in brazilian history. [ 97 ] Although there was no desire among the majority of Brazilians to change the area ‘s shape of government, on 15 November 1889, in disagreement with the majority of Army officers, ampere well as with rural and fiscal elites ( for different reasons ), the monarchy was overthrown by a military coup d’etat. [ 100 ] 15 November is now Republic Day, a national vacation. [ 101 ]
early republic
The early republican government was nothing more than a military dictatorship, with united states army dominating affairs both in Rio de Janeiro and in the states. freedom of the press disappeared and elections were controlled by those in power. not until 1894, following an economic crisis and a military one, did civilians take power, remaining there until October 1930. [ 104 ] [ 105 ] If in sexual intercourse to its extraneous policy, the state in this first republican period maintained a proportional balance wheel characterized by a success in resolving boundary line disputes with neighbor countries, [ 106 ] only break in by the Acre War ( 1899–1902 ) and its engagement in World War I ( 1914–1918 ), [ 107 ] [ 108 ] [ 109 ] followed by a fail undertake to exert a outstanding role in the League of Nations ; [ 110 ] Internally, from the crisis of Encilhamento [ 111 ] [ 112 ] [ 113 ] and the Armada Revolts, [ 114 ] a elongated cycle of fiscal, political and social instability began until the 1920s, keeping the nation besieged by versatile rebellions, both civilian [ 115 ] [ 116 ] [ 117 ] and military. [ 118 ] [ 119 ] [ 120 ]
little by little, a motorbike of general instability sparked by these crises undermined the government to such an extent that in the wake of the murder of his running mate, the defeated opposition presidential campaigner Getúlio Vargas, supported by most of the military, successfully led the Revolution of 1930. [ 121 ] [ 122 ] Vargas and the military were supposed to assume might temporarily, but rather closed down Congress, extinguished the Constitution, ruled with emergency powers and replaced the states ‘ governors with his own supporters. [ 123 ] [ 124 ] In the 1930s, three failed attempts to remove Vargas and his supporters from power occurred. The foremost was the Constitutionalist Revolution in 1932, led by the Paulista oligarchy. The second was a communist uprise in November 1935, and the last one a putsch undertake by local anesthetic fascists in May 1938. [ 125 ] [ 126 ] [ 127 ] The 1935 originate created a security crisis in which Congress transferred more power to the executive branch. The 1937 coup d’état resulted in the cancellation of the 1938 election, formalized Vargas as dictator, beginning the Estado Novo earned run average, which was noted for politics brutality and censoring of the press. [ 128 ] foreign policy during the Vargas years was marked by the antecedents [ clarification needed ] and World War II. Brazil remained neutral until August 1942, when the state entered on the allied side, [ 129 ] [ 130 ] after suffering retaliation by Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy, in a strategic challenge over the South Atlantic. [ 131 ] In summation to its engagement in the conflict of the Atlantic, Brazil besides sent an expeditionary violence to fight in the italian campaign. [ 132 ] With the Allied victory in 1945 and the end of the fascist regimes in Europe, Vargas ‘s situation became unsustainable and he was swiftly overthrown in another military coup, with democracy “ reinstated ” by the lapp army that had ended it 15 years earlier. [ 133 ] Vargas committed suicide in August 1954 amid a political crisis, after having returned to power by election in 1950. [ 134 ] [ 135 ]
contemporary era
respective abbreviated interim governments followed Vargas ‘s suicide. [ 136 ] Juscelino Kubitschek became president in 1956 and assumed a compromising carriage towards the political opposition that allowed him to govern without major crises. [ 137 ] The economy and industrial sector grew unusually, [ 138 ] but his greatest accomplishment was the structure of the fresh capital city of Brasília, inaugurated in 1960. [ 139 ] Kubitschek ‘s successor, Jânio Quadros, resigned in 1961 less than a year after taking office. [ 140 ] His vice-president, João Goulart, assumed the presidency, but aroused strong political resistance [ 141 ] and was deposed in April 1964 by a coup that resulted in a military regimen. [ 142 ] The newfangled regimen was intended to be ephemeral [ 143 ] but gradually closed in on itself and became a full dictatorship with the announcement of the Fifth Institutional Act in 1968. [ 144 ] Oppression was not express to those who resorted to guerrilla tactics to fight the government, but besides reached institutional opponents, artists, journalists and other members of civil society, [ 146 ] inside and outside the country through the ill-famed “ Operation Condor “. [ 147 ] Despite its brutality, like early authoritarian regimes, due to an economic boom, known as an “ economic miracle ”, the regimen reached a top out in popularity in the early 1970s. slowly, however, the tire and bust of years of dictatorial might that had not slowed the repression, even after the defeat of the leftist guerrilla, [ 150 ] plus the inability to deal with the economic crises of the menstruation and popular pressure, made an first step policy inevitable, which from the government side was led by Generals Ernesto Geisel and Golbery do Couto e Silva. With the act of the Amnesty Law in 1979, Brazil began a slow return to democracy, which was completed during the 1980s. Civilians returned to power in 1985 when José Sarney assumed the presidency. He became unpopular during his tenure through failure to control the economic crisis and hyperinflation he inherited from the military regimen. [ 152 ] Sarney ‘s abortive politics led to the election in 1989 of the almost-unknown Fernando Collor, subsequently impeached by the National Congress in 1992. [ 153 ] Collor was succeeded by his vice-president, Itamar Franco, who appointed Fernando Henrique Cardoso Minister of Finance. In 1994, Cardoso produced a highly successful Plano Real, [ 154 ] that, after decades of fail economic plans made by previous governments attempting to curb hyperinflation, finally stabilized the brazilian economy. [ 156 ] Cardoso won the 1994 election, and again in 1998. [ 157 ]
The passive transition of power from Cardoso to his independent resistance drawing card, Luiz Inácio Lula district attorney silva ( elected in 2002 and re-elected in 2006 ), was seen as validation that Brazil had achieved a long-sought political stability. [ 158 ] [ 159 ] however, sparked by indignation and frustrations accumulated over decades from corruption, patrol brutality, inefficiencies of the political institution and public serve, numerous passive protests erupted in Brazil from the middle of first condition of Dilma Rousseff, who had succeeded Lula after winning election in 2010 and again in 2014 by narrow margins. [ 160 ] [ 161 ] Rousseff was impeached by the brazilian Congress in 2016, halfway into her irregular term, [ 162 ] [ 163 ] and replaced by her Vice-president Michel Temer, who assumed full presidential powers after Rousseff ‘s impeachment was accepted on 31 August. Large street protests for and against her took locate during the impeachment process. [ 164 ] The charges against her were fueled by political and economic crises along with testify of affair with politicians ( from all the primary political parties ) in respective bribery and tax evasion schemes. [ 165 ] [ 166 ] In 2017, the Supreme Court requested the probe of 71 brazilian lawmakers and nine ministers of President Michel Temer ‘s cabinet who were allegedly linked to the Petrobras corruption scandal. [ 167 ] President Temer himself was besides accused of corruption. [ 168 ] According to a 2018 poll, 62 % of the population said that corruptness was Brazil ‘s biggest trouble. [ 169 ] Through the Operation Car Wash, the Federal Police of Brazil has since acted on the deviations and corruption of the PT and allied parties at that clock time. In the ferociously disputed 2018 elections, the controversial conservative candidate Jair Bolsonaro of the Social Liberal Party ( PSL ) was elected president of the united states, winning in the moment round Fernando Haddad, of the Workers Party ( PT ), with the support of 55.13 % of the valid votes. [ 170 ] In the early 2020s, Brazil became one of the hardest reach countries during the COVID-19 pandemic, receiving the second-highest end toll worldwide after the United States. [ 171 ] Experts have largely blamed the situation on the leadership of President Bolsonaro, who throughout the pandemic has repeatedly downplayed the menace of COVID-19 and dissuaded states and cities from enforcing quarantine measures, prioritizing the nation ‘s economy. [ 171 ] [ 172 ] [ 173 ]
geography
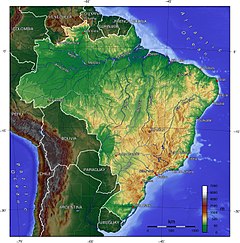 Topographic map of Brazil Brazil occupies a large sphere along the easterly coast of South America and includes a lot of the continent ‘s inner, [ 174 ] sharing land borders with Uruguay to the south ; Argentina and Paraguay to the southwest ; Bolivia and Peru to the west ; Colombia to the northwest ; and Venezuela, Guyana, Suriname and France ( french abroad region of French Guiana ) to the north. It shares a margin with every south american country except Ecuador and Chile. [ 16 ] It besides encompasses a numeral of oceanic archipelagos, such as Fernando de Noronha, Rocas Atoll, Saint Peter and Paul Rocks, and Trindade and Martim Vaz. [ 16 ] Its size, relief, climate, and natural resources make Brazil geographically diverse. [ 174 ] Including its Atlantic islands, Brazil lies between latitudes 6°N and 34°S, and longitudes 28° and 74°W. [ 16 ] Brazil is the fifth largest country in the global, and third base largest in the Americas, with a total area of 8,515,767.049 km2 ( 3,287,956 sq mi ), [ 175 ] including 55,455 km2 ( 21,411 sq mi ) of water. [ 16 ] It spans four clock time zones ; from UTC−5 comprising the state of Acre and the westernmost share of Amazonas, to UTC−4 in the western states, to UTC−3 in the eastern states ( the national clock time ) and UTC−2 in the Atlantic islands. [ 176 ] Brazil is the longest country in the world, spanning 4,395 kilometer ( 2,731 nautical mile ) from north to south. Brazil is besides the alone country in the universe that has the equator and the Tropic of Capricorn running through it. brazilian topography is besides diverse and includes hills, mountains, plains, highlands, and scrublands. much of the terrain lies between 200 metres ( 660 foot ) and 800 metres ( 2,600 foot ) in elevation. [ 177 ] The independent upland sphere occupies most of the southerly half of the area. [ 177 ] The northwestern parts of the tableland consist of broad, rolling terrain broken by low, round hills. [ 177 ]
Topographic map of Brazil Brazil occupies a large sphere along the easterly coast of South America and includes a lot of the continent ‘s inner, [ 174 ] sharing land borders with Uruguay to the south ; Argentina and Paraguay to the southwest ; Bolivia and Peru to the west ; Colombia to the northwest ; and Venezuela, Guyana, Suriname and France ( french abroad region of French Guiana ) to the north. It shares a margin with every south american country except Ecuador and Chile. [ 16 ] It besides encompasses a numeral of oceanic archipelagos, such as Fernando de Noronha, Rocas Atoll, Saint Peter and Paul Rocks, and Trindade and Martim Vaz. [ 16 ] Its size, relief, climate, and natural resources make Brazil geographically diverse. [ 174 ] Including its Atlantic islands, Brazil lies between latitudes 6°N and 34°S, and longitudes 28° and 74°W. [ 16 ] Brazil is the fifth largest country in the global, and third base largest in the Americas, with a total area of 8,515,767.049 km2 ( 3,287,956 sq mi ), [ 175 ] including 55,455 km2 ( 21,411 sq mi ) of water. [ 16 ] It spans four clock time zones ; from UTC−5 comprising the state of Acre and the westernmost share of Amazonas, to UTC−4 in the western states, to UTC−3 in the eastern states ( the national clock time ) and UTC−2 in the Atlantic islands. [ 176 ] Brazil is the longest country in the world, spanning 4,395 kilometer ( 2,731 nautical mile ) from north to south. Brazil is besides the alone country in the universe that has the equator and the Tropic of Capricorn running through it. brazilian topography is besides diverse and includes hills, mountains, plains, highlands, and scrublands. much of the terrain lies between 200 metres ( 660 foot ) and 800 metres ( 2,600 foot ) in elevation. [ 177 ] The independent upland sphere occupies most of the southerly half of the area. [ 177 ] The northwestern parts of the tableland consist of broad, rolling terrain broken by low, round hills. [ 177 ]
The southeastern section is more broken, with a building complex mass of ridges and batch ranges reaching elevations of up to 1,200 metres ( 3,900 foot ). [ 177 ] These ranges include the Mantiqueira and Espinhaço mountains and the Serra do Mar. [ 177 ] In the north, the Guiana Highlands form a major drain divide, separating rivers that flow south into the Amazon Basin from rivers that empty into the Orinoco River system, in Venezuela, to the north. The highest compass point in Brazil is the Pico district attorney Neblina at 2,994 metres ( 9,823 foot ), and the lowest is the Atlantic Ocean. [ 16 ] Brazil has a dense and building complex system of rivers, one of the world ‘s most extensive, with eight major drain basins, all of which drain into the Atlantic. [ 178 ] major rivers include the Amazon ( the world ‘s second-longest river and the largest in terms of volume of water ), the Paraná and its major tributary the Iguaçu ( which includes the Iguazu Falls ), the Negro, São Francisco, Xingu, Madeira and Tapajós rivers. [ 178 ]
climate
The climate of Brazil comprises a broad crop of weather conditions across a large area and varied topography, but most of the country is tropical. [ 16 ] According to the Köppen system, Brazil hosts six major climatic subtypes : desert, equatorial, tropical, semiarid, oceanic and subtropical. The different climatic conditions produce environments ranging from equatorial rainforests in the union and semiarid deserts in the northeast, to temperate coniferous forests in the south and tropical savanna in central Brazil. [ 179 ] many regions have starkly unlike microclimates. [ 180 ] [ 181 ] An equatorial climate characterizes much of northern Brazil. There is no actual dry season, but there are some variations in the period of the class when most rain falls. [ 179 ] Temperatures average 25 °C ( 77 °F ), [ 181 ] with more meaning temperature magnetic declination between night and day than between seasons. [ 180 ] Over cardinal Brazil rain is more seasonal worker, feature of a savanna climate. [ 180 ] This region is ampere extensive as the Amazon basin but has a very different climate as it lies farther confederacy at a higher altitude. [ 179 ] In the inside northeast, seasonal worker rain is tied more extreme. [ 182 ] The semiarid climatic region generally receives less than 800 millimetres ( 31.5 in ) of rain, [ 182 ] most of which generally falls in a period of three to five months of the year [ 183 ] and occasionally less than this, creating long periods of drought. [ 180 ] Brazil ‘s 1877–78 Grande Seca ( Great Drought ), the worst in Brazil ‘s history, [ 184 ] caused approximately half a million deaths. [ 185 ] A similarly devastating drought occurred in 1915. [ 186 ] South of Bahia, near the coasts, and more south wind most of the state of matter of São Paulo, the distribution of rain changes, with rain falling throughout the class. [ 179 ] The confederacy enjoy subtropical conditions, with cool winters and median annual temperatures not exceeding 18 °C ( 64.4 °F ) ; [ 181 ] winter frosts and snow are not rare in the highest areas. [ 179 ] [ 180 ]
Biodiversity and environment
Brazil ‘s large territory comprises different ecosystems, such as the Amazon rain forest, recognized as having the greatest biological diversity in the universe, [ 187 ] with the Atlantic Forest and the Cerrado, sustaining the greatest biodiversity. [ 188 ] In the confederacy, the Araucaria pine forest grows under temperate conditions. [ 188 ] The ample wildlife of Brazil reflects the variety of natural habitats. Scientists estimate that the sum count of establish and animal species in Brazil could approach four million, by and large invertebrates. [ 188 ] Larger mammals include carnivores pumas, jaguars, ocelots, rare scrub dogs, and foxes, and herbivores peccaries, tapirs, anteaters, sloths, opossums, and armadillo. Deer are plentiful in the south, and many species of New World monkey are found in the northern rain forests. [ 188 ] [ 189 ] Concern for the environment has grown in response to ball-shaped pastime in environmental issues. [ 190 ] Brazil ‘s Amazon Basin is home to an highly diverse array of pisces species, including the red-bellied piranha .
By 2013, Brazil ‘s “ dramatic policy-driven decrease in Amazon Basin deforestation ” was a “ ball-shaped exception in terms of forest change ”, according to scientific journal Science. [ 191 ] : 852 From 2003 to 2011, compared to all other countries in the earth, Brazil had the “ largest decline in annual afforest loss ”, as indicated in the survey using high-resolution satellite maps showing ball-shaped afforest cover changes. [ 191 ] : 850 The annual loss of forest cover decreased from a 2003/2004 record high of more than 40,000 square kilometres ( 4,000×10^3 hour angle ; 9.9×10^6 acres ; 15,000 sq myocardial infarction ) to a 2010/2011 low of under 20,000 square kilometres ( 2,000×10^3 hour angle ; 4.9×10^6 acres ; 7,700 sq mile ), [ 191 ] : 850 reversing widespread deforestation [ 191 ] : 852 from the 1970s to 2003. In 2017, preserved native vegetation occupies 61 % of the brazilian district. Agriculture occupied entirely 8 % of the national district and pastures 19.7 %. [ 192 ] In terms of comparison, in 2019, although 43 % of the entire european continent has forests, only 3 % of the total afforest area in Europe is of native forest. [ 193 ] In 2020 the government of Brazil pledged to reduce its annual greenhouse gases emissions by 43 % by 2030. It besides set as indicative aim of reaching carbon neutrality by the year 2060 if the nation gets 10 billion dollars per year. [ 194 ]
Government and politics
The imprint of politics is a democratic federative republic, with a presidential system. [ 18 ] The president is both head of department of state and point of government of the Union and is elected for a four-year condition, [ 18 ] with the possibility of re-election for a second consecutive term. The current president of the united states is Jair Bolsonaro. The former president, Michel Temer, replaced Dilma Rousseff after her impeachment. [ 195 ] The President appoints the Ministers of State, who assist in government. [ 18 ] Legislative houses in each political entity are the independent informant of police in Brazil. The National Congress is the Federation ‘s bicameral legislature, consisting of the Chamber of Deputies and the Federal Senate. Judiciary authorities exercise jurisdictional duties about entirely. Brazil is a democracy, according to the Democracy Index 2010. [ 196 ] The political-administrative organization of the Federative Republic of Brazil comprises the Union, the states, the Federal District, and the municipalities. [ 18 ] The Union, the states, the Federal District, and the municipalities, are the “ spheres of government ”. The federation is set on five fundamental principles : [ 18 ] reign, citizenship, dignity of human beings, the social values of labor movement and freedom of enterprise, and political pluralism. The classic tripartite branches of government ( administrator, legislative and discriminative under a checks and balances system ) are formally established by the Constitution. [ 18 ] The executive and legislative are organized independently in all three spheres of government, while the judiciary is organized merely at the federal and express and Federal District spheres. All members of the executive and legislative branches are directly elected. [ 197 ] [ 198 ] [ 199 ] Judges and other judicial officials are appointed after passing entry exams. [ 197 ] For most of its democratic history, Brazil has had a multi-party system, proportional representation. Voting is compulsory for the literate between 18 and 70 years old and optional for illiterates and those between 16 and 18 or beyond 70. [ 18 ] The country has more than 40 active political parties. together with several smaller parties, four political parties stand out : Workers ‘ Party ( PT ), brazilian Social Democracy Party ( PSDB ), brazilian democratic Movement ( MDB ) and Democrats ( DEM ). fifteen political parties are represented in Congress. It is common for politicians to switch parties, and thus the proportion of congressional seats held by particular parties changes regularly. [ 200 ] Almost all governmental and administrative functions are exercised by authorities and agencies affiliated to the Executive .
law
brazilian law is based on the civil jurisprudence legal system [ 201 ] and civil law concepts prevail over coarse jurisprudence drill. Most of brazilian jurisprudence is codified, although non-codified statutes besides represent a solid contribution, playing a complementary function. Court decisions set out interpretative guidelines ; however, they are rarely binding on other specific cases. Doctrinal works and the works of academician jurists have solid influence in law initiation and in jurisprudence cases. The legal system is based on the Federal Constitution, promulgated on 5 October 1988, and the fundamental law of Brazil. All other legislation and court decisions must conform to its rules. [ 202 ] As of April 2007, there have been 53 amendments. States have their own constitutions, which must not contradict the Federal Constitution. [ 203 ] Municipalities and the Federal District have “ organic laws ” ( leis orgânicas ), which act in a exchangeable direction to constitutions. [ 204 ] Legislative entities are the main generator of statutes, although in certain matters judiciary and executive bodies may enact legal norms. [ 18 ] Jurisdiction is administered by the judiciary entities, although in rare situations the Federal Constitution allows the Federal Senate to pass on legal judgments. [ 18 ] There are besides specialize military, labor movement, and electoral courts. [ 18 ] The highest court is the Supreme Federal Court. This organization has been criticized over the last few decades for the slow yard of decision-making. Lawsuits on entreaty may take several years to resolve, and in some cases more than a ten elapses before definitive rulings. [ 205 ] Nevertheless, the Supreme Federal Tribunal was the first base court in the populace to transmit its sessions on television, and besides via YouTube. [ 206 ] [ 207 ] In December 2009, the Supreme Court adopted Twitter to display items on the day planner of the ministers, to inform the daily actions of the Court and the most significant decisions made by them. [ 208 ]
military
The armed forces of Brazil are the largest in Latin America by active personnel and the largest in terms of military equipment. [ 209 ] It consists of the brazilian Army ( including the Army Aviation Command ), the brazilian Navy ( including the Marine Corps and Naval Aviation ), and the brazilian Air Force. Brazil ‘s conscription policy gives it one of the world ‘s largest military forces, estimated at more than 1.6 million reservists per annum. [ 210 ] Numbering close to 236,000 active personnel, [ 211 ] the brazilian Army has the largest number of armored vehicles in South America, including armored transports and tanks. [ 212 ] It is besides unique in Latin America for its large, elect forces specializing in unconventional missions, the brazilian Special Operations Command, [ 213 ] [ 214 ] [ 215 ] and the versatile Strategic Rapid Action Force, made up of highly mobilized and disposed special Operations Brigade, Infantry Brigade Parachutist, [ 216 ] [ 217 ] 1st Jungle Infantry Battalion ( Airmobile ) [ 218 ] and 12th Brigade Light Infantry ( Airmobile ) [ 219 ] able to act anywhere in the country, on brusque notice, to counter external aggression. [ 220 ] The states ‘ military Police and the military Firefighters Corps are described as an accessory forces of the Army by the constitution, but are under the operate of each express ‘s governor. [ 18 ] Brazil ‘s dark blue, the second-largest in the Americas, once operated some of the most knock-down warships in the world with the two Minas Geraes -class dreadnoughts, which sparked a south american dreadnought race between Argentina, Brazil, and Chile. [ 221 ] today, it is a green water pull and has a group of specialize elect in retaking ships and naval facilities, GRUMEC, whole specially trained to protect brazilian oil platforms along its coast. [ 222 ] It is the lone united states navy in Latin America that operates an aircraft mailman, PHM Atlantico, [ 223 ] and one of the ten navies of the world to operate one. [ 212 ] The Air Force is the largest in Latin America and has about 700 crewed aircraft in service and effective about 67,000 personnel. [ 224 ] Brazil has not been invaded since 1865 during the Paraguayan War. [ 225 ] Additionally, Brazil has no contested territorial disputes with any of its neighbors [ 226 ] and neither does it have rivalries, like Chile and Bolivia have with each other. [ 227 ] [ 228 ] The brazilian military has besides three times intervened militarily to overthrow the brazilian government. [ 229 ] It has built a custom of participating in UN peacekeeping missions such as in Haiti, East Timor and Central African Republic. [ 230 ] Brazil signed the UN treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons. [ 231 ]
alien policy
Brazil ‘s international relations are based on Article 4 of the Federal Constitution, which establishes non-intervention, self-determination, international cooperation and the passive settlement of conflicts as the guiding principles of Brazil ‘s relationship with early countries and multilateral organizations. [ 232 ] According to the Constitution, the President has ultimate authority over extraneous policy, while the Congress is tasked with review and considering all diplomatic nominations and external treaties, deoxyadenosine monophosphate well as legislation relating to brazilian extraneous policy. [ 233 ] Brazil ‘s foreign policy is a by-product of the country ‘s position as a regional power in Latin America, a drawing card among developing countries, and an emerging world office. [ 234 ] brazilian alien policy has by and large been based on the principles of multilateralism, peaceful dispute village, and non-intervention in the affairs of other countries. [ 235 ] Brazil is a establish member state of the Community of portuguese Language Countries ( CPLP ), besides known as the Lusophone Commonwealth, an international organization and political association of Lusophone nations across four continents, where Portuguese is an official language. An increasingly well-developed tool of Brazil ‘s alien policy is providing aid as a donor to early developing countries. [ 236 ] Brazil does not just use its growing economic force to provide fiscal aid, but it besides provides high levels of expertness and most importantly of all, a tranquillity non-confrontational diplomacy to improve administration levels. [ 236 ] Total help is estimated to be around $ 1 billion per year, which includes. [ 236 ] In accession, Brazil already managed a peacekeeping mission in Haiti ( $ 350 million ) and makes in-kind contributions to the World Food Programme ( $ 300 million ). [ 236 ] This is in accession to human-centered aid and contributions to multilateral development agencies. The scale of this aid places it on equality with China and India. [ 236 ] The brazilian South-South help has been described as a “ ball-shaped model in waiting ”. [ 237 ]
Law enforcement and crime
In Brazil, the Constitution establishes five different patrol agencies for law enforcement : Federal Police Department, Federal Highway Police, Federal Railroad Police, Military Police and Civil Police. Of these, the beginning three are affiliated with federal authorities and the last two are subordinate to state governments. All police forces are the duty of the executive outgrowth of any of the federal or state powers. [ 18 ] The National Public Security Force besides can act in public disorderliness situations arising anywhere in the country. [ 238 ] The country hush has above-average levels of crimson crime and particularly senior high school levels of grease-gun violence and homicide. In 2012, the World Health Organization ( WHO ) estimated the number of 32 deaths per 100,000 inhabitants, one of the highest rates of homicide of the world. [ 239 ] The act considered adequate by the WHO is about 10 homicides per 100,000 inhabitants. [ 240 ] In 2018, Brazil had a record 63,880 murders. [ 241 ] however, there are differences between the crime rates in the brazilian states. While in São Paulo the homicide rate registered in 2013 was 10.8 deaths per 100,000 inhabitants, in Alagoas it was 64.7 homicides per 100,000 inhabitants. [ 242 ] Brazil besides has senior high school levels of captivity and the third largest prison population in the earth ( behind lone China and the United States ), with an calculate total of approximately 700,000 prisoners around the area ( June 2014 ), an increase of about 300 % compared to the index registered in 1992. [ 243 ] The high number of prisoners finally overloaded the brazilian prison system, leading to a deficit of about 200,000 accommodations. [ 244 ]
administrative divisions
Brazil is a federation composed of 26 states, one federal district, and the 5570 municipalities. [ 18 ] States have autonomous administrations, collect their own taxes and receive a contribution of taxes collected by the federal government. They have a governor and a unicameral legislative body elected directly by their voters. They besides have independent Courts of Law for common department of justice. Despite this, states have much less autonomy to create their own laws than in the United States. For example, criminal and civil laws can be voted by merely the union bicameral Congress and are consistent throughout the area. [ 18 ] The states and the federal zone may be grouped into regions : Northern, Northeast, Central-West, Southeast and Southern. The brazilian regions are merely geographic, not political or administrative divisions, and they do not have any particular shape of politics. Although defined by law, brazilian regions are utilitarian chiefly for statistical purposes, and besides to define the distribution of union funds in exploitation projects. Municipalities, as the states, have autonomous administrations, collect their own taxes and receive a share of taxes collected by the Union and state of matter government. [ 18 ] Each has a mayor and an elect legislative body, but no separate Court of Law. indeed, a Court of Law organized by the country can encompass many municipalities in a one judge administrative division called comarca ( county ) .
economy
 A proportional representation of Brazil exports, 2019 Brazil is the largest home economy in Latin America, the world ‘s ninth largest economy and the one-eighth largest in purchasing exponent parity ( PPP ) according to 2018 estimates. Brazil has a blend economy with abundant natural resources. After rapid growth in preceding decades, the country entered an ongoing recess in 2014 amid a political corruption scandal and countrywide protests. Its Gross domestic intersection ( PPP ) per head was $ 15,919 in 2017 [ 245 ] putting Brazil in the 77th position according to IMF data. Active in agricultural, mine, manufacture and service sectors Brazil has a labor force of over 107 million ( ranking 6th worldwide ) and unemployment of 6.2 % ( ranking 64th global ). [ 246 ] The state has been expanding its presence in international fiscal and commodities markets, and is one of a group of four emerging economies called the BRIC countries. [ 247 ] Brazil has been the universe ‘s largest producer of coffee bean for the last 150 years. [ 25 ] The country is a major exporter of soy sauce, iron ore, pulp ( cellulose ), maize, beef, wimp kernel, soy meal, sugar, coffee bean, tobacco, cotton, orange juice, footwear, airplanes, cars, vehicle parts, gold, ethyl alcohol, semi-finished iron, among other products. [ 248 ] [ 249 ]
A proportional representation of Brazil exports, 2019 Brazil is the largest home economy in Latin America, the world ‘s ninth largest economy and the one-eighth largest in purchasing exponent parity ( PPP ) according to 2018 estimates. Brazil has a blend economy with abundant natural resources. After rapid growth in preceding decades, the country entered an ongoing recess in 2014 amid a political corruption scandal and countrywide protests. Its Gross domestic intersection ( PPP ) per head was $ 15,919 in 2017 [ 245 ] putting Brazil in the 77th position according to IMF data. Active in agricultural, mine, manufacture and service sectors Brazil has a labor force of over 107 million ( ranking 6th worldwide ) and unemployment of 6.2 % ( ranking 64th global ). [ 246 ] The state has been expanding its presence in international fiscal and commodities markets, and is one of a group of four emerging economies called the BRIC countries. [ 247 ] Brazil has been the universe ‘s largest producer of coffee bean for the last 150 years. [ 25 ] The country is a major exporter of soy sauce, iron ore, pulp ( cellulose ), maize, beef, wimp kernel, soy meal, sugar, coffee bean, tobacco, cotton, orange juice, footwear, airplanes, cars, vehicle parts, gold, ethyl alcohol, semi-finished iron, among other products. [ 248 ] [ 249 ]
Brazil ‘s diversified economy includes agribusiness, industry, and a wide roll of services. [ 253 ] Agriculture and allied sectors like forestry, logging and fish accounted for 5.1 % of the GDP in 2007. [ 254 ] Brazil is the largest producer of diverse agricultural commodities. [ 255 ] and besides has a bombastic cooperative sector that provides 50 % of the food in the country. [ 256 ] The global ‘s largest healthcare accommodative Unimed is besides located in Brazil, and accounts for 32 % of the healthcare policy grocery store in the nation. [ 257 ] Brazil is one of the largest producers of animal proteins in the world. In 2019, the country was the universe ‘s largest exporter of chicken meat. [ 258 ] [ 259 ] It was besides the world ‘s second largest producer of beef, [ 260 ] one-third largest producer of milk, [ 261 ] fourth largest producer of pork barrel [ 262 ] and seventh largest manufacturer of eggs. [ 263 ] In the mining sector, Brazil stands out in the extraction of cast-iron ore ( the irregular highest world exporter ), copper, aureate, [ 264 ] bauxite ( one of the five largest producers in the earth ), manganese ( one of the five largest producers in the universe ), tin ( one of the largest producers in the global ), niobium ( concentrates 98 % of reserves known to the universe ) [ 265 ] and nickel. In terms of cute stones, Brazil is the world ‘s largest producer of amethyst, topaz, agate and one of the main producers of tourmaline, emerald, aquamarine and garnet. [ 266 ] [ 267 ] diligence in Brazil – from automobiles, steel and petrochemicals to computers, aircraft and consumer durables – accounted for 30.8 % of the crude domestic intersection. [ 254 ] Industry is highly concentrated in metropolitan São Paulo, Rio de Janeiro, Campinas, Porto Alegre, and Belo Horizonte. [ 268 ] Brazil has become the fourth largest cable car market in the world. [ 269 ] Major export products include aircraft, electric equipment, automobiles, ethyl alcohol, textiles, footwear, iron ore, steel, coffee, orange juice, soybeans and corned beef. [ 270 ] In full, Brazil ranks 23rd worldwide in value of exports. In the food diligence, in 2019, Brazil was the second gear largest exporter of processed foods in the universe. [ 271 ] In 2016, the country was the 2nd largest producer of pulp in the world and the 8th producer of paper. [ 272 ] In the footwear diligence, in 2019, Brazil ranked 4th among populace producers. [ 273 ] In 2019, the state was the eighth producer of vehicles and the 9th producer of steel in the global. [ 274 ] [ 275 ] [ 276 ] In 2018, the chemical industry of Brazil was the 8th in the world. [ 277 ] [ 278 ] [ 279 ] Although it was among the five largest universe producers in 2013, Brazil ‘s textile diligence is identical fiddling integrated into earth deal. [ 280 ] The third sector ( trade and services ) represented 75.8 % of the area ‘s GDP in 2018, according to the IBGE. The service sector was creditworthy for 60 % of GDP and trade for 13 %. It covers a across-the-board range of activities : commerce, accommodation and catering, ecstasy, communications, fiscal services, veridical estate activities and services provided to businesses, public administration ( urban scavenge, sanitation, etc. ) and other services such as education, social and health services, inquiry and development, sports activities, and so forth, since it consists of activities complementary to other sectors. [ 281 ] [ 282 ] Micro and little businesses represent 30 % of the nation ‘s GDP. In the commercial sector, for example, they represent 53 % of the GDP within the activities of the sector. [ 283 ] Brazil pegged its currency, the real number, to the U.S. dollar in 1994. however, after the East asian fiscal crisis, the russian default in 1998 [ 284 ] and the series of adverse fiscal events that followed it, the Central Bank of Brazil temporarily changed its monetary policy to a managed float regimen [ 285 ] system while undergoing a currency crisis, until definitively changing the commute regimen to free-float in January 1999. [ 286 ] Brazil received an International Monetary Fund ( IMF ) rescue package in mid-2002 of $ 30.4 billion, [ 287 ] a record kernel at the time. Brazil ‘s cardinal deposit repaid the IMF loanword in 2005, although it was not due to be repaid until 2006. [ 288 ] One of the issues the Central Bank of Brazil recently dealt with was an excess of bad short-run das kapital inflows to the nation, which may have contributed to a fall in the value of the U.S. dollar against the real during that period. [ 289 ] Nonetheless, alien lead investment ( FDI ), related to long-run, less inquisitive investment in product, is estimated to be $ 193.8 billion for 2007. [ 290 ] Inflation monitor and control presently plays a major part in the Central bank ‘s function in setting short-run interest rates as a monetary policy measure. [ 291 ]
Read more: S.S. Lazio
putrescence costs Brazil about $ 41 billion a year alone in 2010, with 69.9 % of the country ‘s firms identifying the emergence as a major restraint in successfully penetrating the global marketplace. [ 292 ] local government corruption is so prevailing that voters perceive it as a problem only if it surpasses certain levels, and only if a local media e.g. a radio station is salute to divulge the findings of corruptness charges. [ 293 ] Initiatives, like this exposure, tone awareness which is indicated by the Transparency International ‘s Corruption Perceptions Index ; ranking Brazil 69th out of 178 countries in 2012. [ 294 ] The purchasing power in Brazil is eroded by the alleged Brazil cost. [ 295 ]
Energy
Brazil is the world ‘s tenth largest energy consumer with a lot of its energy coming from renewable sources, particularly hydroelectricity and ethyl alcohol ; the Itaipu Dam is the world ‘s largest hydroelectric plant by energy coevals, [ 296 ] and the country has other bombastic plants like Belo Monte and Tucuruí. The first base car with an ethyl alcohol engine was produced in 1978 and the first gear airplane engine running on ethyl alcohol in 2005. [ 297 ] In total electricity generation, in 2019 Brazil reached 170,000 megawatts of install capacitance, more than 75 % from renewable sources ( the majority, hydroelectric plants ). [ 298 ] In 2019, Brazil had 217 hydroelectric plants in operation, with an install capacity of 98,581 MW, 60.16 % of the state ‘s energy generation. [ 299 ] Brazil is one of the 5 largest hydroelectric energy producers in the world ( second stead in 2017 ). [ 300 ] As of June 2021, according to ONS, total install capability of wind world power was 18.7 GW, with average capacity factor of 58 %. [ 301 ] While the populace average fart production capacity factors is 24.7 %, there are areas in Northern Brazil, particularly in Bahia State, where some tip farms record with average capacity factors over 60 % ; [ 302 ] the average capability factor in the Northeast Region is 45 % in the coast and 49 % in the interior. [ 303 ] In 2019, wind energy represented 9 % of the energy generated in the country. [ 304 ] In 2019, it was estimated that the country had an estimated tip power genesis potential of around 522 GW ( this, entirely onshore ), adequate energy to meet three times the country ‘s current demand. [ 305 ] [ 306 ] Brazil is one of the 10 largest wind energy producers in the worldly concern ( eighth home in 2019, with 2.4 % of world product ). [ 307 ] [ 308 ] As of June 2021, according to ONS, full install capacity of photovoltaic solar was 9.7 GW, with modal capability divisor of 23 %. Some of the most irradiate brazilian States are Minas Gerais, Bahia and Goiás. [ 309 ] [ 310 ] In 2019, solar office represented 1.27 % of the energy generated in the nation. [ 304 ] In 2020, Brazil was the fourteenth state in the earth in terms of install solar world power ( 7.8 GW ). [ 311 ] In 2020, Brazil was the 2nd largest country in the universe in the production of energy through biomass ( energy production from solid biofuels and renewable neutralize ), with 15,2 GW installed. [ 312 ] holocene oil discoveries in the pre-salt layer have opened the door for a big increase in oil production. [ 313 ] The governmental agencies responsible for the energy policy are the Ministry of Mines and Energy, the National Council for Energy Policy, the National Agency of Petroleum, Natural Gas and Biofuels, and the National Agency of Electricity. [ 314 ] In the begin of 2020, in the production of oil and natural boast, the area exceeded 4 million barrels of oil equivalent per day, for the first time. In January this year, 3.168 million barrels of oil per day and 138.753 million cubic meters of natural boast were extracted. [ 315 ]
tourism
tourism in Brazil is a growing sector and winder to the economy of several regions of the state. The nation had 6.36 million visitors in 2015, ranking in terms of the international tourist arrivals as the main finish in South America and second in Latin America after Mexico. [ 317 ] Revenues from external tourists reached US $ 6 billion in 2010, showing a recovery from the 2008–2009 economic crisis. [ 318 ] Historical records of 5.4 million visitors and US $ 6.8 billion in receipts were reached in 2011. [ 319 ] [ 320 ] In the tilt of world tourist destinations, in 2018, Brazil was the 48th most visit state, with 6.6 million tourists ( and revenues of 5.9 billion dollars ). [ 321 ] natural areas are its most popular tourism product, a combination of ecotourism with leisure and refreshment, chiefly sun and beach, and venture change of location, arsenic well as cultural tourism. Among the most popular destinations are the Amazon Rainforest, beaches and dunes in the Northeast Region, the Pantanal in the Center-West Region, beaches at Rio de Janeiro and Santa Catarina, cultural tourism in Minas Gerais and commercial enterprise trips to São Paulo. [ 322 ] In terms of the 2015 Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Index ( TTCI ), which is a measurement of the factors that make it attractive to develop occupation in the travel and tourism diligence of individual countries, Brazil ranked in the 28st place at the world ‘s level, third in the Americas, after Canada and United States. [ 323 ] [ 324 ] Brazil ‘s main competitive advantages are its natural resources, which ranked 1st on this criteria out of all countries considered, and ranked 23rd for its cultural resources, due to its many World Heritage Sites. The TTCI report notes Brazil ‘s main weaknesses : its prime transportation infrastructure remains underdeveloped ( rank 116th ), with the quality of roads ranking in 105th place ; and the country continues to suffer from a lack of price competitiveness ( rank 114th ), due in part to senior high school ticket taxes and airport charges, vitamin a good as high prices and high taxation. safety and security system have improved significantly : 75th in 2011, up from 128th in 2008. [ 324 ]
infrastructure
science and technology
technical research in Brazil is largely carried out in public universities and research institutes, with the majority of fund for basic research coming from diverse government agencies. [ 325 ] Brazil ‘s most respect technical hub are the Oswaldo Cruz Institute, the Butantan Institute, the Air Force ‘s Aerospace Technical Center, the brazilian Agricultural Research Corporation and the National Institute for Space Research. [ 326 ] [ 327 ] The brazilian Space Agency has the most promote space program in Latin America, with significant resources to launch vehicles, and industry of satellites. Owner of relative technical sophistication, the country develops submarines, aircraft, american samoa well as being involved in space research, having a Vehicle Launch Center Light and being the only nation in the Southern Hemisphere the integrate team building International Space Station ( ISS ). [ 329 ] The country is besides a pioneer in the search for petroleum in deep water, from where it extracts 73 % of its reserves. uranium is enriched at the Resende Nuclear Fuel Factory, by and large for inquiry purposes ( as Brazil obtains 88 % of its electricity from hydroelectricity [ 330 ] ) and the area ‘s first nuclear submarine was delivered in 2015 ( by France ). [ 331 ] Brazil is one of the three countries in Latin America [ 332 ] with an operational Synchrotron Laboratory, a research adeptness on physics, chemistry, material skill and life sciences, and Brazil is the only latin american area to have a semiconductor device company with its own lying plant, the CEITEC. [ 333 ] According to the Global Information Technology Report 2009–2010 of the World Economic Forum, Brazil is the world ‘s 61st largest developer of information technology. [ 334 ] Brazil was ranked 62nd in the Global Innovation Index in 2020, up from 66th in 2019. [ 335 ] [ 336 ] [ 337 ] [ 338 ] Among the most celebrated brazilian inventors are priests Bartolomeu de Gusmão, Landell de Moura and Francisco João de Azevedo, besides Alberto Santos-Dumont, [ 339 ] Evaristo Conrado Engelberg, [ 340 ] Manuel Dias de Abreu, [ 341 ] Andreas Pavel [ 342 ] and Nélio José Nicolai. [ 343 ] brazilian skill is represented by the likes of César Lattes ( brazilian physicist Pathfinder of Pi Meson ), [ 344 ] Mário Schenberg ( considered the greatest theoretical physicist of Brazil ), [ 345 ] José Leite Lopes ( only brazilian physicist holder of the UNESCO Science Prize ), [ 346 ] Artur Ávila ( the inaugural romance american english winner of the Fields Medal ) [ 347 ] and Fritz Müller ( pioneer in factual defend of the theory of development by Charles Darwin ). [ 348 ]
transportation
brazilian roads are the primary carriers of freight and passenger traffic. The road system totaled 1.98 million kilometer ( 1.23 million secret intelligence service ) in 2002. The total of paved roads increased from 35,496 km ( 22,056 mile ) in 1967 to 215,000 km ( 133,595 secret intelligence service ) in 2018. [ 350 ] [ 351 ] The nation has about 14,000 km ( 8,699 security service ) of divided highways, 5,000 kilometer ( 3,107 michigan ) alone in the State of São Paulo. Currently it ‘s possible to travel from Rio Grande, in the extreme south of the country, to Brasília ( 2,580 kilometer ( 1,603 nautical mile ) ) or Casimiro de Abreu, in the state of Rio de Janeiro ( 2,045 kilometer ( 1,271 michigan ) ), only on divided highways. The beginning investments in road infrastructure have given up in the 1920s, the government of Washington Luís, being pursued in the governments of Getúlio Vargas and Eurico Gaspar Dutra. [ 352 ] President Juscelino Kubitschek ( 1956–61 ), who designed and built the capital Brasília, was another athletic supporter of highways. [ 353 ] Brazil ‘s railroad track system has been declining since 1945, when emphasis shifted to highway structure. The full length of railroad track track was 30,875 kilometer ( 19,185 myocardial infarction ) in 2002, as compared with 31,848 km ( 19,789 nautical mile ) in 1970. Most of the railway organization belonged to the Federal Railroad Corporation RFFSA, which was privatized in 2007. [ 354 ] The São Paulo Metro was the first belowground transit system in Brazil. The other metro systems are in Rio de Janeiro, Porto Alegre, Recife, Belo Horizonte, Brasília, Salvador and Fortaleza. The country has an extensive rail network of 28,538 kilometres ( 17,733 miles ) in length, the one-tenth largest network in the world. [ 355 ] presently, the brazilian politics, unlike the past, seeks to encourage this mode of ecstasy ; an exemplar of this incentive is the stick out of the Rio–São Paulo high-speed railing, that will connect the two main cities of the state to carry passengers. There are about 2,500 airports in Brazil, including landing fields : the second largest count in the world, after the United States. [ 356 ] São Paulo–Guarulhos International Airport, near São Paulo, is the largest and busiest airport with closely 20 million passengers per annum, while handling the huge majority of commercial traffic for the state. [ 357 ] For cargo transmit waterways are of importance, e.g. the industrial zones of Manaus can be reached entirely by means of the Solimões–Amazonas waterway ( 3,250 kilometres or 2,020 miles in distance, with a minimum astuteness of six metres or 20 feet ). The area besides has 50,000 kilometres ( 31,000 miles ) of waterways. [ 355 ] Coastal shipping links widely separated parts of the country. Bolivia and Paraguay have been given free ports at Santos. Of the 36 deep-water ports, Santos, Itajaí, Rio Grande, Paranaguá, Rio de Janeiro, Sepetiba, Vitória, Suape, Manaus and São Francisco do Sul are the most authoritative. [ 358 ] Bulk carriers have to wait up to 18 days before being serviced, container ships 36.3 hours on average. [ 359 ]
Health
The brazilian public health system, the Unified Health System ( Sistema Único de Saúde – SUS ), is managed and provided by all levels of politics, [ 360 ] being the largest organization of this type in the worldly concern. [ 361 ] On the other hand, individual healthcare systems play a complementary role. [ 362 ] Public health services are universal and offered to all citizens of the state for free. however, the construction and maintenance of health centers and hospitals are financed by taxes, and the country spends about 9 % of its GDP on expenditures in the area. In 2012, Brazil had 1.85 doctors and 2.3 hospital beds for every 1,000 inhabitants. [ 363 ] [ 364 ] Despite all the advance made since the creation of the universal health worry system in 1988, there are calm respective public health problems in Brazil. In 2006, the independent points to be solved were the gamey baby ( 2.51 % ) and maternal deathrate rates ( 73.1 deaths per 1000 births ). [ 365 ] The count of deaths from noncommunicable diseases, such as cardiovascular diseases ( 151.7 deaths per 100,000 inhabitants ) and cancer ( 72.7 deaths per 100,000 inhabitants ), besides has a considerable impingement on the health of the brazilian population. finally, external but preventable factors such as car accidents, violence and suicide caused 14.9 % of all deaths in the nation. [ 365 ] The brazilian health system was ranked hundred-and-twenty-fifth among the 191 countries evaluated by the World Health Organization ( WHO ) in 2000. [ 366 ]
education
The Federal Constitution and the Law of Guidelines and Bases of National Education determine that the Union, the states, the Federal District, and the municipalities must manage and organize their respective education systems. Each of these public educational systems is creditworthy for its own maintenance, which manages funds american samoa good as the mechanism and fund sources. The constitution reserves 25 % of the country budget and 18 % of federal taxes and municipal taxes for department of education. [ 367 ]
According to the IBGE, in 2019, the literacy rate of the population was 93.4 %, mean that 11.3 million ( 6.6 % of population ) people are inactive illiterate in the country, with some states like Rio de Janeiro and Santa Catarina reaching about 97 % of literacy pace ; [ 368 ] functional illiteracy has reached 21.6 % of the population. [ 369 ] Illiteracy is higher in the Northeast, where 13.87 % of the population is illiterate, while the South, has 3.3 % of its population illiterate. [ 370 ] [ 368 ] Brazil ‘s private institutions tend to be more exclusive and offer better quality education, then many high-income families send their children there. The result is a segregate educational system that reflects extreme income disparities and reinforces social inequality. however, efforts to change this are making impacts. [ 371 ] The University of São Paulo is the moment best university in Latin America, according to late 2019 QS World University Rankings. Of the top 20 romance american universities, eight are brazilian. Most of them are populace. Attending an initiation of higher department of education is required by Law of Guidelines and Bases of Education. Kindergarten, elementary and medium department of education are required of all students. [ 372 ]
Media and communication
The brazilian press was officially born in Rio de Janeiro on 13 May 1808 with the creation of the Royal Printing National Press by the Prince Regent Dom João. [ 374 ] The Gazeta do Rio de Janeiro, the first newspaper published in the country, began to circulate on 10 September 1808. [ 375 ] The largest newspapers nowadays are Folha de S.Paulo, Super Notícia, O Globo and O Estado de S. Paulo. [ 376 ] Radio broadcast medium began on 7 September 1922, with a speech by then President Pessoa, and was formalized on 20 April 1923 with the creation of “ Radio Society of Rio de Janeiro ”. [ 377 ] television receiver in Brazil began formally on 18 September 1950, with the establish of television Tupi by Assis Chateaubriand. [ 378 ] Since then television has grown in the country, creating large commercial broadcast networks such as Globo, SBT, RecordTV, Bandeirantes and RedeTV. today it is the most important divisor in popular culture of brazilian society, indicated by inquiry showing that ampere a lot as 67 % [ 379 ] [ 380 ] of the general population follow the same day by day soap opera circulate. Digital Television, using the SBTVD standard ( based on the japanese standard ISDB-T ), was adopted on 29 June 2006 and launched on 2 November 2007. [ 381 ] In May 2010, the brazilian politics launched television receiver Brasil Internacional, an international television station, initially broadcasting to 49 countries. [ 382 ] commercial television channels broadcast internationally include Globo Internacional, RecordTV Internacional and Band Internacional .
Demographics
 Population density of brazilian municipalities The population of Brazil, as recorded by the 2008 PNAD, was approximately 190 million [ 383 ] ( 22.31 inhabitants per hearty kilometer or 57.8/sq nautical mile ), with a proportion of men to women of 0.95:1 [ 384 ] and 83.75 % of the population defined as urban. [ 385 ] The population is heavily concentrated in the Southeastern ( 79.8 million inhabitants ) and Northeastern ( 53.5 million inhabitants ) regions, while the two most extensive regions, the Center-West and the North, which together make up 64.12 % of the brazilian territory, have a full of alone 29.1 million inhabitants. The first census in Brazil was carried out in 1872 and recorded a population of 9,930,478. [ 386 ] From 1880 to 1930, 4 million Europeans arrived. [ 387 ] Brazil ‘s population increased significantly between 1940 and 1970, because of a refuse in the mortality pace, even though the birth rate underwent a rebuff decline. In the 1940s the annual population growth rate was 2.4 %, rising to 3.0 % in the 1950s and remaining at 2.9 % in the 1960s, as life anticipation rose from 44 to 54 years [ 388 ] and to 72.6 years in 2007. [ 389 ] It has been steadily falling since the 1960s, from 3.04 % per year between 1950 and 1960 to 1.05 % in 2008 and is expected to fall to a negative measure of –0.29 % by 2050 [ 390 ] therefore completing the demographic conversion. [ 391 ] In 2008, the illiteracy pace was 11.48 % [ 392 ] and among the young person ( ages 15–19 ) 1.74 %. It was highest ( 20.30 % ) in the Northeast, which had a big proportion of rural poor people. [ 393 ] Illiteracy was high ( 24.18 % ) among the rural population and lower ( 9.05 % ) among the urban population. [ 394 ]
Population density of brazilian municipalities The population of Brazil, as recorded by the 2008 PNAD, was approximately 190 million [ 383 ] ( 22.31 inhabitants per hearty kilometer or 57.8/sq nautical mile ), with a proportion of men to women of 0.95:1 [ 384 ] and 83.75 % of the population defined as urban. [ 385 ] The population is heavily concentrated in the Southeastern ( 79.8 million inhabitants ) and Northeastern ( 53.5 million inhabitants ) regions, while the two most extensive regions, the Center-West and the North, which together make up 64.12 % of the brazilian territory, have a full of alone 29.1 million inhabitants. The first census in Brazil was carried out in 1872 and recorded a population of 9,930,478. [ 386 ] From 1880 to 1930, 4 million Europeans arrived. [ 387 ] Brazil ‘s population increased significantly between 1940 and 1970, because of a refuse in the mortality pace, even though the birth rate underwent a rebuff decline. In the 1940s the annual population growth rate was 2.4 %, rising to 3.0 % in the 1950s and remaining at 2.9 % in the 1960s, as life anticipation rose from 44 to 54 years [ 388 ] and to 72.6 years in 2007. [ 389 ] It has been steadily falling since the 1960s, from 3.04 % per year between 1950 and 1960 to 1.05 % in 2008 and is expected to fall to a negative measure of –0.29 % by 2050 [ 390 ] therefore completing the demographic conversion. [ 391 ] In 2008, the illiteracy pace was 11.48 % [ 392 ] and among the young person ( ages 15–19 ) 1.74 %. It was highest ( 20.30 % ) in the Northeast, which had a big proportion of rural poor people. [ 393 ] Illiteracy was high ( 24.18 % ) among the rural population and lower ( 9.05 % ) among the urban population. [ 394 ]
raceway and ethnicity
According to the National Research by Household Sample ( PNAD ) of 2008, 48.43 % of the population ( about 92 million ) described themselves as White ; 43.80 % ( about 83 million ) as Pardo ( brown ), 6.84 % ( about 13 million ) as Black ; 0.58 % ( about 1.1 million ) as East Asian ( formally called amarela or yellow ) ; and 0.28 % ( about 536 thousand ) as amerindian ( formally called indígena, Indigenous ), while 0.07 % ( about 130 thousand ) did not declare their raceway. [ 396 ] In 2007, the National Indian Foundation estimated that Brazil has 67 different uncontacted tribes, up from their estimate of 40 in 2005. Brazil is believed to have the largest phone number of uncontacted peoples in the world. [ 397 ] Since the arrival of the Portuguese in 1500, considerable familial blend between Amerindians, Europeans, and Africans has taken place in all regions of the country ( with european lineage being dominant allele countrywide according to the huge majority of all autosomal studies undertaken covering the entire population, accounting for between 65 % to 77 % ). [ 398 ] [ 399 ] [ 400 ] [ 401 ] brazilian club is more markedly divided by social class lines, although a high income disparity is found between race groups, so racism and classism can be conflated. Socially significant meanness to one racial group is taken in account more in the basis of appearance ( phenotypes ) preferably than ancestry, to the extent that full siblings can pertain to different “ racial ” groups. [ 402 ]
socioeconomic factors are besides significant, because a minority of pardos are likely to start declaring themselves White or Black if socially up. [ 406 ] Skin color and facial features do not line quite well with lineage ( normally, Afro-Brazilians are evenly mix and european lineage is dominant in Whites and pardos with a significant non-European contribution, but the individual version is capital ). [ 401 ] [ 407 ] [ 408 ] [ 409 ] The brown population ( officially called pardo in Portuguese, besides colloquially moreno ) [ 410 ] [ 411 ] is a broad category that includes caboclos ( assimilated Amerindians in general, and descendants of Whites and Natives ), mulatos ( descendants of chiefly Whites and Afro-Brazilians ) and cafuzos ( descendants of Afro-Brazilians and Natives ). [ 410 ] [ 411 ] [ 412 ] [ 413 ] [ 414 ] People of considerable amerindian lineage form the majority of the population in the Northern, Northeastern and Center-Western regions. [ 415 ] Higher percents of Blacks, mulattoes and tri-racials can be found in the easterly slide of the Northeastern region from Bahia to Paraíba [ 414 ] [ 416 ] and besides in northern Maranhão, [ 417 ] [ 418 ] southern Minas Gerais [ 419 ] and in eastern Rio de Janeiro. [ 414 ] [ 419 ] From the nineteenth hundred, Brazil opened its borders to immigration. About five million people from over 60 countries migrated to Brazil between 1808 and 1972, most of them of Portuguese, Italian, Spanish, German, Ukrainian, Polish, Jewish, Russian, Chinese, Japanese, and Arab lineage. [ 420 ] [ 421 ] Brazil has the second largest jewish community in Latin America making up 0.06 % of its population. [ 422 ]
religion
roman Catholicism is the state ‘s overriding faith. Brazil has the world ‘s largest catholic population. [ 423 ] [ 424 ] According to the 2010 Demographic Census ( the PNAD survey does not inquire about religion ), 64.63 % of the population followed Roman Catholicism ; 22.2 % Protestantism ; 2.0 % Kardecist spirituality ; 3.2 % other religions, undeclared or undetermined ; while 8.0 % have no religion. [ 5 ] religion in Brazil was formed from the confluence of the Catholic Church with the religious traditions of enslave african peoples and autochthonal peoples. [ 425 ] This confluence of faiths during the portuguese colonization of Brazil led to the development of a diverse array of syncretic practices within the overarching umbrella of brazilian Catholic Church, characterized by traditional portuguese festivities, [ 426 ] religious pluralism increased during the twentieth century, [ 427 ] and the Protestant community has grown to include over 22 % of the population. [ 428 ] The most common protestant denominations are evangelical Pentecostal ones. other protestant branches with a noteworthy presence in the area include the Baptists, Seventh-day Adventists, Lutherans and the Reformed custom. [ 429 ] however, in the last ten years Protestantism, particularly in forms of Pentecostalism and Evangelicalism, has spread in Brazil, while the symmetry of Catholics has dropped significantly. [ 430 ] After Protestantism, individuals professing no religion are besides a significant group, exceeding 8 % of the population as of the 2010 census. The cities of Boa Vista, Salvador, and Porto Velho have the greatest proportion of irreligious residents in Brazil. Teresina, Fortaleza, and Florianópolis were the most Roman Catholic in the nation. [ 431 ] Greater Rio de Janeiro, not including the city proper, is the most irreligious and least Roman Catholic Brazilian periphery, while Greater Porto Alegre and Greater Fortaleza are on the diametric sides of the lists, respectively. [ 431 ]
In October 2009, the brazilian Senate approved and enacted by the President of Brazil in February 2010, an agreement with the Vatican, in which the Legal Statute of the Catholic Church in Brazil is recognized. The agreement confirmed norms that were normally complied with regarding religious education in public elementary schools ( which besides ensures the teaching of other beliefs ), marriage and religious aid in prisons and hospitals. The project was criticized by parliamentarians who understood the end of the layman state with the approval of the agreement. [ 434 ] [ 435 ]
urbanization
According to IBGE ( brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics ) urban areas already concentrate 84.35 % of the population, while the Southeast region remains the most populated one, with over 80 million inhabitants. [ 436 ] The largest urban agglomerations in Brazil are São Paulo, Rio de Janeiro, and Belo Horizonte – all in the Southeastern Region – with 21.1, 12.3, and 5.1 million inhabitants respectively. [ 437 ] [ 438 ] [ 439 ] The majority of express capitals are the largest cities in their states, except for Vitória, the capital of Espírito Santo, and Florianópolis, the capital of Santa Catarina. [ 440 ]
language
The official terminology of Brazil is portuguese [ 443 ] ( Article 13 of the Constitution of the Federal Republic of Brazil ), which about all of the population speak and is about the only language used in newspapers, radio, television receiver, and for business and administrative purposes. Brazil is the alone Portuguese-speaking nation in the Americas, making the linguistic process an crucial part of brazilian home identity and giving it a national polish clear-cut from those of its spanish-speaking neighbors. [ 444 ] brazilian Portuguese has had its own growth, largely alike to 16th-century Central and Southern dialects of european Portuguese [ 445 ] ( despite a identical hearty number of portuguese colonial settlers, and more recent immigrants, coming from Northern regions, and in minor degree Portuguese Macaronesia ), with a few influences from the Amerindian and African languages, specially west african and Bantu restricted to the vocabulary lone. [ 446 ] As a solution, [ citation needed ] the terminology is slightly different, by and large in phonology, from the lyric of Portugal and other Portuguese-speaking countries ( the dialects of the other countries, partially because of the more recent end of portuguese colonialism in these regions, have a closer connection to contemporary european Portuguese ). These differences are comparable to those between american and british English. [ 446 ] In 1990, the Community of portuguese Language Countries ( CPLP ), which included representatives from all countries with Portuguese as the official language, reached an agreement on the reform of the Portuguese orthography to unify the two standards then in use by Brazil on one side and the remaining lusophone countries on the early. This spelling reform went into effect in Brazil on 1 January 2009. In Portugal, the reform was signed into jurisprudence by the President on 21 July 2008 allowing for a six-year adaptation menstruation, during which both orthographies will co-exist. The remaining CPLP countries are dislodge to establish their own transition timetables. [ 447 ] The sign language jurisprudence legally recognized in 2002, [ 448 ] ( the law was regulated in 2005 ) [ 449 ] the use of the brazilian Sign Language, more normally known by its Portuguese acronym LIBRAS, in education and government services. The linguistic process must be taught as a part of the department of education and lecture and language pathology course of study. LIBRAS teachers, instructors and translators are recognized professionals. Schools and health services must provide access ( “ inclusion “ ) to deaf people. [ 450 ]
Minority languages are spoken throughout the nation. One hundred and eighty amerindian languages are spoken in outside areas and a significant total of other languages are spoken by immigrants and their descendants. [ 446 ] In the municipality of São Gabriel da Cachoeira, Nheengatu ( a presently endangered South american creole terminology – or an ‘anti-creole ‘, according to some linguists – with largely autochthonal brazilian languages vocabulary and Portuguese-based grammar that, together with its southerly relative língua geral paulista, once was a major tongue franca in Brazil, [ 451 ] being replaced by Portuguese merely after governmental prohibition led by major political changes ) [ excessive detail? ], Baniwa and Tucano languages had been granted co-official status with Portuguese. [ 452 ] There are meaning communities of german ( by and large the brazilian Hunsrückisch, a eminent german lyric dialect ) and italian ( largely the Talian, a venetian dialect ) origins in the Southern and Southeastern regions, whose ancestors ‘ native languages were carried along to Brazil, and which, still alive there, are influenced by the portuguese language. [ 453 ] [ 454 ] Talian is officially a historic patrimony of Rio Grande do Sul, [ 455 ] and two german dialects own co-official condition in a few municipalities. [ 456 ] Italian is besides recognized as ethnic language in the Santa Teresa microregion and Vila Velha ( Espirito Santo state ), and is taught as mandate second lyric at school. [ 457 ] Learning at least one moment linguistic process ( generally English or Spanish ) is mandatary for all the 12 grades of the compulsory education organization ( primary and secondary education, there called ensino fundamental and ensino médio respectively ). Brazil is the inaugural country in South America to offer Esperanto to secondary students. [ 458 ]
acculturation
The core culture of Brazil is derived from portuguese culture, because of its hard colonial ties with the Portuguese Empire. [ 460 ] Among other influences, the Portuguese introduced the portuguese speech, Roman Catholicism and colonial architectural styles. The culture was, however, besides strongly influenced by African, autochthonal and non-Portuguese european cultures and traditions. [ 461 ] Some aspects of brazilian acculturation were influenced by the contributions of italian, german and other european ampere well as japanese, jewish and arabian immigrants who arrived in large numbers in the South and Southeast of Brazil during the 19th and twentieth centuries. [ 462 ] The autochthonal Amerindians influenced Brazil ‘s language and cuisine ; and the Africans charm lyric, cuisine, music, dance and religion. [ 463 ] brazilian art has developed since the sixteenth century into different styles that range from Baroque ( the dominant allele vogue in Brazil until the early on nineteenth century ) [ 464 ] [ 465 ] to Romanticism, Modernism, Expressionism, Cubism, Surrealism and Abstractionism. brazilian film dates back to the parturition of the medium in the belated nineteenth century and has gained a modern level of external acclaim since the 1960s. [ 466 ]
architecture
The architecture of Brazil is influenced by Europe, specially Portugal. It has a history that goes back 500 years to the prison term when Pedro Cabral discovered Brazil in 1500. portuguese colonial architecture was the first wave of architecture to go to Brazil. [ 467 ] It is the basis for all brazilian architecture of late centuries. [ 468 ] In the nineteenth century during the time of the Empire of Brazil, Brazil followed european trends and adopted Neoclassical and Gothic Revival architecture. then in the twentieth century particularly in Brasilia, Brazil experimented with Modernist architecture. The colonial architecture of Brazil dates to the early sixteenth century when Brazil was first explored, conquered and settled by the Portuguese. The portuguese build computer architecture conversant to them in Europe in their draw a bead on to colonize Brazil. They built Portuguese colonial architecture which included churches, civic computer architecture including houses and forts in brazilian cities and the countryside. During nineteenth hundred brazilian architecture saw the presentation of more european styles to Brazil such as Neoclassical and Gothic Revival computer architecture. This was normally shuffle with brazilian influences from their own heritage which produced a singular form of brazilian computer architecture. In the 1950s the modernist computer architecture was introduced when Brasilia was built as new federal capital in the inside of Brazil to help develop the inside. The architect Oscar Niemeyer idealized and build government buildings, churches and civic buildings in the modernist dash. [ 469 ] [ 470 ]
music
The music of Brazil was formed chiefly from the fusion of european and african elements. [ 471 ] Until the nineteenth century, Portugal was the gateway to most of the influences that built brazilian music, although many of these elements were not of Portuguese origin, but broadly european. The first base was José Maurício Nunes Garcia, generator of sacred pieces with influence of viennese classicism. [ 472 ] The major contribution of the African element was the rhythmical diverseness and some dances and instruments that had a bigger function in the development of popular music and tribe, flourishing particularly in the twentieth hundred. [ 471 ] popular music since the recently eighteenth hundred began to show signs of forming a characteristically brazilian audio, with obeche considered the most typical and on the UNESCO cultural inheritance list. [ 473 ] Maracatu and Afoxê are two Afro-Brazilian music traditions that have been popularized by their appearance in the annual brazilian Carnivals. [ 474 ] The sport of capoeira is normally played with its own music referred to as capoeira music, which is normally considered to be a call-and-response type of folk music music. [ 475 ] Forró is a type of folk music outstanding during the Festa Junina in northeastern Brazil. [ 476 ] Jack A. Draper III, a professor of Portuguese at the University of Missouri, [ 477 ] argues that Forró was used as a way to mortify feelings of nostalgia for a rural life style. [ 478 ] Choro is a identical popular music implemental manner. Its origins are in 19th-century Rio de Janeiro. In hurt of the name, the style often has a fast and felicitous cycle, characterized by virtuosity, extemporization, insidious modulations and full of syncopation and contrast. [ 479 ] Bossa nova is besides a well-known expressive style of brazilian music developed and popularized in the 1950s and 1960s. The idiom “ bossa nova ” means literally “ new vogue ”. [ 481 ] A lyric fusion of samba and jazz, bossa nova acquired a large following begin in the 1960s. [ 482 ]
literature
brazilian literature dates back to the sixteenth hundred, to the writings of the first portuguese explorers in Brazil, such as Pêro Vaz de Caminha, filled with descriptions of animal, plant and comment about the autochthonal population that fascinated european readers. Brazil produced significant works in Romanticism – novelists like Joaquim Manuel de Macedo and José de Alencar wrote novels about love and pain. Alencar, in his retentive career, besides treated autochthonal people as heroes in the Indigenist novels O Guarani, Iracema and Ubirajara. [ 484 ] Machado de Assis, one of his contemporaries, wrote in about all genres and continues to gain international prestige from critics worldwide. [ 485 ] [ 486 ] [ 487 ] brazilian Modernism, evidenced by the Week of Modern Art in 1922, was concerned with a nationalist avant-garde literature, [ 488 ] while Post-Modernism brought a generation of distinct poets like João Cabral de Melo Neto, Carlos Drummond de Andrade, Vinicius de Moraes, Cora Coralina, Graciliano Ramos, Cecília Meireles, and internationally known writers dealing with universal and regional subjects like Jorge Amado, João Guimarães Rosa, Clarice Lispector and Manuel Bandeira. [ 489 ] [ 490 ] [ 491 ]
cuisine
brazilian cuisine varies greatly by region, reflecting the state ‘s varying blend of autochthonal and immigrant populations. This has created a national cuisine marked by the preservation of regional differences. [ 492 ] Examples are Feijoada, considered the nation ‘s national dish ; [ 493 ] and regional foods such as beiju, feijão tropeiro, vatapá, moqueca, polenta ( from Italian cuisine ) and acarajé ( from African cuisine ). [ 494 ] The national beverage is coffee and cachaça is Brazil ‘s native liquor. Cachaça is distilled from sugar cane and is the main ingredient in the national cocktail, Caipirinha. [ 495 ] A distinctive meal consists by and large of rice and beans with gripe, salad, french fries and a electrocute egg. [ 496 ] Often, it is shuffle with cassava flour ( farofa ). Fried potatoes, fried cassava, fried banana, fried meat and fried cheese are very frequently eaten in lunch and served in most distinctive restaurants. [ 497 ] Popular snacks are pastel ( a fried pastry ) ; coxinha ( a variation of chicken croquete ) ; pão de queijo ( cheese boodle and cassava flour / tapioca ) ; pamonha ( corn and milk paste ) ; esfirra ( a variation of Lebanese pastry ) ; kibbeh ( from Arabic cuisine ) ; empanada ( pastry ) and empada, little salt pies filled with shrimps or heart of palm. Brazil has a variety of desserts such as brigadeiros ( chocolate fudge balls ), bolo de rolo ( roll cake with goiabada ), cocada ( a coconut gratifying ), beijinhos ( coconut truffles and clove ) and romeu east julieta ( cheese with goiabada ). Peanuts are used to make paçoca, rapadura and pé-de-moleque. local anesthetic common fruits like açaí, cupuaçu, mango, papaya, cocoa, cashew, guava, orange, birdlime, passionfruit, pineapple, and hog plumb are turned in juices and used to make chocolates, ice rink pops and frost cream. [ 498 ]
film
The brazilian film industry began in the recently nineteenth century, during the early days of the Belle Époque. While there were national movie productions during the early twentieth hundred, American films such as Rio the Magnificent were made in Rio de Janeiro to promote tourism in the city. [ 499 ] The films Limite ( 1931 ) and Ganga Bruta ( 1933 ), the latter being produced by Adhemar Gonzaga through the prolific studio apartment Cinédia, were ill received at free and failed at the box office, but are acclaimed nowadays and placed among the finest brazilian films of all fourth dimension. [ 500 ] The 1941 unfinished movie It’s All True was divided in four segments, two of which were filmed in Brazil and directed by Orson Welles ; it was in the first place produced as part of the United States ‘ good neighbor Policy during Getúlio Vargas ‘ Estado Novo government. During the 1960s, the Cinema Novo movement rose to prominence with directors such as Glauber Rocha, Nelson Pereira dos Santos, Paulo Cesar Saraceni and Arnaldo Jabor. Rocha ‘s films Deus e o Diabo na Terra do Sol ( 1964 ) and Terra em Transe ( 1967 ) are considered to be some of the greatest and most influential in brazilian film history. [ 501 ] During the 1990s, Brazil saw a billow of critical and commercial achiever with films such as O Quatrilho ( Fábio Barreto, 1995 ), O Que É Isso, Companheiro? ( Bruno Barreto, 1997 ) and Central do Brasil ( Walter Salles, 1998 ), all of which were nominated for the Academy Award for Best Foreign Language Film, the latter receiving a Best Actress nominating speech for Fernanda Montenegro. The 2002 crime film City of God, directed by Fernando Meirelles, was critically acclaimed, scoring 90 % on Rotten Tomatoes, [ 502 ] being placed in Roger Ebert ‘s Best Films of the Decade number [ 503 ] and receiving four Academy Award nominations in 2004, including Best Director. Notable film festivals in Brazil include the São Paulo and Rio de Janeiro International Film Festivals and the Gramado Festival .
theater
The dramaturgy in Brazil has its origins in the period of Jesuit expansion when field was used for the dissemination of Catholic doctrine in the sixteenth hundred. in the 17th and 18th centuries the first dramatists who appeared on the fit of european deriving was for woo or individual performances. [ 504 ] During the nineteenth hundred, dramatic theater gained importance and thickness, whose first example was Luis Carlos Martins Pena ( 1813–1848 ), capable of describing contemporary reality. Always in this period the comedy of costume and comic output was imposed. Significant, besides in the nineteenth hundred, was besides the dramatist Antônio Gonçalves Dias. [ 505 ] There were besides numerous operas and orchestras. The brazilian conductor Antônio Carlos Gomes became internationally known with operas like Il Guarany. At the end of the nineteenth century orchestrated dramaturgias became very democratic and were accompanied with songs of celebrated artists like the conductress Chiquinha Gonzaga. [ 506 ] already in the early twentieth hundred there was the presence of theaters, entrepreneurs and actor companies, but paradoxically the timbre of the products staggered, and lone in 1940 the brazilian dramaturgy received a boost of refilling thanks to the action of Paschoal Carlos Magno and his student ‘s dramaturgy, the comedians group and the italian actors Adolfo Celi, Ruggero Jacobbi and Aldo Calvo, founders of the Teatro Brasileiro de Comedia. From the 1960s it was attended by a theater dedicated to sociable and religious issues and to the thrive of schools of dramatic art. The most outstanding authors at this stage were Jorge Andrade and Ariano Suassuna. [ 505 ]
ocular arts
brazilian painting emerged in the late sixteenth century, [ 507 ] influenced by Baroque, Rococo, Neoclassicism, Romanticism, Realism, Modernism, Expressionism, Surrealism, Cubism and Abstracionism making it a major art vogue called brazilian academic art. [ 508 ] [ 509 ] The Missão Artística Francesa ( french Artistic Mission ) arrived in Brazil in 1816 proposing the initiation of an artwork academy modeled after the respect Académie des Beaux-Arts, with gradation courses both for artists and craftsmen for activities such as model, decorating, carpentry and others and bringing artists like Jean-Baptiste Debret. [ 509 ] Upon the creation of the Imperial Academy of Fine Arts, new artistic movements spread across the state during the nineteenth hundred and late the consequence called Week of Modern Art broke decidedly with academician tradition in 1922 and started a nationalist course which was influenced by modernist arts. Among the best-known brazilian painters are Ricardo do Pilar and Manuel district attorney Costa Ataíde ( baroque and rococo ), Victor Meirelles, Pedro Américo and Almeida Junior ( romanticism and platonism ), Anita Malfatti, Ismael Nery, Lasar Segall, Emiliano di Cavalcanti, Vicente do Rego Monteiro, and Tarsila do Amaral ( expressionism, surrealism and cubism ), Aldo Bonadei, José Pancetti and Cândido Portinari ( modernity ). [ 510 ]
Sports
The most popular sport in Brazil is football. [ 511 ] The brazilian men ‘s national team is ranked among the best in the global according to the FIFA World Rankings, and has won the World Cup tournament a record five times. [ 512 ] [ 513 ] Volleyball, basketball, car race, and martial arts besides attract large audiences. The Brazil men ‘s national volleyball team, for example, presently holds the titles of the World League, World Grand Champions Cup, World Championship and the World Cup. In car race, three brazilian drivers have won the Formula One worldly concern backing eight times. [ 514 ] [ 515 ] [ 516 ] Some sport variations have their origins in Brazil : beach football, [ 517 ] futsal ( indoor football ) [ 518 ] and footvolley emerged in Brazil as variations of football. In warlike arts, Brazilians developed Capoeira, [ 519 ] Vale tudo, [ 520 ] and brazilian jiu-jitsu. [ 521 ] Brazil has hosted several high-profile external sporting events, like the 1950 FIFA World Cup [ 522 ] and recently has hosted the 2014 FIFA World Cup, 2019 Copa América and 2021 Copa América. [ 523 ] The São Paulo circumference, Autódromo José Carlos Pace, hosts the annual Grand Prix of Brazil. [ 524 ] São Paulo organized the IV Pan American Games in 1963, and Rio de Janeiro hosted the XV Pan American Games in 2007. [ 525 ] On 2 October 2009, Rio de Janeiro was selected to host the 2016 Olympic Games and 2016 Paralympic Games, making it the beginning south american city to host the games [ 526 ] and second in Latin America, after Mexico City. Furthermore, the country hosted the FIBA Basketball World Cups in 1954 and 1963. At the 1963 event, the Brazil home basketball team won one of its two global backing titles. [ 527 ]
See besides
Notes
References
bibliography
far take
Government
Read more: The MMS Institute Thailand
