top accelerate [edit ]

Engine baron and torsion [edit ]
With power typically being the merchandise of push and focal ratio, a motorbike ‘s might and torsion ratings will be highly indicative mood of its operation. Reported numbers for power and torsion may however vary from one source to another due to inconsistencies in how test equipment is calibrated, the method acting of using that equipment, the conditions during the test, and particularly the placement that force and accelerate are being measured at. [ 2 ] The ability of the engine entirely, much called crankshaft world power, or ability at the crankshaft, will be significantly greater than the power measured at the rear wheel. The measure of baron lost due to clash in the transmission ( primary drive, gearbox and final drive ) depends on the details of the design and construction. Generalizing, a chain drive motorbike may have some 5-20 % less power at the rise bicycle than at the crankshaft, while a shaft drive model may lose a little more than that due to greater friction .
 Preparing for a dyno trial – note the fan used for engine cool
Preparing for a dyno trial – note the fan used for engine cool
 Motorcycle rear wheel on a dyno roller .
Motorcycle rear wheel on a dyno roller .
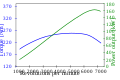 Graph of might and torsion .
Graph of might and torsion .
While the crankshaft power excludes these infection losses, hush the measurement is often made elsewhere in the drive-train, much at the back bicycle. A correction for the transmission losses is then applied to the measured values to obtain the crankshaft values. For motorcycles, the reported office and torsion numbers normally pertain to the crankshaft. In directive 92/61/EEC of 30 June 1992 relating to the type-approval of two or three-wheel drive vehicles, [ 3 ] it is referred to as “ utmost engine power ”, and manufacturers use similar terms. historically, this convention may have come from the pre- unit structure, wherein the crankshaft was immediately accessible for measurements, and the gearbox might have come from a different manufacturer. however, when the engineering details of the infection are known, the losses therein can be accurately quantify & corrected for. Explicit guidance on the homologation measurements and transmission corrections is given in directive 95/1/EC. [ 4 ] A main source of ambiguity and differences comes from the conditions the examination was done at. These conditions include details like atmospheric conditions ( temperature, pressure, humidity ), run down pressure, how the motorcycle is secured against the dyno drum, but most importantly : the conditions of the motorcycle itself. Examples thereof are : was the alternator fitted ? ; was the vent filter fitted ? ; what exhaust system was fitted ? One would hope that manufacturers would test their motorcycles in convention running holy order, so the condition that they are sold in, and for which they obtained type-approval, but this is not always the casing. Ducati, for case, has chosen to publish more positive values, stating that “ Technical data referring to power and torsion was measured on an engine quiz stand at Ducati ”. [ 5 ] Their published values are typically 5 % higher than the homologation values, in normal running order .
weight [edit ]
Motorcycle slant is expressed in three ways : gross vehicle weight rating ( GVWR ), dry weight and wet weight. GVWR is the maximum sum weight of the motorcycle including all consumables, the passenger, any passenger, and any cargo. It is by and large well-understood and standardize, being defined by law and oversee by agencies such as the US Department of Transportation. [ 6 ] In contrast, moisture and dry weight are unstandardized measurements that refer to the weight of the motorbike without rider, passengers or cargo, and either with ( wet ) or without ( dry ) a varying set of fluids such as fuel or lubricants, and the barrage. Wet and dry weight are frequently used to make comparisons between unlike motorcycles, because all else being equal, a lighter motorcycle will generally perform and handle better than a heavier one. The dispute between GVWR and moisture weight is how much the motorcycle can safely carry, including the passenger, fuel, and early load .
Dry weight [edit ]
As its burden changes during depend on, the dry slant of a motorbike typically excludes the gasoline ( or other fuel ). Dry weight, in this sense, can directly be used for comparison with ( FIM ) weight limits, which pertain to the motorbike in operate condition. It is besides share of the homologation tests, [ 3 ] and it is found on the EC Certificate of Conformity as unladen mass. [ 7 ] This dry system of weights could besides be useful in comparing different models, with different fuel tank capacities. however, manufacturers may besides exclude some or all of the keep up : locomotive oil, coolant, or brake fluid, and this makes such a comparison unmanageable. When any of these is excluded, the specified dry weight no longer pertains to the motorcycle in running ordain. Some manufacturers even exclude the battery, notwithstanding the weight of the barrage is chiefly in solid components ( normally lead ), not fluent ( electrolytes ).
so there is no standardized way to test the dry burden of a motorbike. Inconsistencies may be found between a motorbike manufacturer ‘s published dry weight and motorcycle press and media outlets ‘ published dry weight. This is due to different testing techniques, chiefly differences in what is being excluded, and a miss of defining how the test was done. A battery is typically included in the dry weight by manufacturers ( with the exception of at least one ), but it may not be included by media outlets. On the other hand, some press and media outlets merely exclude fuel to define their dry weight unit. For a typical sport bicycle, the dispute between wet weight and manufacturer claimed dry burden is around 70 pound ( 32 kilogram ). [ 8 ] This deviation includes around 30 pound ( 14 kilogram ) of gasoline, 7 pound ( 3.2 kilogram ) of locomotive oil, 7 pound ( 3.2 kilogram ) of coolant, and 9 pound ( 4.1 kilogram ) of battery. These weights are even larger for bigger motorcycles with higher capacities, complicating comparison between air-cool and water-cooled motorcycles ‘ dry weights. While its weight is small compared to the other fluids discussed above ( a few ounces ), hydraulic fluent might be excluded during shipping. It is not safe to assume that it is either included or excluded in the reported dry system of weights. Hydraulic fluid might be found on a particular motorcycle ‘s front man brake and reservoir, plus possibly a rear bracken with a reservoir, and possibly besides in a hydraulic clutch with its own reservoir. Ducati has in the past used the term “ Ducati weight ”, pertaining to a value excluding the battery deoxyadenosine monophosphate well as all fluids, but have since begun using “ dry weight ” for this. [ 9 ] Beginning in 2009, the japanese Big Four manufacturers and BMW began publishing the wet weight preferably than dry, normally providing some explanation for what this means. Since then most early manufacturers have followed, in order to comply with EC directives that explicitly state that the values pertain to the vehicle in running order. Honda describes it as curb weight ( aka curb weight ) and says this means the bicycle is “ cook to ride. ” Others say all fluids are included and the fuel tank is at least 90 % full. Erik Buell Racing gives “ wet weight unit ( no fuel ) ” for the 2012 1190RS motorcycle, [ 10 ] while KTM gives a “ burden without fuel approx. ” [ 11 ]
Wet burden [edit ]
The wet weight of a motorbike includes, but is not limited to fuel, engine anoint, coolant, brake fluid, and battery. There is no global standardize way to test the wet weight of a motorcycle. In the EU, Council Directive 93/93/EEC specifies wet weight as “ aggregate in running order ”, which includes all equipment normally fitted to a bicycle such as windshield, joyride kit out and at least 90 % of its fuel capacity. [ 12 ] Motorcycle manufacturers will rarely publish wet burden measurements and inconsistencies will about always be found between different motorbike press and media outlets. This is due to different testing techniques, differences in what is being included, and by the organization doing the testing omitting an explanation of how they weighed the motorcycle. Cycle World has published wet weights with all consumables on board, but only half a tank of fuel, while Honda has recently published specification tables that use the typically automotive-oriented term curb weight, and stated that it included full fluent levels and the motorcycle was “ fix to ride. ”
Gross fomite system of weights rate [edit ]
Gross vehicle slant rat ( GVWR ) is the manufacturer ‘s stated utmost dependable mass of the motorcycle, including its own mass and everything it carries, taking into consideration the tire profile and lode capacitance ; bracken, suspension and frame capacity. It is printed on a motorcycle ‘s VIN Plate. The deviation between GVWR and wet weight is how much the motorbike can safely carry, including fuel ; the rider, passenger and their clothe ; cargo ; and other accessories. Using this calculation, a typical large cruiser might have a maximum utilitarian cargo of 400 pounds ( 180 kilogram ). This is specially of interest in touring motorcycles because when comparing motorcycles ridden by the lapp operator and passenger, clothe in the like base hit clothe, the machine with the greatest difference between its GVWR and moisture weight unit can safely bear the most extra weight ; for exemplify, camping food and gear, extra fuel, or spare parts. It besides indicates that a large rider and passenger might overload the machine flush without carrying any extra lode, in which character they might need two vehicles for a planned tour. [ 13 ]
Aerodynamics [edit ]
automotive aerodynamics of motorcycles are not as frequently measured by third base parties or reported by manufacturers as other figures like power. The dimensionless measure of puff coefficient, Cd, varies from .55 to .65 ( comparable to a pickup truck ), five Cd .29 for many sports cars and even .20 for high efficiency cars. however a more relevant design of merit, CdA, factors in the vehicle ‘s frontal area, and frankincense actual might required to overcome wind resistor. [ 15 ] A typical projected frontal sphere for motorcycles is in the vicinity of 2.9–3.9 sq foot ( 0.27–0.36 m2 ). When the CdA figure is reported, it is sometimes in nonstandard units making it hard to compare between motorcycles and automobiles. candle could be reduced through the use of “ ashcan fairings ” or in full enclosed and streamlined fairings ( like the Vetter Streamliner prototype ) to reduce wake turbulence and flow separation, but these were banned in racing in the 50s and so are out of manner among street motorcycles. The attachment to “ styling aerodynamics ” ( as opposed to measurably improved aerodynamics ) and ergonomic considerations have affected output motorbike design. [ 18 ] Another factor making aerodynamic measurements relatively rare in the popular iron is the miss of access to research-quality scent tunnels by journalists. complete analysis of motorbike aerodynamics would include measurement of drag, pilfer and side force at assorted speeds, wreathe angles, and passenger postures ; deoxyadenosine monophosphate well as pitching here and now, rolling moment, and yawing moment ( see yaw, pitch and scroll for descriptions ).
Read more: Wikipedia
early parameters [edit ]
The following have been normally used at one meter or another to describe motorcycles. not all of them apply to every motorcycle, and most sources publish only a subset of this list, while others have singular measurements not seen elsewhere .
